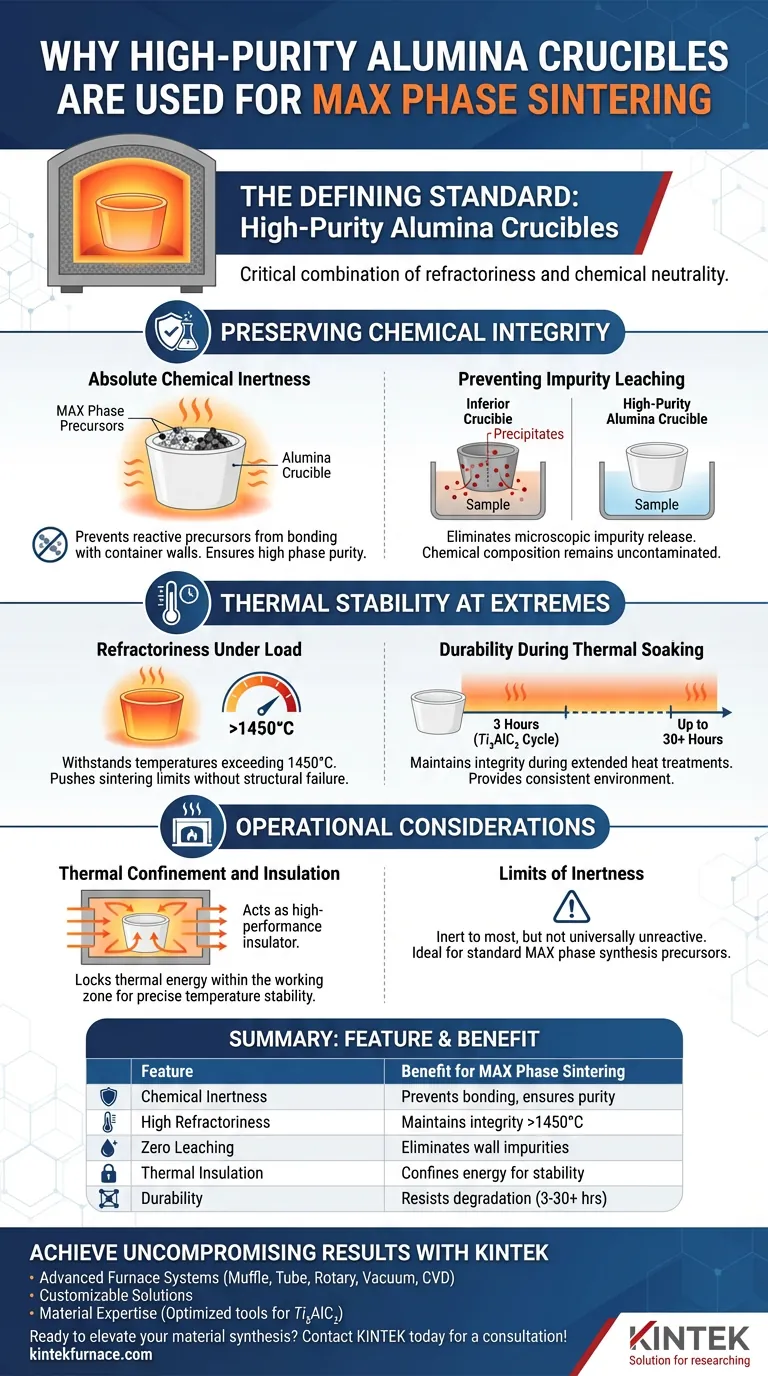
High-purity alumina crucibles are the defining standard for sintering MAX phase powders because they offer a critical combination of refractoriness and chemical neutrality. During the rigorous high-temperature sintering process—such as the three-hour cycle required for $Ti_3AlC_2$—these crucibles act as stable containment vessels that do not chemically interact with the precursor powders, thereby guaranteeing the high phase purity of the final material.
The Core Insight In materials synthesis, the vessel is as critical as the ingredients. High-purity alumina is chosen not just because it survives the heat, but because it remains "invisible" to the chemical reaction, preventing container-induced contamination from ruining the delicate stoichiometry of MAX phases.
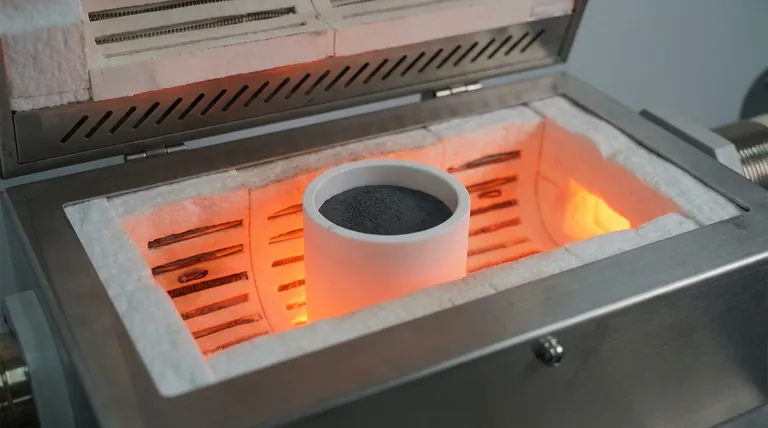

Preserving Chemical Integrity
The primary challenge in sintering MAX phases like $Ti_3AlC_2$ is preventing the reactive precursor powders from bonding with the container walls.
