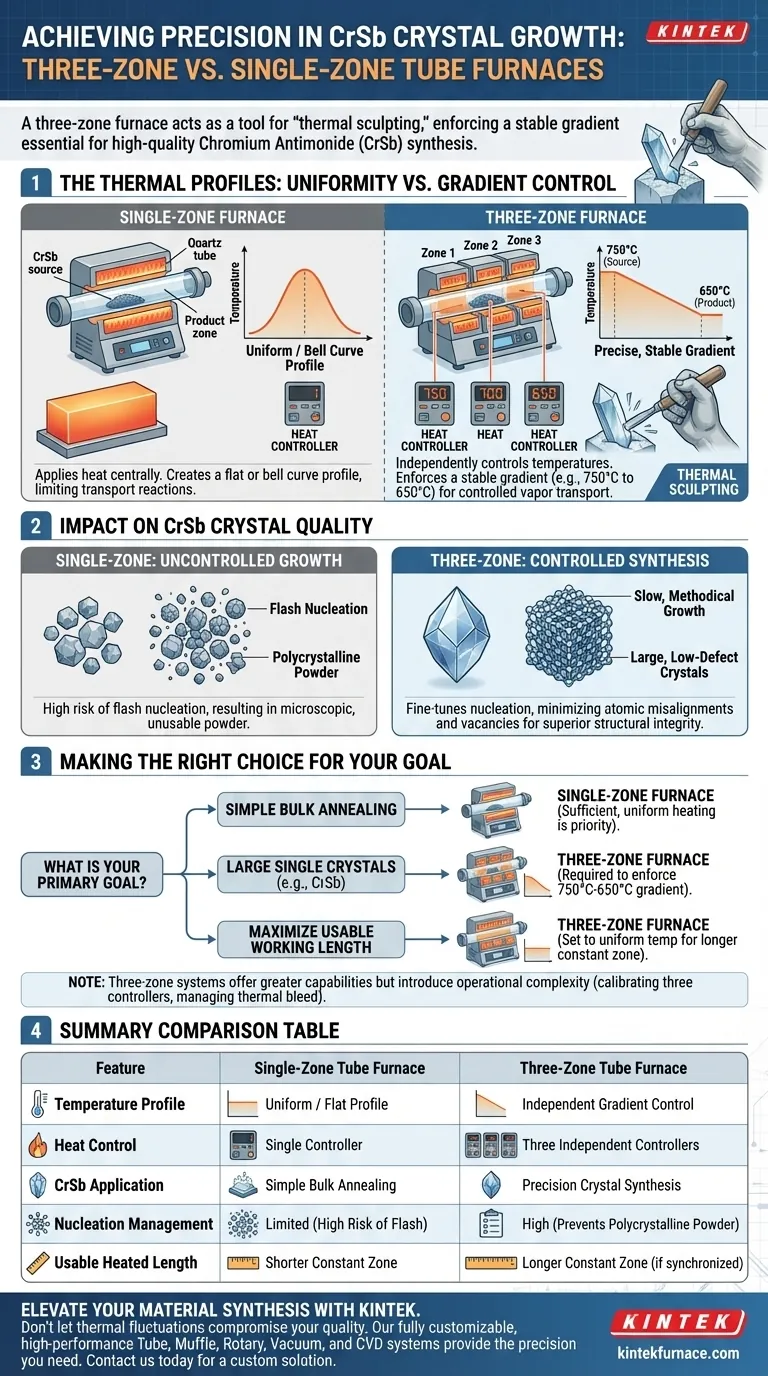
The primary technical advantage of a three-zone furnace is the ability to enforce a precise, stable temperature gradient across the reaction tube, which is impossible in a standard single-zone configuration. For Chromium Antimonide (CrSb), this allows you to maintain the reaction end at exactly 750°C while simultaneously holding the product end at 650°C. This specific thermal differential is the governing factor in synthesizing high-quality crystals.
Core Takeaway While a single-zone furnace excels at creating a uniform heat environment, a three-zone furnace acts as a tool for thermal sculpting. By independently controlling the temperature at different points along the tube, you gain direct authority over crystal nucleation and growth rates, resulting in significantly larger, lower-defect CrSb crystals.

The Mechanics of Gradient Control
Independent Zone Management
A single-zone furnace applies heat centrally, creating a bell curve or a flat thermal profile that creates limitations for transport reactions.
