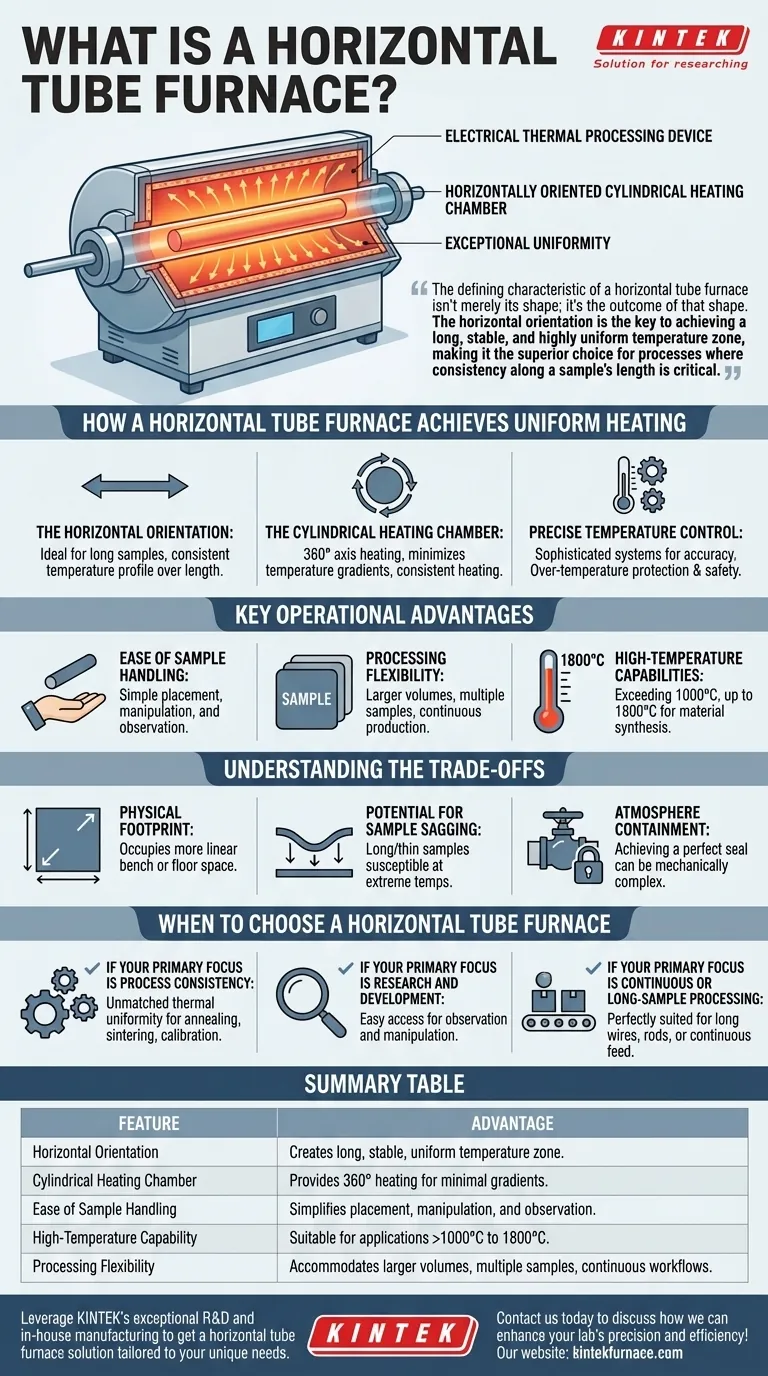
At its core, a horizontal tube furnace is an electric thermal processing device defined by its horizontally oriented cylindrical heating chamber. It is engineered to apply heat with exceptional uniformity to a sample placed inside the tube, using heating elements that surround the chamber to ensure consistent temperature distribution.
