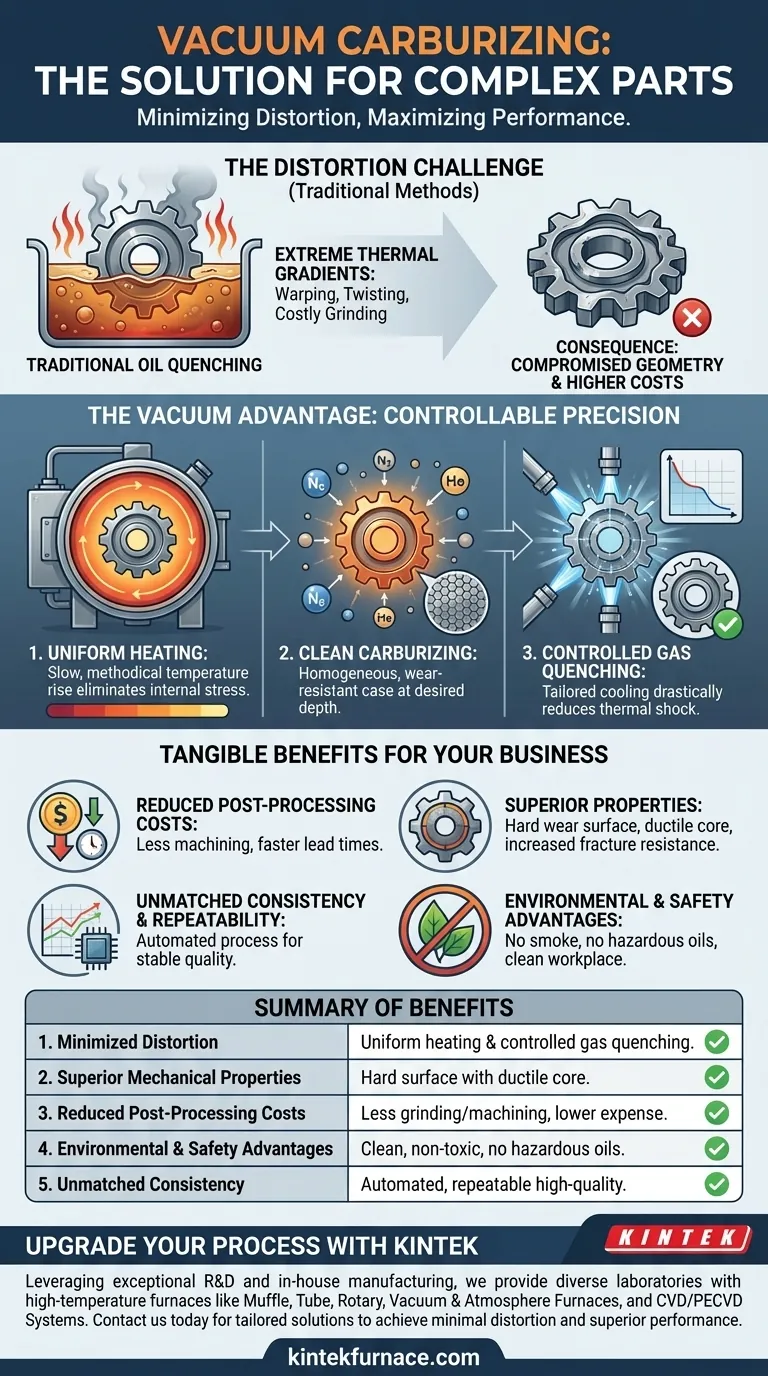
For parts with complex shapes, the primary benefit of vacuum carburizing is its exceptional ability to minimize distortion. This is achieved through highly controllable heating and a less severe gas quenching process, which together reduce the thermal stresses that cause warping in intricate geometries.
The core advantage of vacuum carburizing lies not just in the carburizing step, but in the total process control it provides. By precisely managing both the heating and cooling (quenching) cycles, it solves the fundamental problem of thermal shock and distortion that plagues complex parts in traditional heat treatment.

Why Distortion is the Enemy of Complex Parts
The Problem with Traditional Methods
Traditional atmospheric carburizing followed by oil quenching introduces extreme thermal gradients. When a hot, complex part is plunged into cool oil, different sections cool at vastly different rates.
