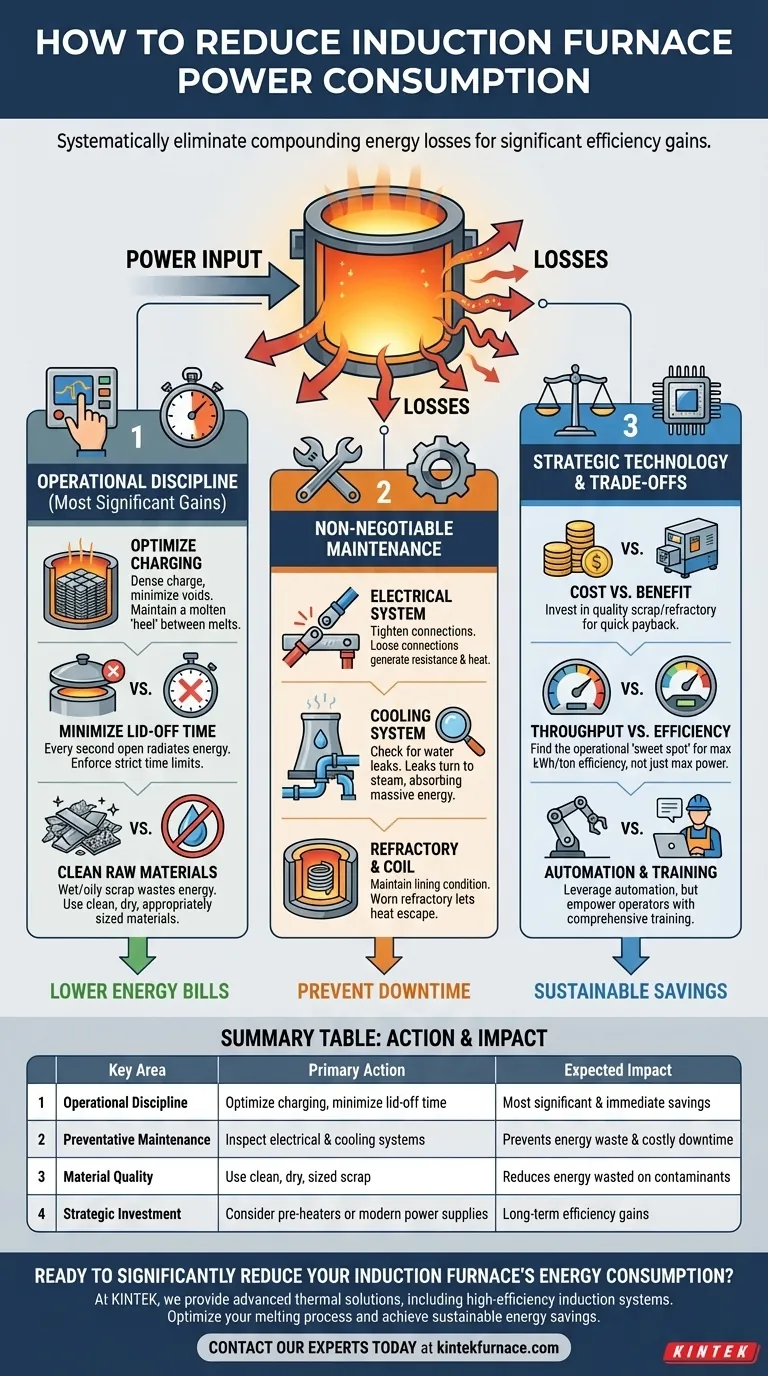
Reducing induction furnace power consumption is achieved through a multi-faceted approach that combines operational discipline, diligent maintenance, and strategic technology management. The most significant and immediate gains are found by optimizing your charging practices, minimizing the time the furnace lid is open, and ensuring your raw materials are clean and dry.
The core principle of energy efficiency in an induction furnace is not about a single silver bullet. It is about systematically eliminating small, compounding energy losses across your entire melting process, from raw material handling to the final pour.

Foundational Pillar: Operational Discipline
The largest and most accessible energy savings are found in how you operate the furnace day-to-day. These changes often require minimal capital investment but have a profound impact on your electricity bill.
Master Your Charging Practice
The way you load material, or charge, into the furnace directly influences melt time and energy use. A poorly managed charge wastes significant power.
A dense charge with minimal voids ensures maximum coupling between the induction coil and the metal. This allows for the most efficient transfer of energy.
Always try to maintain a molten "heel" of metal at the bottom of the furnace between melts. Starting a new melt with a solid charge on a cold floor is far less efficient than charging into an existing molten bath.
Minimize Heat Loss at All Costs
An open furnace lid is your biggest source of thermal loss. Every second the lid is open, you are radiating valuable energy and heat into the atmosphere.
