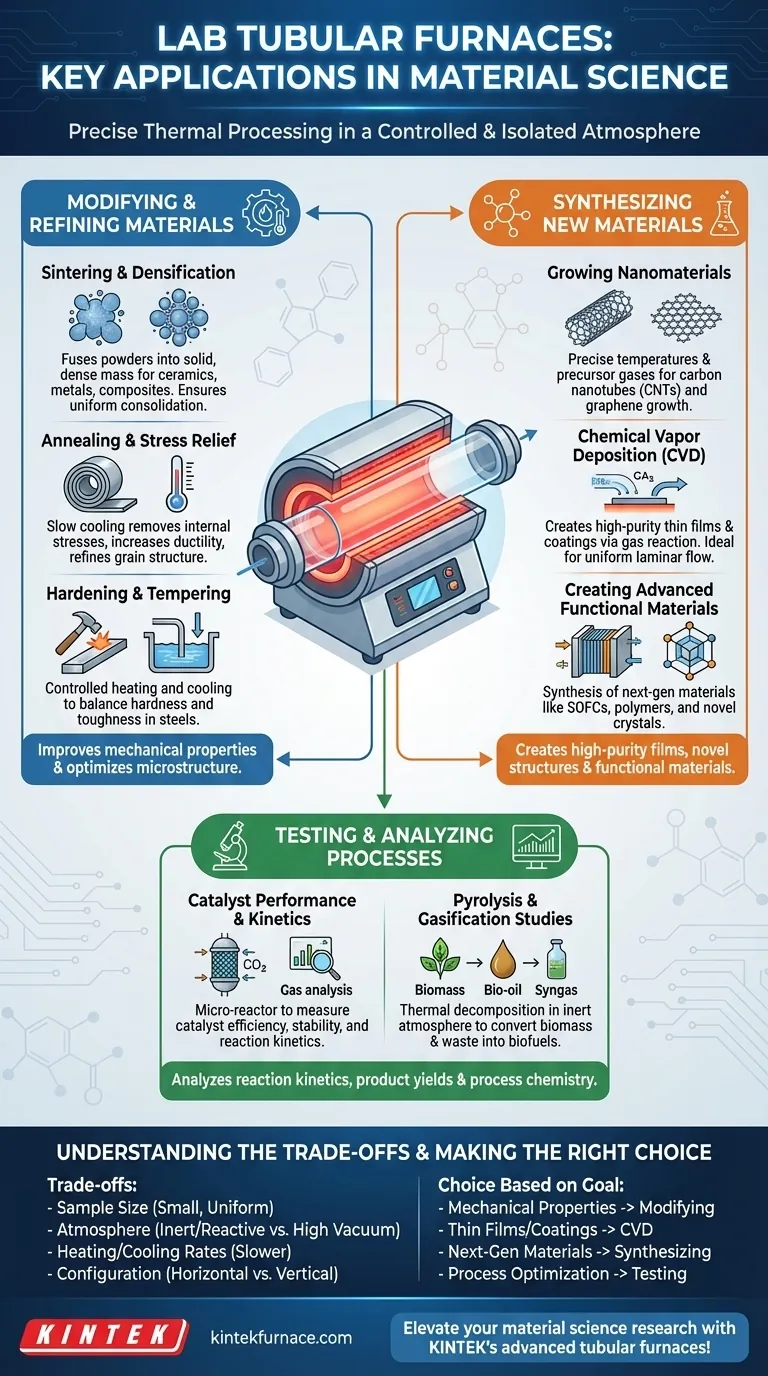
At its core, a laboratory tubular furnace is an indispensable tool for material science, enabling the precise thermal processing required to create, modify, and test a vast range of materials. Its common applications fall into three main categories: refining material properties through heat treatment like sintering and annealing, synthesizing new materials like graphene and advanced coatings via chemical vapor deposition, and analyzing process chemistry in fields like catalysis and renewable energy.
The true value of a tubular furnace is not just its ability to generate high temperatures. Its power lies in combining that heat with a tightly controlled and isolated atmosphere, giving researchers an unparalleled ability to dictate the outcome of material transformations.
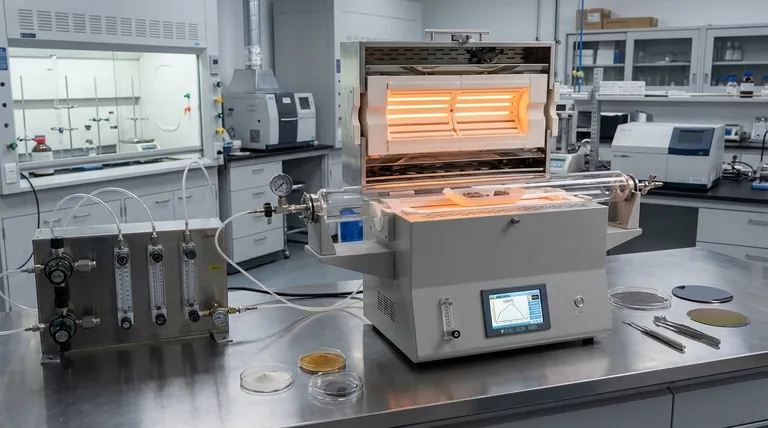

Modifying and Refining Existing Materials
The most fundamental use of a tubular furnace is to alter the microstructure and properties of a material through carefully controlled heating and cooling cycles.
