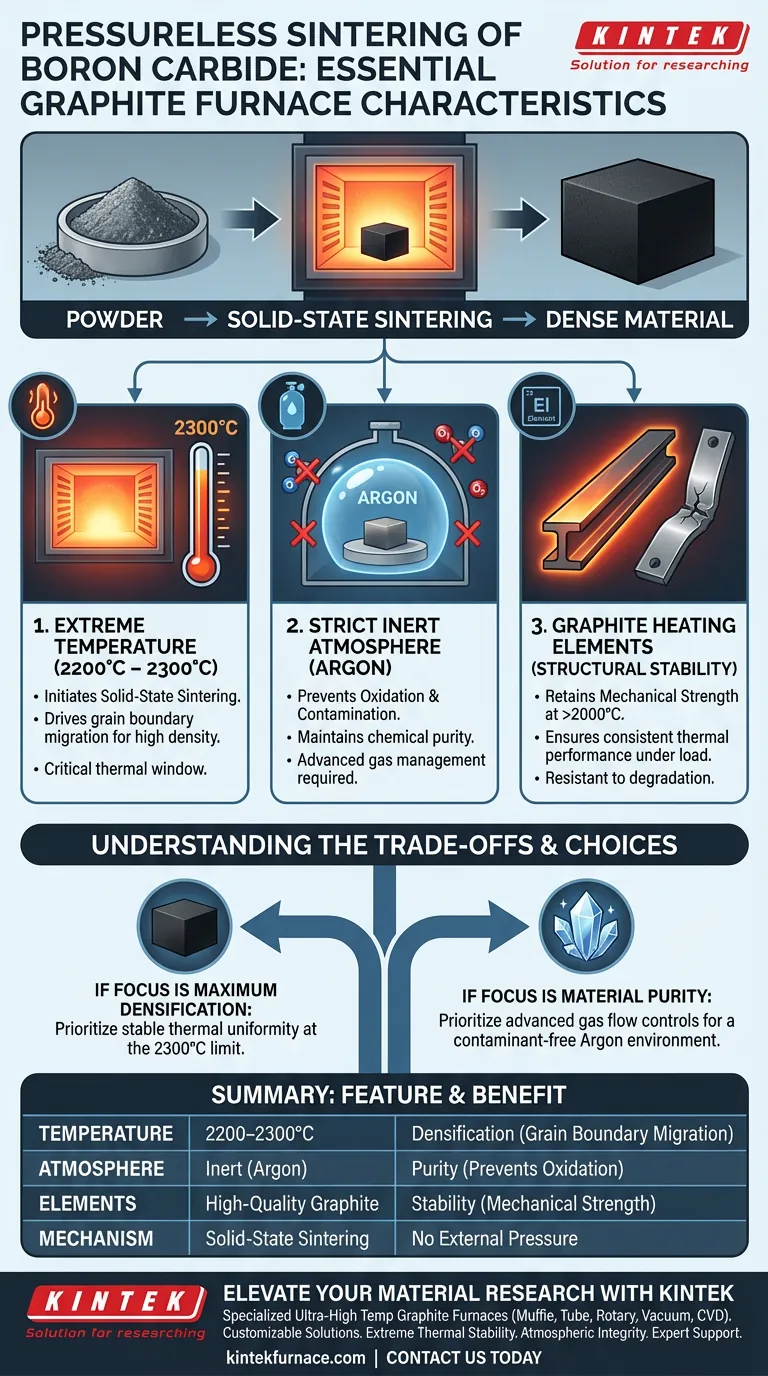
The essential performance characteristics of ultra-high temperature graphite furnaces for this application are the ability to sustain temperatures between 2200°C and 2300°C, the capacity to maintain a strictly inert atmosphere (typically Argon), and the utilization of graphite heating elements that retain mechanical strength at these extremes. These features are critical for facilitating the solid-state sintering mechanism required to densify Boron Carbide powder without the application of external pressure.
The success of pressureless sintering relies on the furnace's ability to drive grain boundary migration through extreme, stable heat while preventing oxidation, a balance achievable only through high-performance graphite elements and inert atmosphere control.

Achieving Densification Through Extreme Heat
Reaching the Critical Sintering Window
Pressureless sintering of Boron Carbide requires a highly specific and aggressive thermal range.
The furnace must be capable of reaching and stabilizing at temperatures between 2200°C and 2300°C.
Operating below this threshold will fail to provide the energy necessary for adequate densification.
