The design of a rotary kiln is fundamentally dictated by the material it will process. More than any other factor, a material's physical, thermal, and chemical characteristics determine the kiln's dimensions, power requirements, construction materials, and auxiliary systems. Understanding these properties is the critical first step in specifying a kiln that is both efficient and reliable.
A rotary kiln is not a generic piece of equipment; it is a custom-engineered solution. The final design is a direct translation of the material's properties into mechanical and thermal specifications, where overlooking a single characteristic can lead to significant operational inefficiency or outright failure.

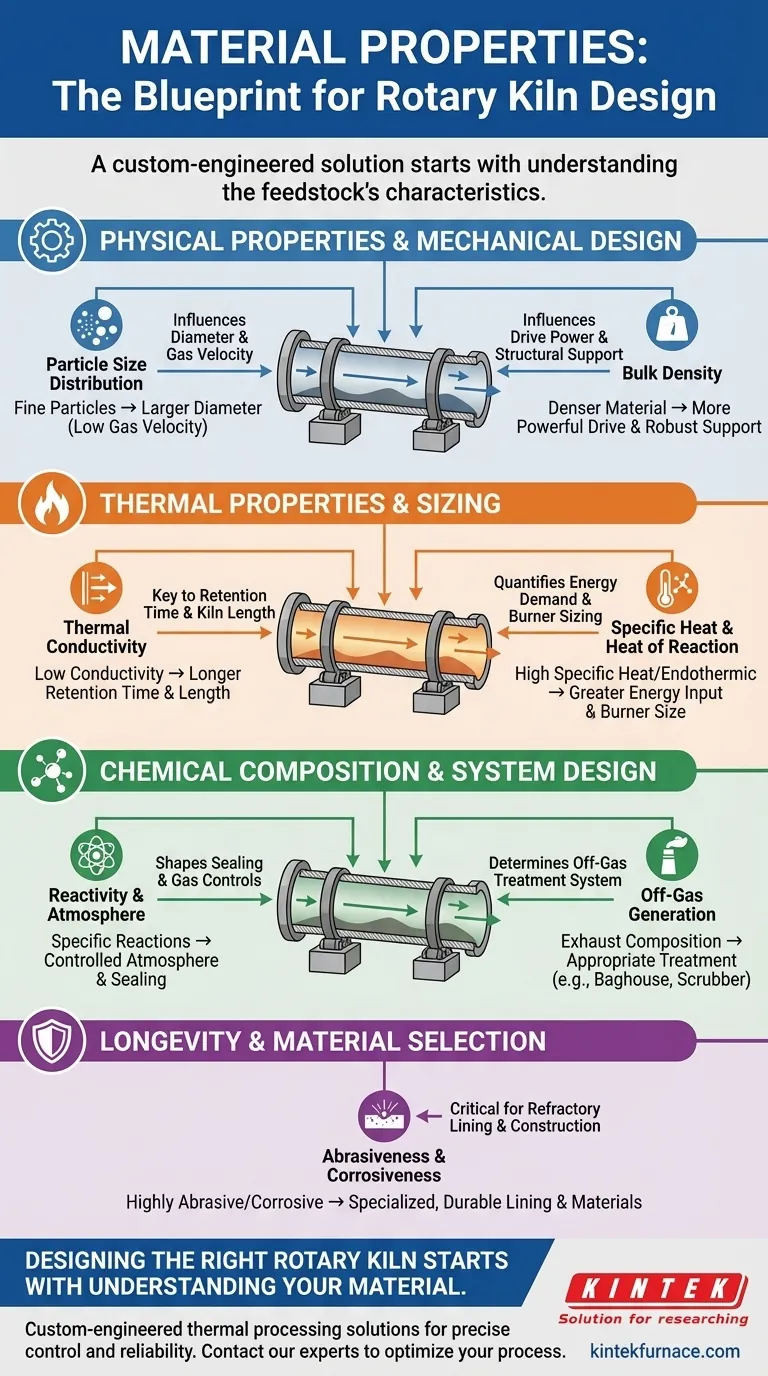
How Physical Properties Dictate Mechanical Design
The mechanical structure of the kiln—its size, power, and support system—is a direct response to the physical nature of the feedstock.
Particle Size Distribution and Its Impact on Diameter
The size of the material particles directly influences the required kiln diameter. Fine materials are easily entrained, meaning they can be swept out of the kiln by the process gas flow.
To prevent this material loss, the gas velocity must be kept low. A lower gas velocity for a given volumetric flow rate requires a larger kiln diameter.
Conversely, larger pellets or agglomerated materials can tolerate higher gas velocities, allowing for a comparatively smaller kiln diameter, which can reduce capital costs.
Bulk Density and Its Influence on Power
A material's bulk density is its mass per unit volume. A denser material is heavier, placing a greater load on the entire system.
This increased weight demands a more robust and powerful drive system (motor and gearbox) to provide the necessary torque for rotation. It also requires stronger support structures, including the tyres and rollers that the kiln shell rides on.