In contrast, a three-zone system utilizes three separate heating elements with independent controllers. This allows you to "pin" specific temperatures at the start, middle, and end of the quartz tube.
Establishing the Thermal Slope
For CrSb specifically, the process requires a driving force to move material from the source to the deposition zone.
By setting the zones to create a drop from 750°C to 650°C, you establish a stable gradient. This slope dictates the speed and stability of the vapor transport, preventing the chaotic deposition often seen in thermally uniform environments.
Impact on CrSb Crystal Quality
Controlling Nucleation Rates
The defining challenge in crystal growth is managing supersaturation—the state that forces the material to solidify.
The three-zone configuration allows you to fine-tune the temperature of the product end (650°C) relative to the source. This prevents "flash" nucleation, where too many crystals form at once, resulting in a microscopic, polycrystalline powder rather than a usable crystal.
Minimizing Defects
Thermal stability is directly correlated to the structural integrity of the final product.
By maintaining a highly uniform gradient, the three-zone furnace ensures that the crystal lattice builds slowly and methodically. This reduces atomic misalignments and vacancies, producing large, low-defect crystals that superior to those grown in fluctuating or uniform thermal fields.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Operational Complexity
A three-zone system introduces more variables into your process. You must calibrate three controllers rather than one, and understanding the interplay between adjacent zones (thermal bleed) requires careful characterization.
Uniformity vs. Gradient Capabilities
It is worth noting that a three-zone furnace can mimic a single-zone furnace if required. By setting all three zones to the same temperature, you can create a longer constant temperature zone than a standard single-zone furnace offers. However, a single-zone furnace can never mimic the gradient capabilities of a multi-zone system.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize your success with CrSb thermal treatment, align your equipment choice with your specific quality requirements:
- If your primary focus is obtaining large, single crystals: You must use a three-zone furnace to strictly enforce the 750°C to 650°C gradient required for controlled nucleation.
- If your primary focus is simple bulk annealing: A single-zone furnace is sufficient, as uniform heating is the priority over vapor transport.
- If your primary focus is maximizing the usable working length: A three-zone furnace set to a uniform temperature provides a longer stable heat zone than a comparable single-zone unit.
Ultimately, the three-zone furnace converts temperature from a passive environmental factor into an active, tunable variable for crystal engineering.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Single-Zone Tube Furnace | Three-Zone Tube Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Profile | Uniform / Flat Profile | Independent Gradient Control |
| Heat Control | Single Controller | Three Independent Controllers |
| CrSb Application | Simple Bulk Annealing | Precision Crystal Synthesis |
| Nucleation Management | Limited (High Risk of Flash) | High (Prevents Polycrystalline Powder) |
| Usable Heated Length | Shorter Constant Zone | Longer Constant Zone (if synchronized) |
Elevate Your Material Synthesis with KINTEK
Don’t let thermal fluctuations compromise your crystal quality. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to meet your unique research requirements.
Whether you are synthesizing CrSb or developing next-generation semiconductors, our precision three-zone furnaces provide the thermal sculpting power you need to reduce defects and maximize crystal size.
Ready to upgrade your lab's thermal capabilities? Contact KINTEK today for a custom solution.
Visual Guide
References
- B. Rai, Nitesh Kumar. Direction‐Dependent Conduction Polarity in Altermagnetic CrSb. DOI: 10.1002/advs.202502226
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a Drop Tube Furnace (DTF) play in large-scale wheat straw combustion? Unlock Industrial Performance Data
- What is the significance of a rapid quenching device at the bottom of a lab tube furnace? Capture High-Temp Snapshot
- What is the basic function of a High Temperature Tube Furnace? Precision Thermal Processing for Material Synthesis
- Why is quartz tube vacuum sealing technology utilized during the synthesis of [Pd@Bi10][AlCl4]4 cluster compounds?
- What role does a high-temperature tube furnace play in synthesizing SiQDs? Precision Control for HSQ Pyrolysis
- How does the heat treatment temperature in a tube furnace influence RPW electrodes? Optimize Carbonization Performance
- What is the primary function of a high-temperature tube furnace in Bi-doped CaZnOS synthesis? Achieving Phase Purity
- What role do sealed quartz or glass tubes play in the synthesis of ternary copper sulfides? Mastering Micro-Reactors



















