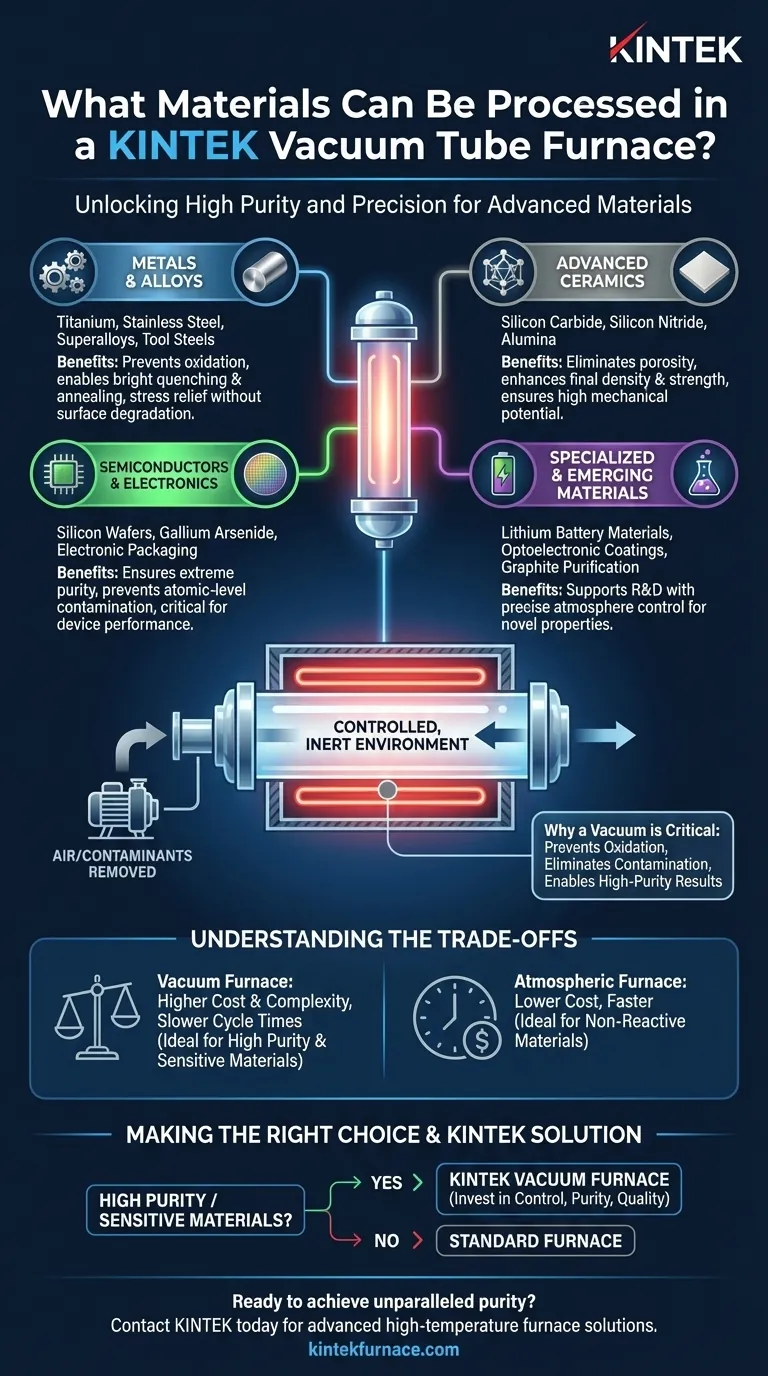
In short, a vacuum tube furnace can process an exceptionally wide range of materials. Its capabilities extend across metals, advanced ceramics, glass, and semiconductors. This versatility makes it an indispensable tool for high-stakes industries like aerospace, electronics, and materials research, where material purity and performance are paramount.
The critical question is not what materials can be processed in a vacuum furnace, but why a vacuum is necessary. The core function of the vacuum is to create a controlled, inert environment that prevents unwanted chemical reactions—primarily oxidation—enabling high-purity results that are impossible to achieve in open air.

Why a Vacuum Environment is Critical
Heating a material can trigger chemical reactions with the surrounding atmosphere. A vacuum furnace eliminates the primary reactant—air—allowing for precise control over the material's final properties.