The Dominant Role of Thermal Properties in Sizing
How a material absorbs and transfers heat is arguably the most critical factor in determining the kiln's thermal design and overall length.
Thermal Conductivity: The Key to Heat Transfer
Thermal conductivity measures how easily heat moves through a material. A material with high conductivity heats evenly and quickly, which can allow for a shorter retention time and thus a shorter kiln.
Materials with low thermal conductivity are insulating. They heat slowly and can develop cold cores, requiring a much longer retention time to achieve the target temperature throughout the material bed. This may necessitate a longer kiln, slower rotation, or the installation of internal dams or bed disturbers to improve mixing.
Specific Heat: Quantifying Energy Demand
Specific heat is the amount of energy needed to raise a material's temperature. A high specific heat value means the material resists heating.
This requires a greater energy input from the burner or a longer exposure time to the heat source. This directly impacts the burner sizing and the required length of the kiln to ensure the material reaches its target temperature.
Heat of Reaction: Accounting for Chemical Changes
Many kiln processes involve chemical reactions that either consume energy (endothermic) or release it (exothermic).
This heat of reaction must be factored into the kiln's overall energy balance. An endothermic process adds to the heat demand, while an exothermic one can reduce it, influencing burner specifications and temperature control logic.
Why Chemical Composition Shapes the Entire System
A material's chemical makeup affects not only the core process but also the critical support and safety systems surrounding the kiln.
Reactivity and Atmosphere Control
Understanding a material's chemical composition is crucial for safety and process control. Some materials can burn at high temperatures, releasing excess energy that the kiln and refractory must be designed to withstand.
Other reactions require a specific chemical atmosphere, such as one free of oxygen or rich in carbon dioxide. This dictates the design of the kiln's sealing system and process gas controls.
Off-Gas Generation and Treatment
The chemical reactions within the kiln will generate exhaust gases. The composition of these gases is determined entirely by the feedstock's chemical makeup.
Knowing what gases will be produced is essential for designing the appropriate off-gas treatment system (e.g., baghouse, scrubber, thermal oxidizer) to meet environmental regulations and ensure safe operation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
It's crucial to distinguish between properties that affect kiln sizing and those that affect its longevity and material selection.
Abrasiveness and Corrosiveness: Protecting the Kiln Shell
A material's abrasiveness or corrosiveness does not directly influence the kiln's diameter or length. However, ignoring these properties leads to rapid equipment failure.
These characteristics are critical for selecting the materials of construction, particularly the refractory lining. A highly abrasive or corrosive material demands a specialized, durable lining to protect the steel shell from premature wear and chemical attack.
The Interplay of Properties
No single property exists in a vacuum. A material with low thermal conductivity that is also a very fine powder presents a complex design challenge. It requires a long retention time (suggesting a long, slow kiln) but also a low gas velocity (suggesting a large diameter), forcing engineers to find a balanced and often custom solution.
Making the Right Design Choices for Your Material
Your material's complete profile dictates the optimal kiln configuration.
- If your primary focus is processing fine, low-conductivity powders: You will need a kiln with a larger diameter to manage gas velocity and a longer length or slower rotation to ensure adequate heat transfer.
- If your primary focus is processing dense, high-conductivity pellets: A smaller diameter and potentially shorter kiln may be sufficient, but the drive system and support structure must be robustly designed for the high load.
- If your primary focus is a process with significant chemical reactions: Your design must prioritize precise atmosphere control, a durable refractory, and a comprehensive off-gas treatment system, with thermal sizing heavily influenced by the heat of reaction.
A thorough material analysis is not an optional step; it is the fundamental blueprint for a successful and efficient rotary kiln design.
Summary Table:
| Material Property | Primary Impact on Kiln Design |
|---|---|
| Particle Size | Kiln Diameter & Gas Velocity |
| Bulk Density | Drive Power & Structural Support |
| Thermal Conductivity | Retention Time & Kiln Length |
| Specific Heat | Burner Sizing & Energy Demand |
| Abrasiveness/Corrosiveness | Refractory Lining & Material Selection |
Designing the right rotary kiln starts with understanding your material.
At KINTEK, we specialize in custom-engineered thermal processing solutions. Our expert team uses detailed material analysis to design kilns that deliver precise temperature control, optimal throughput, and long-term reliability—ensuring your process is both efficient and cost-effective.
Ready to optimize your thermal processing? Contact our experts today to discuss your specific material and application requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
People Also Ask
- What is an electric heating rotary kiln and what industries use it? Discover Precision Heating for High-Purity Materials
- What are some drying applications of electromagnetic rotary kilns? Discover Efficient, Precise Drying Solutions
- How does the raw meal move inside the rotary kiln? Master Controlled Flow for Efficient Processing
- What are the main components in the construction of a rotary kiln? A Guide to the Core Systems
- What advantages do electrically heated rotary kilns offer in temperature control? Achieve Precision and Uniformity for Superior Results



