Driving Solid-State Mechanisms
The primary objective of these ultra-high temperatures is to initiate solid-state sintering.
At this heat level, the furnace environment promotes grain boundary migration.
This migration is the physical mechanism that allows Boron Carbide powder to coalesce into a dense, solid material.
The Necessity of Environmental Control
Preventing Contamination with Inert Atmospheres
Subjecting materials to 2300°C increases their reactivity, making atmospheric control vital.
The furnace must be designed to support operation under inert atmospheres, specifically using gases like Argon.
This prevents oxidation and ensures the chemical purity of the Boron Carbide is maintained during the heating cycle.
Structural Stability of Heating Elements
Mechanical Strength Under Thermal Load
Generating temperatures above 2000°C places immense stress on internal components.
Graphite heating elements are essential because they maintain excellent mechanical strength even at these thermal extremes.
Unlike other materials that might soften or deform, graphite retains its structural integrity, ensuring consistent heat delivery.
Consistent Thermal Performance
The stability of graphite directly translates to process reliability.
Because the heating elements do not degrade mechanically at high heat, the furnace can maintain the precise thermal conditions required for the duration of the sintering cycle.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Temperature vs. Equipment Stress
While the target range is 2200°C to 2300°C, operating at the upper limit of this window accelerates wear on furnace components.
You must ensure the graphite elements are of high quality to withstand prolonged exposure to these temperatures without rapid degradation.
Atmosphere Purity vs. Sintering Success
Achieving the correct temperature is futile if the inert atmosphere is compromised.
Even slight leaks or impurities in the Argon supply can disrupt the sintering process.
The furnace's sealing and gas management systems are just as critical as its heating capacity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the right furnace configuration for your specific needs, consider your primary process objectives:
- If your primary focus is Maximum Densification: Prioritize a furnace proven to maintain stable thermal uniformity at the upper limit of 2300°C to maximize grain boundary migration.
- If your primary focus is Material Purity: Prioritize a furnace with advanced gas flow controls to ensure a contaminant-free Argon environment throughout the cycle.
By leveraging the thermal stability of graphite and precise atmospheric control, you create the exact conditions necessary to transform loose powder into high-performance Boron Carbide.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Requirement | Benefit in Boron Carbide Sintering |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range | 2200°C to 2300°C | Initiates grain boundary migration for densification |
| Atmosphere | Strict Inert (Argon) | Prevents oxidation and maintains chemical purity |
| Heating Elements | High-Quality Graphite | Maintains mechanical strength and thermal stability |
| Mechanism | Solid-State Sintering | Enables coalescing of powders without external pressure |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK
Achieving the extreme conditions required for Boron Carbide sintering demands precision engineering and uncompromising durability. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers specialized Ultra-High Temp Graphite Furnaces, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all customizable to meet your unique laboratory or production needs.
Our value to you:
- Extreme Thermal Stability: Reach and maintain 2300°C with precision.
- Atmospheric Integrity: Advanced gas management for contaminant-free environments.
- Expert Customization: Furnaces designed specifically for your sintering workflows.
Ready to transform your powder processing? Contact us today to discuss your high-temperature requirements with our technical specialists!
Visual Guide
References
- Hala Mohamed, Rehab Mahmoud. Waste Biomass Utilization for the Production of Adsorbent and Value-Added Products for Investigation of the Resultant Adsorption and Methanol Electro-Oxidation. DOI: 10.3390/catal14090574
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of using screening equipment to pretreat magnesium slag before its recovery via vacuum distillation? Optimize Your Recovery Process
- How does the vacuum environment affect gas porosity in castings? Eliminate Defects for Stronger Parts
- How are vacuum furnaces utilized in the electronics and semiconductor industries? Unlock High-Purity Manufacturing for Superior Devices
- Why is a closed reaction vessel necessary for the thermal reduction of graphene oxide? Unlock High-Purity rGO Synthesis
- What operational advantages do vacuum furnaces provide? Achieve Superior Material Quality and Process Control
- Why must the brazing of Tungsten-EUROFER heterometal joints be performed in an ultra-high vacuum furnace? Get Dense Bonds
- What benefits does vacuum carburizing offer for parts with complex shapes? Minimize Distortion and Boost Performance
- What role does high vacuum heating equipment play in copper-boron wetting? Achieve 10^-6 mbar Precision



