Enforce strict procedures to keep lid-off time to an absolute minimum during charging, sampling, and slagging. A difference of just a few minutes per melt cycle adds up to massive waste over a year.
The Hidden Cost of Raw Materials
The quality of your charge material is not just a metallurgical concern; it's an energy concern. Clean, dry, and appropriately sized materials are crucial.
Wet or oily scrap requires extra energy to burn off the moisture and contaminants before the metal can even begin to melt. This wasted energy doesn't contribute to your production.
Empower Your Operators
Your furnace operators are the frontline defense against energy waste. Comprehensive training is essential for consistent, efficient operation.
Operators should understand not just what to do, but why specific procedures—like maintaining a dense charge or minimizing lid-off time—are critical for energy savings.
The Non-Negotiable Role of Maintenance
A well-maintained furnace is an efficient furnace. Deferred maintenance inevitably leads to higher energy consumption and increases the risk of costly downtime or catastrophic failure.
The Electrical System: Your Power Artery
The entire power delivery system must be in optimal condition. This includes the capacitors, bus bars, and power leads.
Regularly inspect and tighten all electrical connections. A loose connection generates resistance, which creates heat and wastes power before it ever reaches the coil.
The Cooling System: The Unsung Hero
The water-cooling system is designed to protect the coil, not to cool the melt. Any heat transferred to the cooling water is wasted energy.
Check diligently for water leaks inside the furnace. Even a small leak can turn to steam, which absorbs an enormous amount of energy from the melt and significantly drives up power consumption.
The Refractory and Coil: Your Core Containment
The condition of your furnace lining (refractory) and the grout around the coil is critical. A worn or thin refractory allows more heat to escape from the melt.
This heat loss not only wastes energy but also puts thermal stress on the induction coil itself, reducing its lifespan and increasing the risk of a dangerous metal breakout.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Pursuing maximum energy efficiency requires balancing competing priorities. Understanding these trade-offs is key to making sound operational and financial decisions.
Cost vs. Benefit
Investing in higher-quality, clean scrap or a new refractory lining has an upfront cost. However, this investment is often paid back quickly through reduced energy consumption per ton and improved melt quality.
Similarly, a robust preventative maintenance program requires labor and parts, but it prevents the far greater costs associated with unplanned downtime and inefficient operation.
Throughput vs. Efficiency
Running a furnace at maximum power will produce molten metal faster, increasing throughput. However, this is not always the most energy-efficient point of operation.
There is often an operational "sweet spot" at a slightly reduced power level that maximizes energy efficiency (kWh/ton). Finding this balance requires careful monitoring and analysis of your specific furnace and production schedule.
Automation vs. The Human Factor
Modern control systems can automate many aspects of the melt cycle for peak efficiency. However, even the most advanced system is only as good as the operators who manage it and the maintenance team that supports it. Technology is a tool, not a replacement for a well-trained and motivated team.
Your Path to Lower Energy Consumption
The right strategy depends on your immediate goals and resources. Use these points to guide your action plan.
- If your primary focus is immediate, low-cost savings: Focus entirely on operational discipline, specifically enforcing minimum lid-off times and optimizing charging techniques.
- If you are planning your next maintenance shutdown: Prioritize a thorough inspection of the electrical connections for tightness and the cooling system for any signs of leaks.
- If you are considering capital investment: Analyze the return on investment for a scrap pre-heating system or an upgrade to a modern, high-efficiency power supply.
Ultimately, achieving sustained energy reduction is the result of making efficiency a core part of your operational culture.
Summary Table:
| Key Area | Primary Action | Expected Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Operational Discipline | Optimize charging practice; minimize lid-off time | Most significant & immediate savings |
| Preventative Maintenance | Inspect electrical connections & cooling system | Prevents energy waste & costly downtime |
| Material Quality | Use clean, dry, and appropriately sized scrap | Reduces energy wasted on contaminants |
| Strategic Investment | Consider scrap pre-heaters or modern power supplies | Long-term efficiency gains |
Ready to significantly reduce your induction furnace's energy consumption and operational costs?
At KINTEK, we understand that energy efficiency is critical to your bottom line. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide foundries and metal producers with advanced thermal solutions, including high-efficiency induction systems and complementary equipment.
Our expertise can help you:
- Optimize your entire melting process for peak energy efficiency (kWh/ton).
- Implement robust maintenance schedules to prevent energy losses.
- Explore custom solutions, from pre-heaters to modern power supplies, tailored to your unique operational requirements.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can help you achieve sustainable energy savings and improve your profitability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- How does the Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) process work? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Control
- What are the core functions of the High Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace? Optimize DD5 Superalloy Purification
- What is vacuum induction melting technology and why is it important? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- How does vacuum melting technology contribute to sustainability? Boost Durability and Recycling Efficiency
- How has vacuum smelting impacted the development of superalloys? Unlock Higher Strength and Purity



















