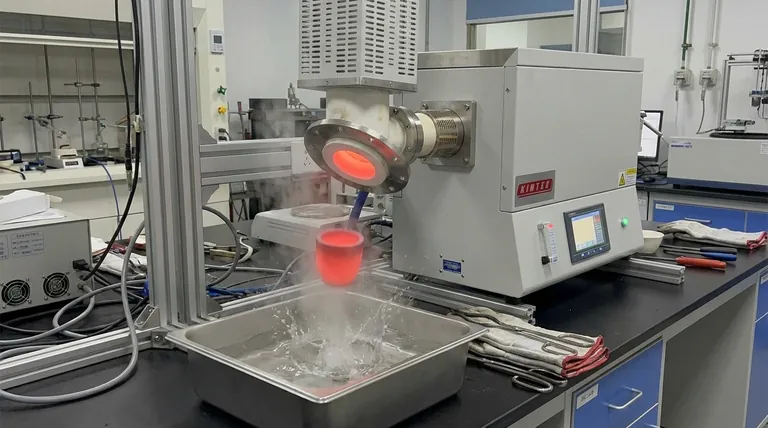
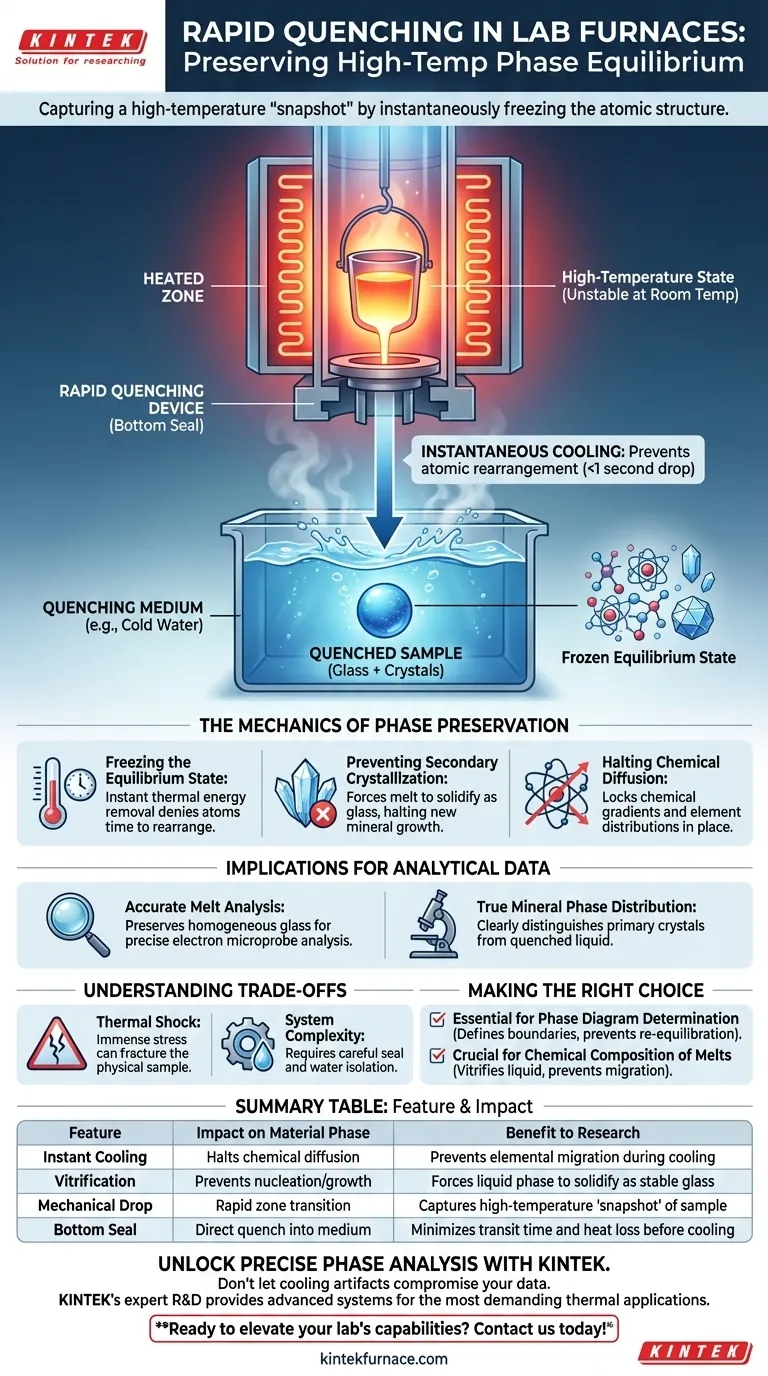
Rapid quenching is the critical mechanism for capturing a high-temperature "snapshot" of a material. By utilizing a device that releases a sample through a bottom seal directly into cold water, researchers effectively "lock" the atomic structure in its equilibrium state. This instantaneous cooling is the only way to prevent the material from altering its chemical or physical makeup as it transitions back to room temperature.
