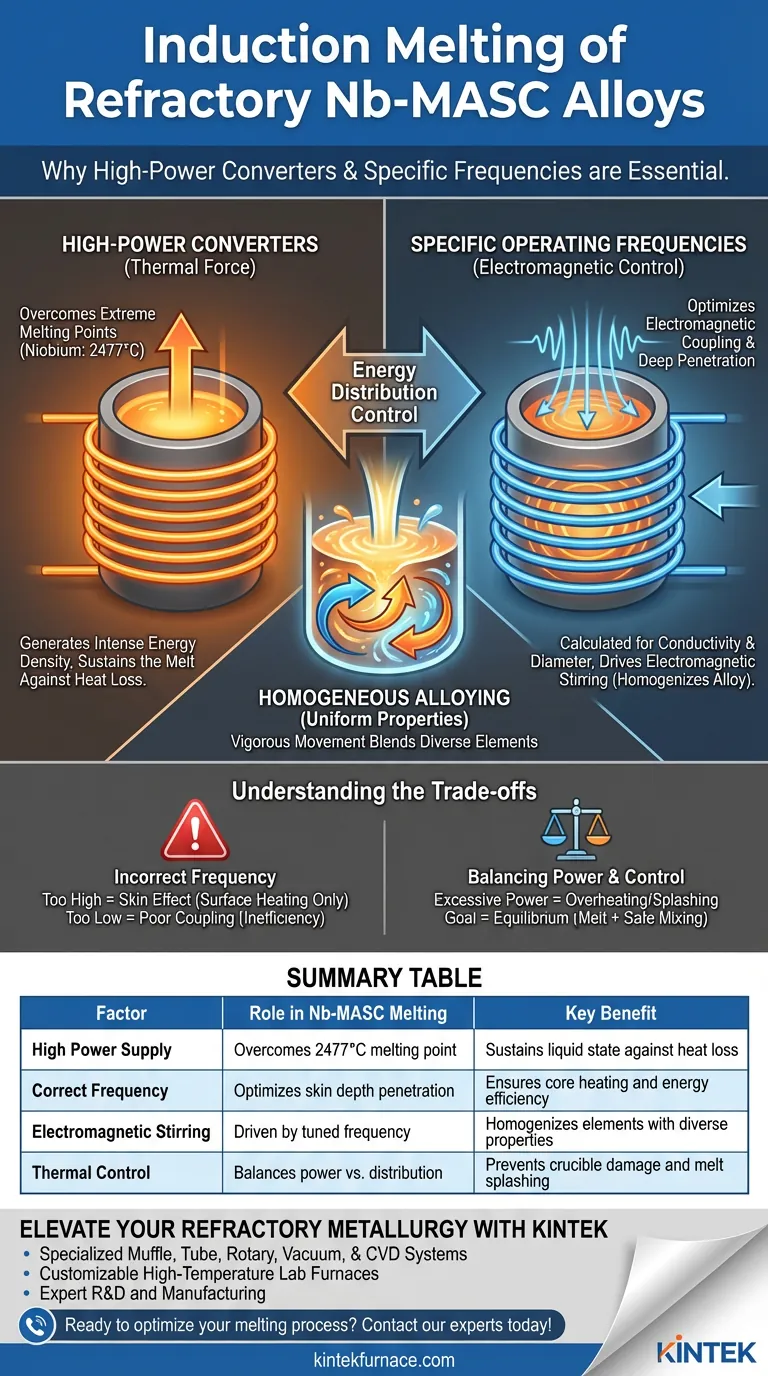
Successful processing of Nb-MASC alloys relies on high-power converters to overcome the extreme melting point of niobium (2477°C). Simultaneously, precise operating frequency selection is required to optimize electromagnetic coupling based on the material's conductivity and diameter, ensuring the heat penetrates deeply enough to drive the stirring necessary for uniform alloying.
Melting refractory alloys is not just about reaching high temperatures; it is about controlling energy distribution. High power overcomes thermal thresholds, while the correct frequency ensures the magnetic field penetrates the material effectively to drive the stirring required for a homogeneous alloy.
The Role of High Power in Refractory Melting
Overcoming Extreme Thermal Thresholds
Refractory metals like niobium present a significant thermal challenge due to their high melting points. Niobium specifically requires temperatures reaching 2477°C to transition to a liquid state.