Thin sections cool and contract instantly, while thick sections remain hot and expanded. This internal battle of thermal stress is what warps, twists, and distorts the part's final geometry.
The Consequence: Cost and Compromise
This distortion forces manufacturers into expensive and time-consuming secondary operations. Grinding, straightening, or hard machining are often required to bring the part back into its specified tolerance, adding significant cost and production delays.
How Vacuum Carburizing Solves the Distortion Problem
Step 1: Precise and Uniform Heating
Vacuum furnaces allow for highly adjustable heating speeds. For a complex part, the temperature can be raised slowly and methodically, ensuring the entire part—from its thickest core to its thinnest fins—reaches a uniform temperature.
This eliminates the internal stresses that build up during the initial heating phase, setting the stage for a stable process.
Step 2: Clean and Homogeneous Carburizing
In the vacuum environment, the carburizing process is exceptionally clean. This results in a superior metallurgical structure with a highly homogeneous hardened case at the desired depth.
This uniformity ensures consistent wear resistance across all surfaces of the part, which is critical for components with intricate contact points.
Step 3: The Critical Advantage of Gas Quenching
Instead of a violent oil quench, vacuum carburizing uses high-pressure gas (like nitrogen or helium) to cool the part. The pressure and velocity of this gas can be precisely controlled.
This allows the cooling rate to be tailored specifically to the part's geometry and material. A controlled, less severe quench drastically reduces thermal shock, making it the single most important factor in minimizing distortion.
Understanding the Tangible Benefits
Reduced Post-Processing Costs
Because distortion is minimized at the source, the need for corrective grinding and machining is significantly reduced or even eliminated. This translates directly to lower total manufacturing costs and faster lead times.
Superior Mechanical Properties
Parts develop a hard, wear-resistant surface while retaining a softer, more ductile core. This combination is ideal for high-performance applications, as the soft core can absorb shock and impact stress, providing increased resistance to fracture.
Unmatched Consistency and Repeatability
The entire vacuum carburizing process is typically automated and controlled by a microprocessor. All critical parameters are monitored and recorded, ensuring that every part in a batch—and every subsequent batch—receives the exact same treatment. This guarantees stable, repeatable quality.
Environmental and Safety Advantages
Vacuum carburizing is an environmentally friendly process. It produces no smoke, no CO2 emissions, and eliminates the need for managing and disposing of hazardous quenching oils, resulting in a clean, non-toxic working environment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Choosing a heat treatment process requires balancing part complexity, performance requirements, and total cost.
- If your primary focus is minimizing distortion on high-precision parts: Vacuum carburizing with gas quenching is the definitive choice, as it provides unparalleled control over the cooling cycle.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest metallurgical consistency: The clean, highly controlled, and repeatable nature of the vacuum process ensures superior and predictable results for critical components.
- If your primary focus is processing simple shapes where minor distortion is acceptable: Traditional atmospheric carburizing and oil quenching may remain a more cost-effective option for less critical applications.
Ultimately, investing in vacuum carburizing is a strategic decision to trade higher process costs for lower total part costs and superior engineering performance.
Summary Table:
| Benefit | Key Details |
|---|---|
| Minimized Distortion | Achieved through uniform heating and controlled gas quenching, reducing warping in intricate geometries. |
| Superior Mechanical Properties | Hard, wear-resistant surface with a ductile core for increased fracture resistance and durability. |
| Reduced Post-Processing Costs | Less need for grinding or machining, lowering total manufacturing expenses and lead times. |
| Environmental and Safety Advantages | No smoke, CO2 emissions, or hazardous oils, ensuring a clean, non-toxic work environment. |
| Unmatched Consistency and Repeatability | Automated process with microprocessor control for stable, high-quality results in every batch. |
Upgrade your heat treatment process with KINTEK's advanced solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, helping you achieve minimal distortion and superior performance for complex parts. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored furnace solutions can enhance your efficiency and reduce costs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the general operational features of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity & Precision
- Why does heating steel rod bundles in a vacuum furnace eliminate heat transfer paths? Enhance Surface Integrity Today
- What are the functions of a high-vacuum furnace for CoReCr alloys? Achieve Microstructural Precision and Phase Stability
- What are the benefits of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in LP-DED? Optimize Alloy Integrity Today



















