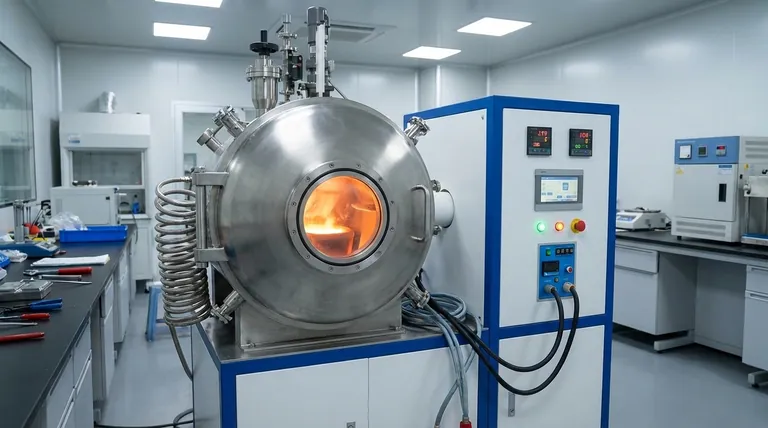
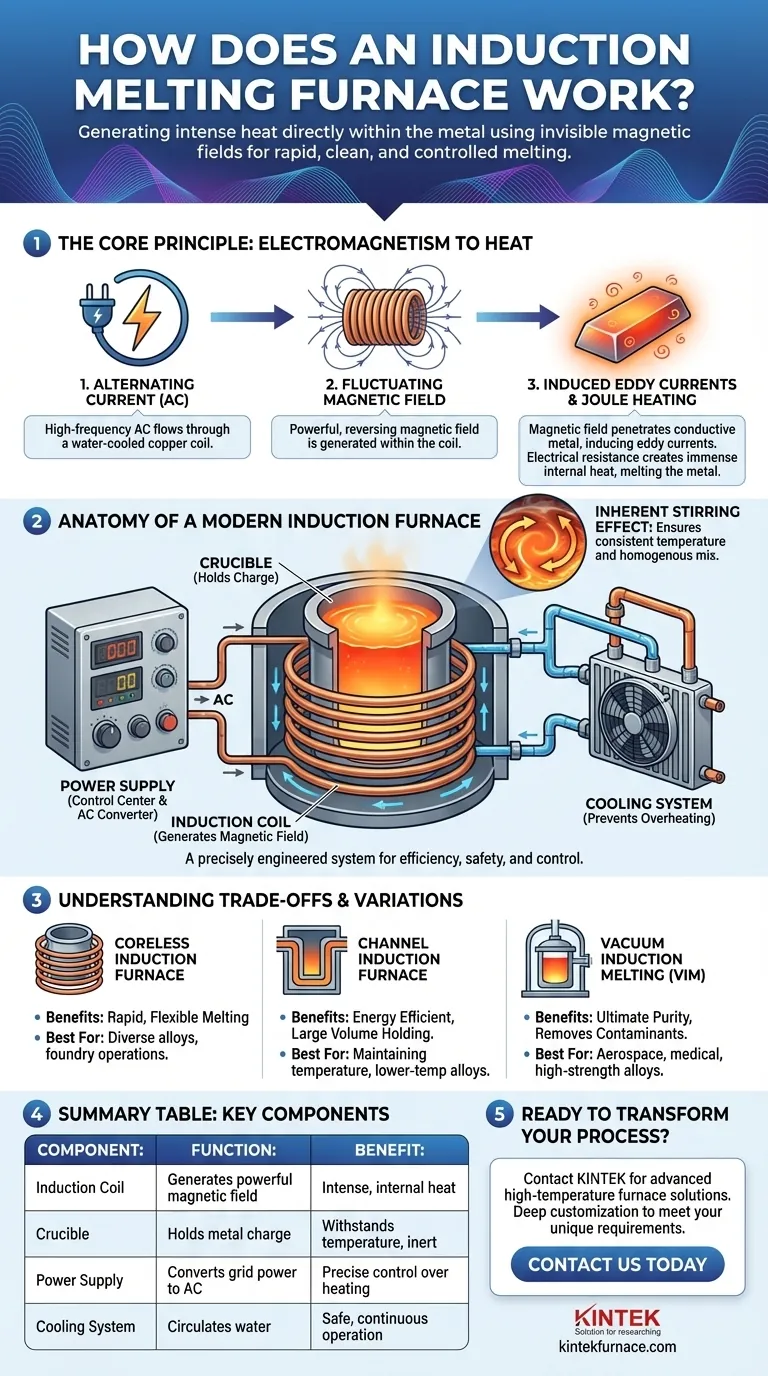
At its core, an induction furnace melts metal using a powerful, invisible magnetic field. It operates without any flame or external heating element, instead using the principles of electromagnetism to generate intense heat directly within the material itself. This method allows for rapid, clean, and highly controlled melting, making it a cornerstone of modern metallurgy.
The fundamental genius of induction melting is that it doesn't apply heat to the metal. Instead, it uses a fluctuating magnetic field to trick the conductive metal into generating its own internal heat, resulting in an exceptionally efficient and pure melting process.

The Physics of Induction Heating
To understand how an induction furnace works, you must first grasp the core principles of electromagnetic induction and resistance heating. The process is a seamless conversion of electrical energy into a magnetic field, and then back into thermal energy.