The primary significance of rapid quenching is the instantaneous cessation of chemical diffusion and secondary crystallization. It allows researchers to capture a high-temperature state permanently, ensuring that subsequent analysis reflects the true conditions of the experiment rather than artifacts of the cooling process.

The Mechanics of Phase Preservation
Freezing the Equilibrium State
At high temperatures, materials exist in specific phase equilibriums that are often unstable at room temperature. The quenching device functions by physically dropping the sample from the heated zone into a cooling medium, typically cold water.
This drastic drop in temperature happens in a fraction of a second. It denies the atoms the thermal energy required to rearrange themselves into low-temperature structures.
Preventing Secondary Crystallization
One of the primary threats to data accuracy is secondary crystallization. If a sample cools slowly, the melt (liquid portion) may begin to crystallize into new minerals that did not exist at the target experimental temperature.
Rapid quenching prevents this nucleation and growth. It forces the liquid phase to solidify as glass, preserving its chemical composition exactly as it was during the experiment.
Halting Chemical Diffusion
In addition to preventing new crystal growth, quenching stops chemical diffusion. Without this rapid freeze, elements would continue to migrate between the solid and liquid phases as the temperature dropped.
By instantly halting this movement, the device ensures that the chemical gradients and element distributions remain static for analysis.
Implications for Analytical Data
Accurate Melt Component Analysis
To understand the properties of a melt (magma or slag) at high temperatures, you must analyze its composition without interference from cooling artifacts.
Quenching preserves the melt as a homogeneous glass. This allows researchers to use tools like electron microprobes to measure the exact chemistry of the liquid phase as it existed at equilibrium.
True Mineral Phase Distribution
Researchers often need to know exactly which solid minerals coexist with liquid at a specific temperature.
By freezing the sample, the mineral phase distribution is preserved. This allows you to distinguish clearly between the primary crystals formed at equilibrium and the quenched liquid (glass) surrounding them.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Thermal Shock and Mechanical Integrity
The physical stress of dropping a sample from extreme heat into cold water is immense. This process creates significant thermal shock.
While this effectively freezes the chemistry, it often fractures the physical sample. If physical structural integrity (e.g., measuring the strength of the solidified piece) is required, this method may be destructive.
Seal and Retrieval Complexity
The mechanism relies on opening a seal at the bottom of the furnace. This adds mechanical complexity to the furnace design compared to a static setup.
Furthermore, introducing water near high-temperature electrical components requires careful isolation to prevent steam generation or equipment damage.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine if a bottom-loading quenching device is essential for your work, consider your specific analytical needs:
- If your primary focus is Phase Diagram Determination: You absolutely require rapid quenching to define accurate phase boundaries and prevent re-equilibration during cooling.
- If your primary focus is Chemical Composition of Melts: You must use quenching to vitrify (turn to glass) the liquid, preventing elements from migrating into crystals during slow cooling.
Rapid quenching transforms a dynamic, high-temperature experiment into a static, analyzable record of reality.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Impact on Material Phase | Benefit to Research |
|---|---|---|
| Instant Cooling | Halts chemical diffusion | Prevents elemental migration during cooling |
| Vitrification | Prevents nucleation/growth | Forces liquid phase to solidify as stable glass |
| Mechanical Drop | Rapid zone transition | Captures high-temperature 'snapshot' of sample |
| Bottom Seal | Direct quench into medium | Minimizes transit time and heat loss before cooling |
Unlock Precise Phase Analysis with KINTEK
Don't let cooling artifacts compromise your research data. KINTEK's expert R&D and manufacturing provide advanced Tube, Muffle, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed for the most demanding thermal applications. Whether you require a specialized bottom-loading quenching device or a custom high-temperature furnace, our team delivers the precision and reliability you need to capture perfect equilibrium states.
Ready to elevate your lab's capabilities? Contact us today to discuss your custom furnace needs!
Visual Guide
References
- Erin Keltie, James M. Brenan. Experiments and Models Bearing on the Role of Magma Mixing and Contamination on Chromite Crystallization in Ultramafic Magmas. DOI: 10.1093/petrology/egaf076
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does the temperature control program of a tube furnace affect NiSSe nanocrystal formation? Optimize Your Synthesis
- What distinguishes a compact tube furnace from other types? Ideal for Small-Scale Lab Precision
- How does a high-precision tube furnace contribute to the reduction process of Cu/ZIF-8 catalysts?
- How does sample handling differ between vertical and horizontal tube furnaces? Choose the Right Furnace for Your Lab
- How do tube furnaces contribute to transport reactions and crystal production? Master High-Purity Synthesis with Precision Control
- What changes occur in materials processed in a tube furnace? Discover Physical, Chemical, and Heat Treatment Transformations
- What is the difference between a tube furnace and a muffle furnace? Choose the Right High-Temp Solution
- How are tube furnaces designed for temperatures exceeding 1200°C? Unlock High-Temp Precision with Advanced Elements



