Preventing Oxidation and Contamination
When most materials are heated to high temperatures in the presence of air, they react with oxygen. This process, oxidation, forms a brittle, undesirable surface layer that can degrade mechanical, electrical, and aesthetic properties.
A vacuum furnace removes the air, thereby removing the oxygen. This prevents oxidation and ensures the material surface remains clean, or "bright," a key requirement for processes like brazing and annealing sensitive alloys.
Enabling High-Purity Processes
Many advanced processes require an environment free from any potential contaminants. A vacuum provides the ultimate clean slate.
This is essential for sintering, where powdered materials are heated to bond together. Any trapped gases or impurities can create voids and compromise the final density and strength of the part. It is also critical for processing semiconductors, where even microscopic contaminants can ruin a device.
A Breakdown of Compatible Material Groups
The controlled environment of a vacuum furnace makes it suitable for a diverse array of sensitive and high-performance materials.
Metals and Alloys
This is the most common application. A vacuum is essential for heat-treating metals that are highly reactive with oxygen.
Examples include titanium alloys, stainless steel, superalloys, and tool steels. Processes like vacuum annealing relieve internal stresses without causing surface oxidation, while bright quenching achieves hardness without discoloration. Magnetic materials and rare earth metals also require this purity.
Advanced Ceramics
Vacuum furnaces are ideal for sintering high-performance ceramics where final density and strength are critical.
Materials like silicon carbide, silicon nitride, and alumina are processed in a vacuum to eliminate porosity and achieve their full mechanical potential.
Semiconductors and Electronics
The electronics industry relies on extreme purity. Vacuum processing is not just beneficial; it is mandatory for many steps.
This includes processing silicon wafers, gallium arsenide, and other semiconductor materials where any atomic-level contamination can disrupt electrical properties. It is also used for creating reliable electronic packaging and components.
Specialized and Emerging Materials
The precision of vacuum furnaces makes them a key tool for research and development.
This category includes lithium battery materials like solid-state electrolytes, materials for optoelectronic coatings, and the purification of materials like graphite. The ability to control the atmosphere is crucial when developing new materials with novel properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a vacuum furnace is a specialized tool. It is not always the necessary or most efficient choice for every application.
Cost and Complexity
Vacuum furnaces are significantly more expensive and complex to operate and maintain than conventional atmospheric furnaces. They require vacuum pumps, sophisticated seals, and careful monitoring, all of which add to the operational overhead.
Slower Cycle Times
Achieving a deep vacuum and then carefully backfilling with an inert gas can add considerable time to the overall process cycle compared to simply heating a part in air. For high-volume production of non-sensitive materials, this can be a major bottleneck.
Not Always the Best Choice
For materials that are not sensitive to oxidation or for processes where a slight oxide layer is acceptable or even desired, a standard atmospheric furnace is a far more practical and cost-effective solution.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct heating technology depends entirely on your material and the desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is high-purity metal processing (annealing, brazing, hardening): A vacuum furnace is essential to prevent oxidation and ensure superior mechanical properties and surface finish.
- If your primary focus is developing advanced ceramics or semiconductors: The controlled, contaminant-free environment of a vacuum furnace is non-negotiable for achieving target performance and reliability.
- If your primary focus is general heat treatment of non-reactive materials: A conventional atmospheric furnace is likely the more practical and cost-effective solution for your needs.
Ultimately, choosing a vacuum furnace is a decision to invest in control, purity, and the highest possible quality for your material.
Summary Table:
| Material Group | Key Examples | Primary Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Metals and Alloys | Titanium alloys, stainless steel, superalloys | Prevents oxidation, enables bright quenching and annealing |
| Advanced Ceramics | Silicon carbide, silicon nitride, alumina | Eliminates porosity, enhances density and strength |
| Semiconductors and Electronics | Silicon wafers, gallium arsenide | Ensures extreme purity, prevents contamination |
| Specialized Materials | Lithium battery materials, optoelectronic coatings | Supports R&D with precise atmosphere control |
Ready to achieve unparalleled purity and precision in your material processing? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our vacuum tube furnaces can enhance your research and production outcomes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide



















