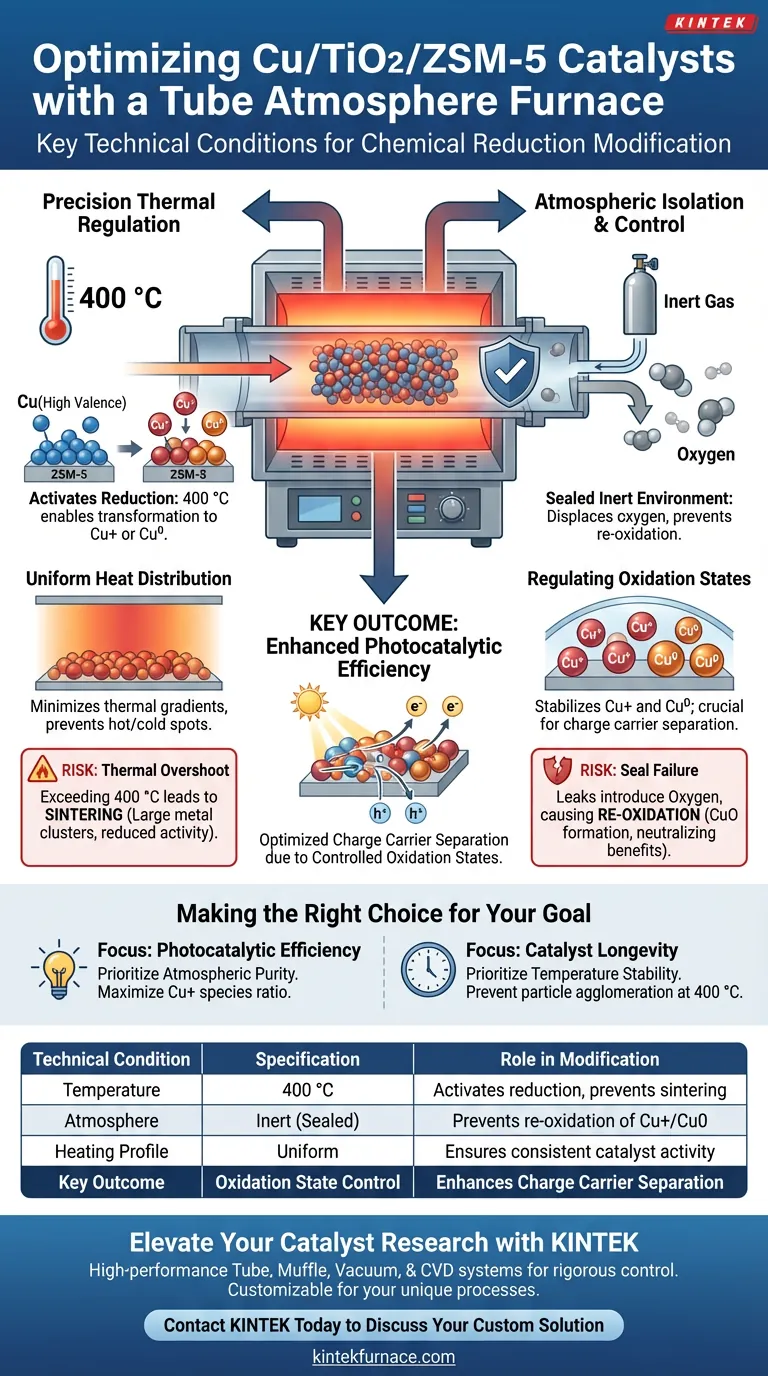
A tube atmosphere furnace establishes two critical technical conditions for the modification of Cu/TiO2/ZSM-5 catalysts: a precise high-temperature environment of 400 °C and a rigorously sealed, inert atmosphere. This specific combination creates a protected thermal zone that drives the chemical reduction of copper species while strictly preventing their re-oxidation.
The primary objective of this setup is to stabilize copper in partially reduced states (Cu+ or Cu0). By controlling these oxidation states, the furnace directly enhances the separation efficiency of photogenerated charge carriers, which is the defining factor in the catalyst's performance.

Precision Thermal Regulation
Driving the Reduction Reaction
The tube furnace provides a stable thermal environment at exactly 400 °C. This temperature is the activation threshold required to chemically reduce the copper species on the ZSM-5 support.
At this specific temperature, thermal energy enables the transformation of copper from high valence states into the desired Cu+ or metallic Cu0 forms.