Sintering and Densification
Sintering is the process of using heat to fuse powders into a solid, dense mass without melting them completely. This is the primary method for creating advanced ceramics, metal components from powder metallurgy, and certain composites.
The uniform heating zone of a tube furnace ensures the entire part consolidates evenly, preventing defects and ensuring consistent mechanical properties.
Annealing and Stress Relief
Annealing involves heating a material and then cooling it slowly to remove internal stresses, increase ductility, and refine its grain structure.
This process is critical for metals and alloys that have become brittle after manufacturing processes like rolling or drawing. A controlled atmosphere prevents oxidation on the material's surface during this high-temperature process.
Hardening and Tempering
Other heat treatments, such as hardening (rapid cooling or quenching) and tempering (reheating to a lower temperature), are also performed in tubular furnaces. These processes are used to achieve a desired balance of hardness and toughness, particularly in steels and other alloys.
Synthesizing Entirely New Materials
Beyond modifying existing materials, tubular furnaces are workhorses for creating novel materials from chemical precursors.
Growing Nanomaterials (Graphene & Carbon Nanotubes)
The synthesis of nanomaterials often requires precise temperatures and specific precursor gases. Tubular furnaces, especially specialized graphite models, are essential for growing materials like carbon nanotubes (CNTs) and graphene.
Catalyst particles are heated within the tube while a carbon-containing gas flows over them, leading to the controlled growth of these high-performance materials.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
CVD is a technique used to create high-purity, high-performance thin films and coatings. In this process, volatile precursor gases react or decompose on a heated substrate surface inside the furnace tube.
The tubular design is ideal for CVD because it allows for laminar gas flow over the substrate, leading to uniform film thickness. Vertical tube furnaces are often preferred to prevent particle contamination.
Creating Advanced Functional Materials
Tubular furnaces are central to research on next-generation materials like solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs), polymer composites, and novel crystals. They provide the controlled, high-temperature environment needed to synthesize the unique ceramic and composite structures that give these materials their special electronic or structural properties.
Testing and Analyzing Material Processes
The furnace often serves as a small-scale reactor, allowing scientists to study chemical and physical transformations under controlled conditions.
Catalyst Performance and Kinetics
In chemical engineering and research, a tube furnace acts as a micro-reactor. A catalyst bed is placed inside the tube, heated to a specific temperature, and reactant gases are passed through it.
By analyzing the output gas stream, researchers can accurately measure the catalyst's efficiency, stability, and reaction kinetics, which is vital for developing better industrial catalysts.
Pyrolysis and Gasification Studies
Pyrolysis is the thermal decomposition of materials at high temperatures in an inert atmosphere. This process is heavily researched for converting biomass and waste into valuable biofuels and chemicals (bio-oil and syngas).
A tube furnace allows scientists to precisely control the heating rate and final temperature to study how these variables affect the yield and composition of the final products.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While incredibly versatile, the tubular furnace is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Sample Size and Geometry
The defining "tube" shape is also its main constraint. These furnaces are ideal for small, uniform samples like powders, wafers, or small rods but are unsuitable for large or irregularly shaped components.
Atmosphere vs. High Vacuum
Standard quartz or ceramic tubes are excellent for processing in inert (Nitrogen, Argon) or reactive gas atmospheres. However, achieving and maintaining a high vacuum requires specialized, more expensive turbo pumps and leak-tight flange systems.
Heating and Cooling Rates
While temperature control is precise, the thermal mass of the furnace and insulation means that heating and cooling rates are typically slower than specialized techniques like rapid thermal annealing (RTA) or induction heating.
Configuration Matters (Horizontal vs. Vertical)
A horizontal furnace is the most common and works for most sintering and annealing tasks. However, a vertical orientation is superior for CVD, crystal growth, or any process where you want to avoid sample contact with the tube walls or want gravity to assist the process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your research objective will determine how you use a tubular furnace.
- If your primary focus is improving mechanical properties: You will primarily use the furnace for sintering, annealing, and other heat treatments to optimize the microstructure of metals and ceramics.
- If your primary focus is creating novel thin films or coatings: Your key application will be Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), likely using a system with sophisticated gas flow control.
- If your primary focus is developing next-generation materials: You will use it for synthesizing nanomaterials like graphene or testing components for advanced energy and electronic applications.
- If your primary focus is process optimization and research: You will use the furnace as a controlled reactor for catalysis studies or pyrolysis experiments to understand reaction chemistry.
Ultimately, the tubular furnace is a cornerstone of the modern materials lab, providing the controlled environment necessary to drive innovation from fundamental research to applied engineering.
Summary Table:
| Application Category | Key Uses | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Modifying Materials | Sintering, Annealing, Hardening | Improves mechanical properties, removes stresses |
| Synthesizing Materials | Graphene growth, CVD, Functional materials | Creates high-purity films and novel structures |
| Testing Processes | Catalyst studies, Pyrolysis | Analyzes reaction kinetics and product yields |
Elevate your material science research with KINTEK's advanced tubular furnaces! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide tailored solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, whether you're refining materials, synthesizing coatings, or optimizing processes. Contact us today to discuss how our high-temperature furnace solutions can drive your innovations forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis



















