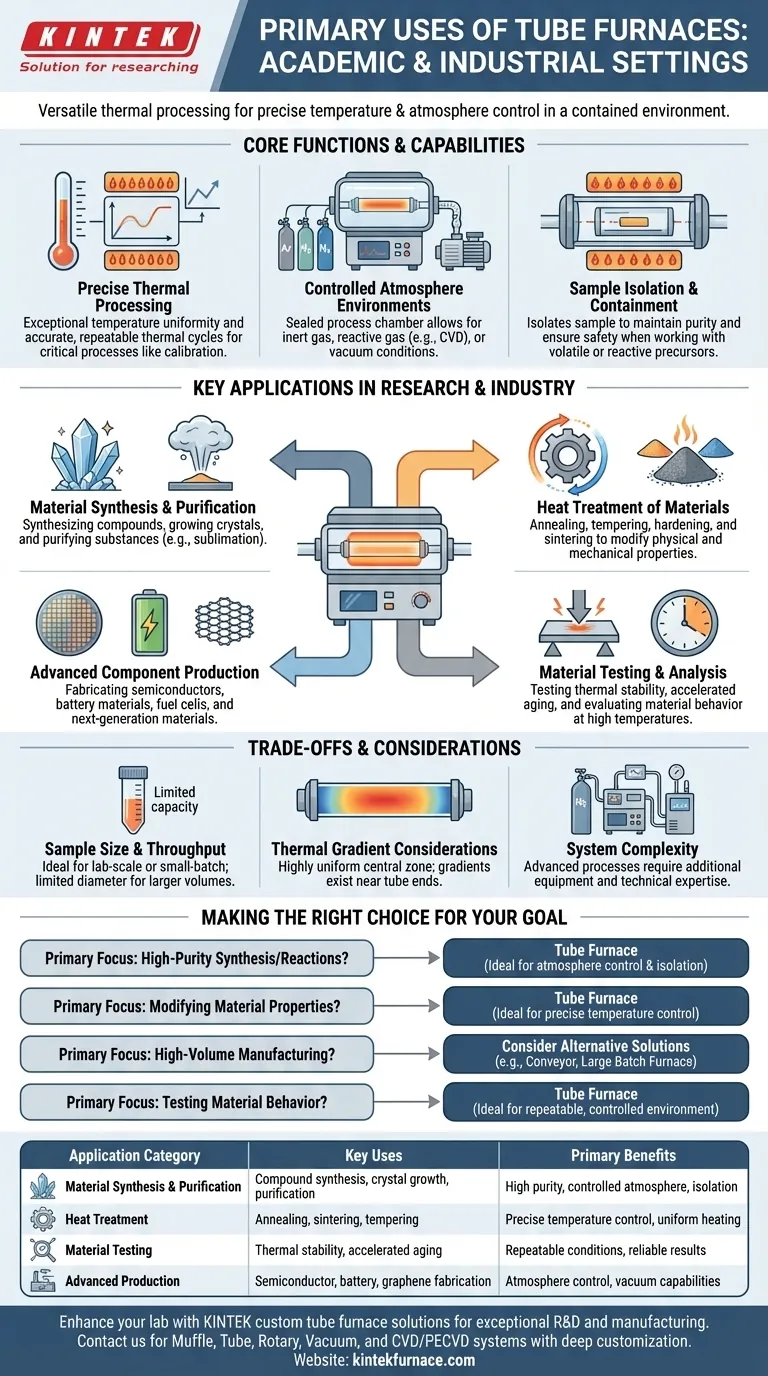
In essence, a tube furnace is a highly versatile thermal processing instrument used across academic and industrial labs for any task requiring precise temperature and atmosphere control within a contained environment. Its primary uses fall into three main categories: synthesizing or purifying compounds, heat-treating materials to alter their properties, and testing materials under specific thermal conditions.
The core value of a tube furnace is not just its ability to generate high temperatures, but its capacity to create a highly controlled and isolated environment. This allows for processes that are sensitive to atmospheric contamination or require specific gas compositions, making it an indispensable tool for advanced materials science and chemistry.
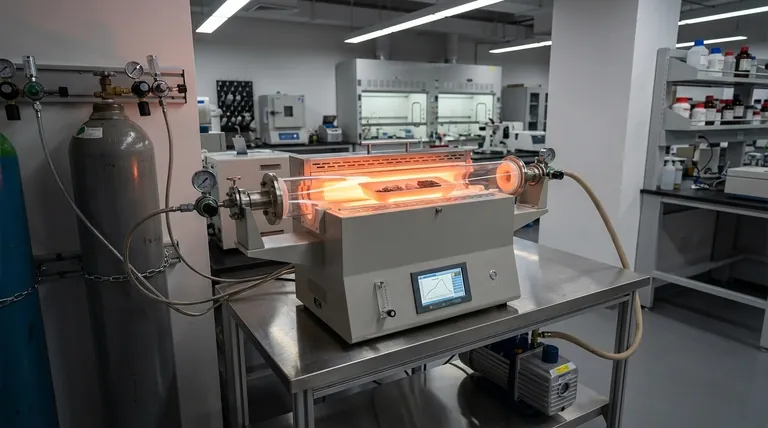

The Core Functions: Why Tube Furnaces Are So Versatile
To understand the vast range of applications, you must first understand the three fundamental capabilities that set tube furnaces apart.