Ensuring Uniform Heat Distribution
Tube furnaces are designed to minimize thermal gradients. This ensures that the 400 °C condition is applied uniformly across the entire catalyst bed.
Uniform heating prevents "hot spots" that could sinter the copper particles, while avoiding "cold spots" that would leave the catalyst under-reduced and inactive.
Atmospheric Isolation and Control
The Function of the Inert Atmosphere
The furnace maintains a strictly controlled inert atmosphere during the thermal treatment. This is not merely about excluding air; it is an active preservation mechanism.
By displacing oxygen with an inert gas, the furnace creates a sealed environment. This seal is critical because Cu+ and Cu0 species are highly reactive and would instantly re-oxidize if exposed to air at 400 °C.
Regulating Oxidation States
The synergy between the sealed atmosphere and the thermal environment allows for precise regulation of metal oxidation states.
Rather than a chaotic mix of oxides, the furnace conditions force the copper to settle into specific reduced valencies. This fine-tuning of the chemical state is what optimizes the electronic properties of the Cu/TiO2/ZSM-5 system.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While the tube furnace provides precision, the parameters must be balanced carefully to avoid degrading the catalyst.
The Risk of Thermal Overshoot
If the temperature exceeds 400 °C significantly, you risk sintering the copper particles. Large metal clusters have reduced surface area, which diminishes catalytic activity regardless of the oxidation state.
The Consequence of Seal Failure
The "inert" condition is absolute. Even a minor leak or impurity in the gas feed will re-introduce oxygen.
This leads to the formation of unwanted copper oxides (CuO), which act as recombination centers for charge carriers, effectively neutralizing the benefits of the modification process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When configuring a tube atmosphere furnace for Cu/TiO2/ZSM-5 modification, your operational focus should shift based on your specific performance metrics.
- If your primary focus is Photocatalytic Efficiency: Prioritize atmospheric purity to maximize the ratio of Cu+ species, which are crucial for improving charge carrier separation.
- If your primary focus is Catalyst Longevity: Prioritize temperature stability at 400 °C to prevent particle agglomeration and ensure the copper species remain well-dispersed on the ZSM-5 support.
Success relies on using the furnace not just as a heater, but as a precision tool to lock in specific chemical states.
Summary Table:
| Technical Condition | Specification/Value | Role in Catalyst Modification |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | 400 °C | Activates chemical reduction and prevents sintering |
| Atmosphere | Inert (Sealed) | Prevents re-oxidation of Cu+ and metallic Cu0 |
| Heating Profile | Uniform Distribution | Ensures consistent catalyst activity across the bed |
| Key Outcome | Oxidation State Control | Enhances charge carrier separation efficiency |
Elevate Your Catalyst Research with KINTEK
Precision is non-negotiable when stabilizing sensitive metal oxidation states. KINTEK provides high-performance Tube, Muffle, Vacuum, and CVD systems engineered for rigorous atmospheric control and thermal stability.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, our systems are fully customizable to meet the unique requirements of your chemical modification processes. Whether you need to maintain a strict inert seal or precise 400°C regulation, KINTEK ensures your catalysts perform at their peak.
Ready to optimize your lab's high-temperature processes?
Contact KINTEK Today to Discuss Your Custom Solution
Visual Guide
References
- Wibawa Hendra Saputera, Dwiwahju Sasongko. Understanding the Role of Copper Oxidation State on a TiO<sub>2</sub>/ZSM‐5 Catalyst for Photocatalytic CO<sub>2</sub> Reduction to Methanol. DOI: 10.1002/admi.202500010
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
People Also Ask
- What are the primary uses of tube furnaces in academic and industrial settings? Unlock Precision Thermal Processing
- What types of materials can be processed in a vacuum tube furnace? Unlock High-Purity Processing for Metals, Ceramics, and More
- What are some common applications of lab tubular furnaces in material science? Unlock Precision in Heat Treatment and Synthesis
- What critical process conditions does a tube atmosphere furnace provide for Sr2CuWO6? Control Atmosphere & Temperature
- What are the key factors to consider when choosing a vertical tube furnace? Ensure Optimal Performance for Your Lab
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- How does multi-zone heating benefit the 70mm tube furnace? Unlock Precise Thermal Control for Advanced Materials
- What is a horizontal tube furnace? Achieve Superior Thermal Uniformity for Your Samples



