Absolute Chemical Inertness
The defining characteristic of high-purity alumina is its resistance to chemical reaction. During synthesis, the precursor powders are subjected to intense energy to form new bonds.
Alumina crucibles ensure that this reactivity is confined strictly to the powders themselves. They do not react with the precursors, ensuring the final bulk material retains high phase purity.
Preventing Impurity Leaching
At elevated temperatures, inferior crucible materials can release microscopic impurities or "precipitates" from their walls into the sample.
High-purity alumina effectively prevents this precipitation. By eliminating interaction between the container and the sample, the chemical composition remains uncontaminated, ensuring that experimental results reflect the material's true properties rather than artifacts of the vessel.
Thermal Stability at Extremes
Sintering MAX phases requires sustained exposure to temperatures that would degrade lesser materials.
Refractoriness Under Load
Alumina demonstrates exceptional refractoriness, capable of withstanding temperatures exceeding 1450°C.
This capability allows researchers to push sintering protocols to the necessary limits for MAX phase formation without risking structural failure of the crucible.
Durability During Thermal Soaking
Synthesis is rarely instantaneous; it often requires maintaining high heat for extended periods.
Whether for a typical 3-hour sintering process for $Ti_3AlC_2$ or longer thermal soaking periods (up to 30 hours in analogous high-temp syntheses), alumina maintains its structural integrity. It provides a consistent environment throughout the entire duration of the heat treatment.
Operational Considerations
While alumina is the superior choice for this application, understanding its thermal role within the furnace is necessary for optimal results.
Thermal Confinement and Insulation
In high-temperature resistance furnaces, the role of the crucible extends beyond simple containment.
Alumina acts as a high-performance insulator. It helps lock thermal energy within the working zone, preventing heat from diffusing to non-functional parts of the furnace. This confinement is crucial for maintaining the precise temperature stability required to melt or sinter the target materials uniformly.
Limits of Inertness
While alumina is inert to most chemical raw materials, it is not universally unreactive.
Selection relies on the premise that the specific precursors (like those for MAX phases) do not fall into the small category of materials that corrode alumina. For standard MAX phase synthesis, however, it serves as an ideal, non-contaminating barrier.
Making the Right Choice for Your Project
When designing a sintering protocol, your choice of crucible must align with your specific experimental constraints.
- If your primary focus is Phase Purity: Rely on high-purity alumina to prevent the container walls from reacting with precursors like $Ti_3AlC_2$, effectively eliminating leaching and cross-contamination.
- If your primary focus is Thermal Endurance: Utilize alumina for processes requiring sustained temperatures between 1350°C and 1450°C, ensuring the vessel maintains structural stability without softening.
By selecting high-purity alumina, you remove the variable of "vessel interaction" from your experiment, allowing you to focus entirely on the physics of your material synthesis.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit for MAX Phase Sintering |
|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Prevents bonding between precursors and crucible walls, ensuring phase purity. |
| High Refractoriness | Maintains structural integrity at extreme temperatures exceeding 1450°C. |
| Zero Leaching | Eliminates precipitation of wall impurities into the sample during thermal soaking. |
| Thermal Insulation | Confines energy within the working zone for precise temperature stability. |
| Durability | Resists degradation during extended sintering cycles (3-30+ hours). |
Achieve Uncompromising Results with KINTEK
Don't let vessel contamination compromise your research. KINTEK provides high-purity alumina crucibles and high-temperature furnace solutions specifically designed for the rigorous demands of MAX phase synthesis.
Backed by expert R&D and precision manufacturing, we offer:
- Advanced Furnace Systems: Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems.
- Customizable Solutions: Tailored lab high-temp furnaces to meet your unique sintering profiles.
- Material Expertise: Optimized tools for $Ti_3AlC_2$ and other advanced ceramic materials.
Ready to elevate your material synthesis? Contact KINTEK today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
References
- Oyku Cetin, Hüsnü Emrah Ünalan. MXene‐Deposited Melamine Foam‐Based Iontronic Pressure Sensors for Wearable Electronics and Smart Numpads. DOI: 10.1002/smll.202403202
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
People Also Ask
- Why is the selection of crucibles with specific internal linings necessary? Protect Purity in Superalloy Melting
- Why is zirconia grinding media preferred for NN-10ST ceramic powders? Ensure Purity & Dielectric Performance
- What role do high-purity graphite molds and punches play during the sintering of silicon carbide ceramics in SPS?
- How do digital mass flow controllers (MFC) maintain a constant smelting atmosphere? Ensure Precise Gas Control
- Why is a graphite thermal baffle necessary for thermal field control? Master Single-Crystal Growth Quality
- What is the primary function of a high-purity vacuum-sealed quartz tube in the Modified Bridgman technique? Key Role
- Why use high-purity quartz glass tubes for copper sulfide synthesis? Ensure Thermal Stability & Purity
- What role does a rotary evaporator play in microalgae-based nanomaterials? Protect Bio-Reductive Activity for Synthesis



