High-power induction power supplies are essential to generate the intense energy density needed to reach these temperatures. Lower power systems simply cannot overcome the heat losses inherent at these extreme ranges.
Sustaining the Melt
Reaching the melting point is only the first step. High power ensures the system can sustain the melt temperature long enough for processing. This constant energy input combats radiant heat loss, maintaining the metal in a workable liquid state.
The Science of Frequency Selection
Optimizing Electromagnetic Coupling
Frequency selection is not arbitrary; it must be calculated based on the electrical conductivity and the diameter of the charge material.
Matching the frequency to these physical parameters achieves optimal electromagnetic coupling efficiency. This ensures the maximum amount of energy is transferred from the induction coil into the charge, rather than being wasted.
Ensuring Deep Penetration
The operating frequency dictates the "skin depth," or how deep the induced current penetrates the metal.
For Nb-MASC alloys, the frequency must be tuned to ensure the power penetrates deep into the charge. If the frequency is incorrect, heating may be superficial, leaving the core of the material solid or semi-solid.
Driving Electromagnetic Stirring
Perhaps the most critical function of frequency in this context is its impact on mixing.
Nb-MASC alloys consist of elements with significantly different physical properties. To blend these diverse elements into a uniform alloy, the melt requires vigorous movement.
An optimized frequency induces strong electromagnetic stirring forces. This natural churning action homogenizes the melt, ensuring that all elements are fully alloyed and the final material has consistent properties throughout.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Risk of Incorrect Frequency
If the selected frequency is too high, the "skin effect" becomes too pronounced. Current flows only on the surface, heating the exterior rapidly while leaving the center cold and preventing effective stirring.
Conversely, a frequency that is too low for the charge diameter may result in poor coupling. The magnetic field may pass through the material without inducing sufficient current, leading to drastic inefficiencies and an inability to melt the charge.
Balancing Power and Control
While high power is necessary, excessive power without proper frequency control can lead to overheating the crucible or turbulent splashing of the melt.
The goal is to find the equilibrium where power is sufficient to melt the niobium, but the frequency manages the distribution of that energy to mix the alloy safely.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct induction system requires balancing raw thermal capability with precise mixing control.
- If your primary focus is alloy uniformity: Prioritize frequency selection based on charge diameter and conductivity to maximize the electromagnetic stirring effect.
- If your primary focus is achieving the liquid state: Prioritize high-power capacity to ensure you can overcome the 2477°C melting threshold of niobium.
Correctly pairing power with frequency transforms the melting process from a thermal struggle into a controlled, precise metallurgical operation.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Role in Nb-MASC Melting | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| High Power Supply | Overcomes 2477°C melting point | Sustains liquid state against heat loss |
| Correct Frequency | Optimizes skin depth penetration | Ensures core heating and energy efficiency |
| Electromagnetic Stirring | Driven by tuned frequency | Homogenizes elements with diverse properties |
| Thermal Control | Balances power vs. distribution | Prevents crucible damage and melt splashing |
Elevate Your Refractory Metallurgy with KINTEK
Precision in induction melting is the difference between a failed melt and a high-performance alloy. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers specialized Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, along with customizable high-temperature lab furnaces designed to handle the extreme demands of materials like Nb-MASC.
Whether you need to achieve precise temperature thresholds or optimized electromagnetic stirring, our systems provide the control you need for superior metallurgical results.
Ready to optimize your melting process? Contact our experts today to discuss your unique laboratory requirements!
Visual Guide
References
- M. Guglielmi, Sebastian Herbst. Induction melting in cold crucible furnace for the production of components in turbine applications. DOI: 10.22364/mhd.61.1-2.5
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the working principle of a medium frequency induction furnace? Achieve Rapid, Precise Metal Melting
- Why are hollow copper tubes used for induction furnace coils? Essential Cooling for High-Power Melting
- What causes the melting of the solid scrap in the arc furnace? Unlock Efficient Steel Production
- What role does a vacuum induction melting furnace play in AHSS research? Master Purity in High-Strength Steel Ingots
- How does an induction melting furnace work? Achieve Rapid, Clean, and Controlled Metal Melting
- What are the key components of an IGBT-based induction heater circuit? Unlock Efficient High-Frequency Heating
- How can I reduce the power consumption of my induction furnace? Achieve Major Energy Savings Now
- How does a high-frequency induction heating system contribute to the surface hardening of steel? Enhance Wear Resistance



















