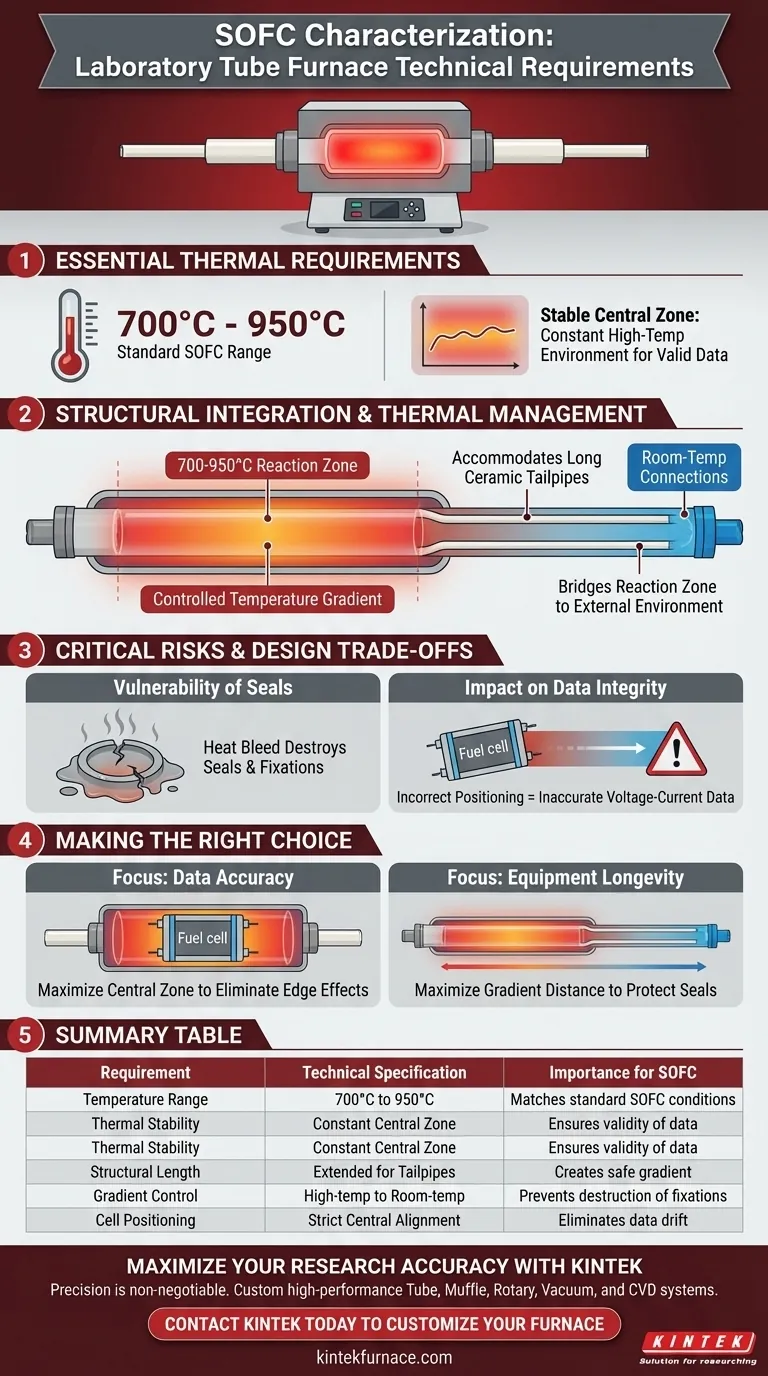
A laboratory tube furnace for SOFC characterization requires a stable high-temperature zone capable of sustaining 700°C to 950°C. Beyond simple heat generation, the physical geometry must accommodate long ceramic thermal compensation tailpipes to ensure a safe thermal gradient from the core to the connections.
The success of your performance testing depends on a design that isolates the high-temperature reaction zone from the room-temperature connections, preserving the integrity of your seals and the accuracy of your voltage-current data.