The defining characteristic of a horizontal tube furnace isn't merely its shape; it's the outcome of that shape. The horizontal orientation is the key to achieving a long, stable, and highly uniform temperature zone, making it the superior choice for processes where consistency along a sample's length is critical.

How a Horizontal Tube Furnace Achieves Uniform Heating
The performance of a horizontal tube furnace comes from its fundamental design, where each component contributes to thermal precision.
The Horizontal Orientation
The horizontal layout is ideal for processes that require a consistent temperature profile over a significant length. This allows for the uniform treatment of long samples or multiple smaller samples laid out in a row.
The Cylindrical Heating Chamber
Heating elements encircle the ceramic or metallic tube that contains the sample. This design ensures heat is applied from all sides (360° axis), which minimizes temperature gradients and delivers consistent heating to the entire workpiece.
Precise Temperature Control
These furnaces are equipped with sophisticated control systems that monitor and maintain the desired temperature with high accuracy. This is often coupled with safety features like over-temperature protection and interlocks to safeguard both the sample and the equipment.
Key Operational Advantages
The design of a horizontal tube furnace provides several practical benefits that make it a versatile tool in both laboratory and industrial settings.
Ease of Sample Handling
The horizontal design allows for simple placement, manipulation, and removal of samples. This makes it particularly effective for experiments that require observation, rotation, or adjustments during the heating process.
Processing Flexibility
Horizontal furnaces can often accommodate larger working volumes compared to other designs. This flexibility allows for the processing of bigger components, multiple samples in a single batch, or even continuous production where material is fed through the tube.
High-Temperature Capabilities
These systems are built to operate at very high temperatures, frequently exceeding 1000°C and in some cases reaching up to 1800°C. This makes them suitable for a wide range of material synthesis, testing, and processing applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, the horizontal design presents specific considerations that must be weighed against its benefits.
Physical Footprint
By nature, a long horizontal tube furnace will occupy more linear bench or floor space than a vertical furnace with an equivalent processing volume. This can be a limiting factor in crowded lab environments.
Potential for Sample Sagging
At extreme temperatures, long or thinly supported samples can be susceptible to sagging or deformation under the force of gravity. This is a physical constraint that vertical furnaces do not face.
Atmosphere Containment
While many tube furnaces are designed for use with controlled atmospheres, achieving a perfect seal can sometimes be more mechanically complex with a horizontal orientation, especially in designs that require frequent opening and closing for sample access.
When to Choose a Horizontal Tube Furnace
Your specific goal will determine if a horizontal tube furnace is the right solution for your thermal processing needs.
- If your primary focus is process consistency: The unmatched thermal uniformity is ideal for applications like annealing, sintering, or calibration where every part of the sample must receive identical heat treatment.
- If your primary focus is research and development: The easy access for sample observation and manipulation makes it invaluable for experimental work and material testing.
- If your primary focus is continuous or long-sample processing: The horizontal layout is perfectly suited for treating long wires, rods, or materials that need to be fed continuously through the heating zone.
By understanding its core design principles, you can leverage a horizontal tube furnace not just for what it is, but for the precise and repeatable results it enables.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Advantage |
|---|---|
| Horizontal Orientation | Creates a long, stable, and highly uniform temperature zone for consistent heating along a sample's length. |
| Cylindrical Heating Chamber | Provides 360° heating for minimal temperature gradients and uniform heat distribution. |
| Ease of Sample Handling | Simplifies placement, manipulation, and observation of samples during experiments. |
| High-Temperature Capability | Suitable for demanding applications, operating at temperatures exceeding 1000°C and up to 1800°C. |
| Processing Flexibility | Accommodates larger volumes, multiple samples, or continuous processing workflows. |
Leverage KINTEK's exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to get a horizontal tube furnace solution tailored to your unique needs.
Our advanced product line, including Tube Furnaces, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities. We work with you to precisely meet your experimental requirements for annealing, sintering, calibration, or material synthesis.
Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your lab's precision and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety



