Precise Thermal Processing
A tube furnace's design ensures exceptional temperature uniformity along the central heated zone. This precision is critical for processes where even minor temperature fluctuations can ruin a result.
They are engineered for accurate and repeatable thermal cycles, making them ideal for applications like thermocouple calibration, where the furnace acts as a known temperature reference.
Controlled Atmosphere Environments
The defining feature is the tube, which acts as a process chamber. It can be sealed and connected to gas or vacuum systems, allowing for complete atmosphere control.
This enables processing under an inert gas (like argon) to prevent oxidation, a reactive gas for chemical reactions like chemical vapor deposition (CVD), or a vacuum for degassing or brazing.
Sample Isolation and Containment
The process tube isolates the sample from the furnace's heating elements and the outside air. This is crucial for maintaining the purity of a sample during synthesis or purification.
This containment also ensures safety when working with volatile or reactive precursors, a common requirement in both academic research and industrial R&D.
Key Applications in Research and Industry
These core functions enable a wide array of specific, high-value applications.
Material Synthesis and Purification
Tube furnaces are a standard tool for synthesizing inorganic compounds and growing crystals. The controlled environment prevents unwanted side reactions and contamination.
They are also widely used for the purification of compounds through processes like sublimation, where a solid is vaporized and then re-condensed in a purer form elsewhere in the tube.
Heat Treatment of Materials
Annealing, tempering, and hardening are common heat treatment processes used to modify the physical and mechanical properties of metals and ceramics. A tube furnace provides the precise temperature control needed to achieve desired characteristics like ductility or hardness.
Sintering is another key application, where powders are heated to bond them together into a solid object, a fundamental step in producing ceramics and some metal components.
Advanced Component Production
The manufacturing of high-tech components relies heavily on the control offered by tube furnaces. This includes fabricating semiconductors, producing materials for batteries and solid oxide fuel cells, and developing next-generation materials like graphene.
Their ability to perform vacuum brazing is also critical for joining dissimilar materials in aerospace and electronics applications.
Material Testing and Analysis
In R&D and quality control, tube furnaces are used to test the thermal stability of materials. This includes testing aerospace ceramics and metals under simulated high-temperature conditions.
Accelerated aging tests are also performed by exposing samples to elevated temperatures to predict their long-term performance and reliability.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly versatile, tube furnaces are not the right tool for every job.
Sample Size and Throughput
Tube furnaces are generally designed for lab-scale research or small-batch production. The diameter of the process tube inherently limits the size and volume of the material that can be processed at one time.
Thermal Gradient Considerations
While the central zone is highly uniform, temperature gradients exist near the ends of the tube. This must be considered for sample placement to ensure the entire workload receives the intended thermal treatment.
System Complexity
Implementing advanced processes like vacuum or specific gas flow requires additional equipment such as pumps, seals, and mass flow controllers. Operating these systems effectively requires a higher level of technical expertise.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine if a tube furnace fits your needs, consider your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is high-purity synthesis or reactions: A tube furnace is an ideal choice due to its excellent atmosphere control and sample isolation.
- If your primary focus is modifying material properties: A tube furnace offers the precise temperature control required for heat treatments like annealing, sintering, or tempering.
- If your primary focus is high-volume manufacturing: You should consider alternative solutions like a conveyor or large batch furnace, as a tube furnace is not designed for mass production.
- If your primary focus is testing material behavior at temperature: A tube furnace provides a repeatable and controlled environment perfect for R&D and quality control testing.
Ultimately, a tube furnace is the definitive tool when control over the processing environment is just as important as the temperature itself.
Summary Table:
| Application Category | Key Uses | Primary Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Material Synthesis & Purification | Compound synthesis, crystal growth, purification | High purity, controlled atmosphere, sample isolation |
| Heat Treatment | Annealing, sintering, tempering | Precise temperature control, uniform heating |
| Material Testing | Thermal stability testing, accelerated aging | Repeatable conditions, reliable results |
| Advanced Production | Semiconductor, battery, graphene fabrication | Atmosphere control, vacuum capabilities |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with a custom tube furnace solution? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you're in academic research or industrial R&D, we can help you achieve superior thermal processing with tailored designs. Contact us today to discuss your needs and discover how KINTEK can bring precision and efficiency to your projects!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What are the material requirements for furnace tubes? Optimize Performance and Safety in High-Temperature Labs
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What core process conditions does a tube furnace provide? Mastering Catalyst Precursor Treatment
- What is flash vacuum pyrolysis and how is a tube furnace utilized in this process? Unlock High-Temp Chemical Reactions



















