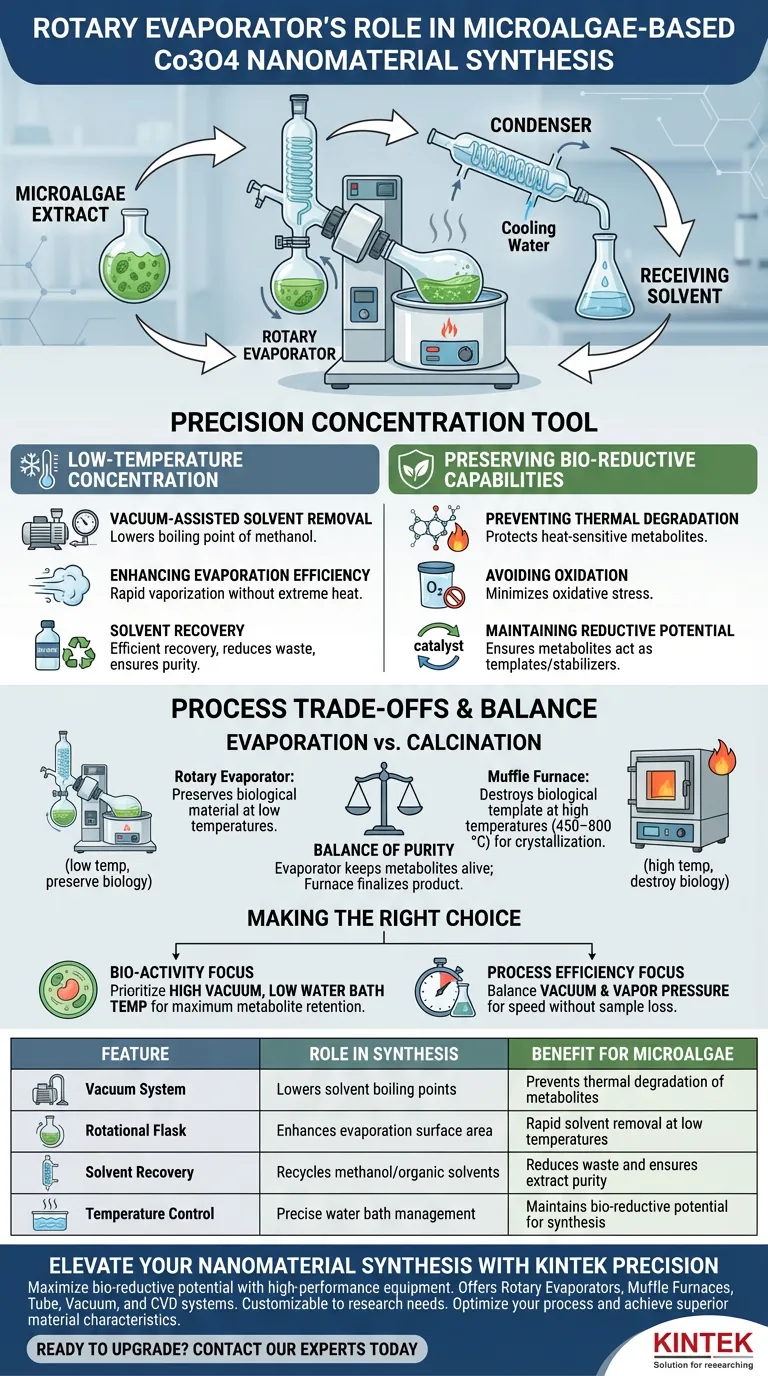
The rotary evaporator functions as a precision concentration tool designed to preserve the chemical integrity of microalgae extracts. Its primary role in this synthesis is to remove methanol solvents under vacuum conditions, allowing the extract to be concentrated at low temperatures without thermally damaging the delicate biological components.
By lowering the boiling point of the solvent, the rotary evaporator allows for rapid concentration while protecting heat-sensitive metabolites. This preservation is vital, as these metabolites provide the bio-reductive activity required to successfully synthesize cobalt oxide nanomaterials.
The Critical Function of Low-Temperature Concentration
Vacuum-Assisted Solvent Removal
The rotary evaporator operates by creating a vacuum within the system. This reduces the pressure, which significantly lowers the boiling point of the methanol solvent used to extract compounds from the microalgae.