Essential Thermal Requirements
The Operating Temperature Range
For effective performance characterization, your furnace must reliably operate between 700°C and 950°C.
This range covers the standard operating temperatures for Solid Oxide Fuel Cells (SOFCs).
Stability in the Central Zone
The furnace must provide a constant high-temperature environment within its central zone.
Fluctuations in this area can compromise the validity of the data collected during testing.
Structural Integration for Thermal Management
Accommodating Ceramic Tailpipes
The furnace design must be physically long enough to house long ceramic thermal compensation tailpipes.
These components are essential for bridging the gap between the reaction zone and the external environment.
Establishing a Controlled Gradient
The primary function of the tailpipes and furnace length is to create a controlled temperature gradient.
The system must transition from the high-temperature central zone down to room temperature at the connection ends.
Critical Risks and Design Trade-offs
Vulnerability of Sealing Components
A common pitfall in furnace selection is ignoring the temperature at the connection points.
If the thermal gradient is insufficient, heat will bleed into the connection ends, potentially destroying sealing and fixation components.
The Impact on Data Integrity
To acquire accurate voltage-current characteristic data, the fuel cell must be positioned precisely.
It is critical that the cell remains strictly centered in the constant temperature zone, rather than drifting into the gradient areas.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure your equipment meets the rigorous demands of SOFC testing, prioritize the following based on your specific needs:
- If your primary focus is Data Accuracy: Ensure the furnace's central zone is large enough to fully encompass the fuel cell without edge effects from the temperature drop-off.
- If your primary focus is Equipment Longevity: specificy a furnace length that maximizes the gradient distance, keeping your seals and fixations strictly at room temperature.
Select a furnace that treats thermal management as a structural feature, not just a heating capability.
Summary Table:
| Requirement | Technical Specification | Importance for SOFC |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range | 700°C to 950°C | Matches standard SOFC operating conditions |
| Thermal Stability | Constant Central Zone | Ensures validity of voltage-current data |
| Structural Length | Extended for Tailpipes | Creates safe gradient to protect seals |
| Gradient Control | High-temp to Room-temp | Prevents destruction of fixation components |
| Cell Positioning | Strict Central Alignment | Eliminates edge effects and data drift |
Maximize Your SOFC Research Accuracy with KINTEK
Precision is non-negotiable in fuel cell characterization. At KINTEK, we understand that your data integrity depends on perfect thermal management. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer high-performance Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to handle the most rigorous laboratory requirements.
Our furnaces are fully customizable to accommodate specific ceramic tailpipe lengths and thermal gradient needs, ensuring your seals remain intact and your fuel cells stay centered in the optimal heat zone. Don't let equipment limitations compromise your results.
Contact KINTEK today to customize your high-temp furnace solution and experience the power of expert-engineered thermal systems.
Visual Guide
References
- Serikzhan Opakhai, Zh. Zhumadilova. DEVELOPMENT AND CREATION OF RESEARCH CELLS FOR SOLID OXIDE FUEL CELLS. DOI: 10.52676/1729-7885-2025-1-148-154
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What roles does a tube furnace play during the high-temperature calcination? Engineering Cobalt-Free Cathodes
- What critical conditions does a tube furnace provide for Cu-Fe-NC-3 pyrolysis? Achieve Precision Catalyst Synthesis
- What is the function of a dual-zone tube furnace in LPCVD? Master Precise MnSe Nanosheet Synthesis
- Why is a precision temperature control tube furnace necessary for CNT and AlN synthesis? Ensure Vertical Alignment
- What are the main operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Ensure Precision and Safety in Your Experiments
- What factors affect the price of a vacuum tube furnace? Key Drivers and Smart Investment Tips
- What are the technical advantages of using SPS vs. tube furnaces for SiC? Achieve Superior SiC Properties
- Why is a horizontal electric furnace ideal for small-diameter samples? Achieve Superior Uniform Heating



