Generating the Magnetic Field
The process begins with a powerful alternating current (AC) being sent through a large, water-cooled copper coil that surrounds the furnace's crucible. This flow of current generates a strong and rapidly reversing magnetic field in the space within the coil.
Inducing Eddy Currents
When a conductive material, like a charge of steel or aluminum, is placed inside this magnetic field, the field penetrates the metal. According to Faraday's Law of Induction, the constantly changing magnetic field induces small, circular electrical currents within the metal. These are known as eddy currents.
The Role of Electrical Resistance
Every conductive material has some natural resistance to the flow of electricity. As these eddy currents swirl through the metal, they encounter this resistance, which generates immense friction on an atomic level. This friction creates intense heat, a phenomenon known as Joule heating, which rapidly raises the metal's temperature past its melting point.
The Inherent Stirring Effect
A unique benefit of this process is the natural stirring action it creates. The same magnetic forces that induce the eddy currents also exert a force on the molten metal, causing it to circulate continuously. This ensures a consistent temperature and a homogenous mix of alloys without any mechanical stirring.
Anatomy of a Modern Induction Furnace
A modern furnace is a precisely engineered system where each component plays a critical role in the efficiency and safety of the melting process.
The Crucible: Containing the Charge
The crucible is the non-conductive container that holds the metal to be melted. It is typically made of high-temperature-resistant ceramic or graphite materials, chosen to withstand extreme thermal stress while remaining unreactive with the molten metal.
The Induction Coil: The Engine of the Furnace
This is the heart of the system. The hollow copper coil is meticulously shaped to surround the crucible. It carries the high-frequency current and must be actively cooled with a continuous flow of water to prevent itself from melting.
The Power Supply: The Control Center
The power supply is the brain of the operation. It converts standard-frequency AC from the grid into the high-frequency AC required for efficient induction. By adjusting the power output, operators can precisely control the heating rate and final temperature of the melt.
The Cooling System: Preventing Overheating
A closed-loop water cooling system is essential for protecting the expensive copper coils and power supply components. This system dissipates the immense waste heat generated during operation, ensuring the furnace can run safely and reliably.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Variations
While the core principle is consistent, different furnace designs and configurations exist to meet specific metallurgical goals. Understanding these differences is key to appreciating the technology's versatility.
Coreless vs. Channel Furnaces
The most common design is the coreless induction furnace, where the crucible sits directly inside the coil. It is highly versatile and excellent for primary melting of a wide range of metals.
A channel induction furnace, by contrast, operates more like a transformer where a loop of molten metal itself forms the secondary coil. These are extremely efficient for holding large volumes of metal at temperature or for melting lower-temperature alloys, but less flexible than coreless designs.
The Pursuit of Purity: Vacuum Induction Melting
For applications demanding the highest material quality, such as aerospace or medical implants, a Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace is used. By performing the entire process inside a vacuum chamber, it eliminates all oxygen and other atmospheric contaminants, preventing oxidation and producing exceptionally clean and strong alloys.
Operational Complexity
The primary trade-off of induction technology is its complexity. The high-power electronics, sophisticated control panels, and critical water-cooling systems require specialized knowledge for operation and maintenance. They represent a higher initial investment compared to simpler fuel-fired furnaces.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
Your choice of induction technology depends entirely on your end-product requirements.
- If your primary focus is rapid, flexible melting of diverse alloys: A standard coreless induction furnace offers the best balance of speed, efficiency, and versatility for most foundry operations.
- If your primary focus is ultimate material purity and performance: A Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace is non-negotiable for producing the clean, high-strength alloys required for critical applications.
- If your primary focus is holding large volumes of metal at a consistent temperature: A channel induction furnace provides unmatched energy efficiency for maintaining large melts over extended periods.
By mastering the flow of energy from electricity to magnetism to heat, the induction furnace gives you precise control over the fundamental properties of your final material.
Summary Table:
| Key Component | Function | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Induction Coil | Generates a powerful, alternating magnetic field | Creates intense, internal heat within the metal charge |
| Crucible | Holds the metal charge (e.g., steel, aluminum) | Withstands extreme temperatures; chemically inert |
| Power Supply | Converts grid power to high-frequency AC | Enables precise control over heating rate and temperature |
| Cooling System | Circulates water to cool the coil and electronics | Ensures safe, reliable, and continuous operation |
| Furnace Type | Coreless (versatile) vs. Channel (efficient holding) vs. Vacuum (ultimate purity) | Matches specific metallurgical goals and production needs |
Ready to Transform Your Metal Melting Process?
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories and foundries with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Whether your goal is rapid primary melting, efficient metal holding, or achieving ultimate material purity with vacuum technology, our expertise is your advantage.
Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet your unique experimental and production requirements.
Contact us today to discuss how our induction melting solutions can enhance your efficiency, purity, and control. Let's achieve your metallurgical goals together.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- How does vacuum melting technology contribute to sustainability? Boost Durability and Recycling Efficiency
- What are the core functions of the High Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace? Optimize DD5 Superalloy Purification
- What are some common applications of vacuum induction melting and casting (VIM&C)? Essential for Aerospace, Medical, and Nuclear Industries
- Why is a Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace essential? Unlock Purity for Aerospace and Semiconductors
- What is vacuum induction melting technology and why is it important? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications



