Enhancing Evaporation Efficiency
Because the boiling point is lowered, the solvent can vaporize rapidly without requiring extreme heat. This ensures the majority of the methanol is removed quickly and efficiently, streamlining the preparation process.
Solvent Recovery
Beyond concentration, this process allows for the efficient recovery of organic solvents. This prevents chemical waste and ensures the remaining biological material is pure and ready for the subsequent reaction phases.
Preserving Bio-Reductive Capabilities
Preventing Thermal Degradation
Microalgae extracts contain complex biological metabolites that are highly sensitive to heat. Traditional heating methods would likely denature or degrade these compounds, rendering them useless for nanomaterial synthesis.
Avoiding Oxidation
The rotary evaporator’s controlled environment minimizes the extract's exposure to oxidative stress. By preventing oxidation during the concentration phase, the chemical structure of the metabolites remains intact.
Maintaining Reductive Potential
The successful formation of cobalt oxide nanomaterials relies on the "bio-reductive" activity of the algae extract. The rotary evaporator ensures these biological reducing agents act as effective templates and stabilizers during the synthesis.
Understanding the Process Trade-offs
Evaporation vs. Calcination
It is crucial to distinguish the role of the rotary evaporator from later stages of synthesis. While the evaporator preserves biological material at low temperatures, instruments like the muffle furnace are used later to destroy that same biological template at high temperatures (450–800 °C).
The Balance of Purity
The rotary evaporator aims to remove the solvent but keep the biological "impurities" (metabolites) alive. Conversely, the high-temperature treatment is designed to crystallize the oxide and govern grain size. Conflating these two thermal stages is a common pitfall; the evaporator safeguards the ingredients, while the furnace finalizes the product.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To optimize your microalgae-based synthesis, consider how you manage the evaporation parameters:
- If your primary focus is Bio-Activity: Prioritize high vacuum levels to keep the water bath temperature as low as possible, ensuring maximum retention of reductive metabolites.
- If your primary focus is Process Efficiency: Balance the vacuum pressure against the solvent's vapor pressure to maximize the speed of methanol recovery without causing "bumping" or sample loss.
The rotary evaporator is not just a drying tool; it is the safeguard that ensures your biological precursors survive long enough to drive the chemical reaction.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role in Nanomaterial Synthesis | Benefit for Microalgae |
|---|---|---|
| Vacuum System | Lowers solvent boiling points | Prevents thermal degradation of metabolites |
| Rotational Flask | Enhances evaporation surface area | Rapid solvent removal at low temperatures |
| Solvent Recovery | Recycles methanol/organic solvents | Reduces waste and ensures extract purity |
| Temperature Control | Precise water bath management | Maintains bio-reductive potential for synthesis |
Elevate Your Nanomaterial Synthesis with KINTEK Precision
Maximize the bio-reductive potential of your precursors with KINTEK’s high-performance laboratory equipment. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of Rotary Evaporators, Muffle Furnaces, Tube, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all customizable to your unique research needs.
Whether you are concentrating delicate microalgae extracts or performing high-temperature calcination, our systems provide the precision and reliability your lab demands. Let us help you optimize your process and achieve superior material characteristics.
Ready to upgrade your lab? Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution!
Visual Guide
References
- Agnieszka Sidorowicz, Günther Rupprechter. Microalgae-derived Co<sub>3</sub>O<sub>4</sub> nanomaterials for catalytic CO oxidation. DOI: 10.1039/d4ra00343h
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What happens during the 180-degree rotation of the impeller in a water circulating vacuum pump? Uncover the Suction Mechanism
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- Why are corundum or ceramic crucibles required for high-temperature magnesium evaporation processes? Ensure Purity and Prevent Crucible Failure
- Why is the use of high-vacuum pump groups critical for photothermal catalytic chamber pre-treatment?
- What role do refractory bricks and graphite paper play within a quartz tube? Optimize RuMoOx/NC Synthesis Efficiency
- Why use high-performance insulation bricks in radiant tube simulations? Ensure precision and industrial accuracy.
- Why is a laboratory vacuum drying oven necessary for processing nano MOFs? Preserve nLn-bdc Structural Integrity
- Why is modified PTFE used as a liner in high-pressure reactors for MoS2/C? Enhancing Purity and Yield.



















