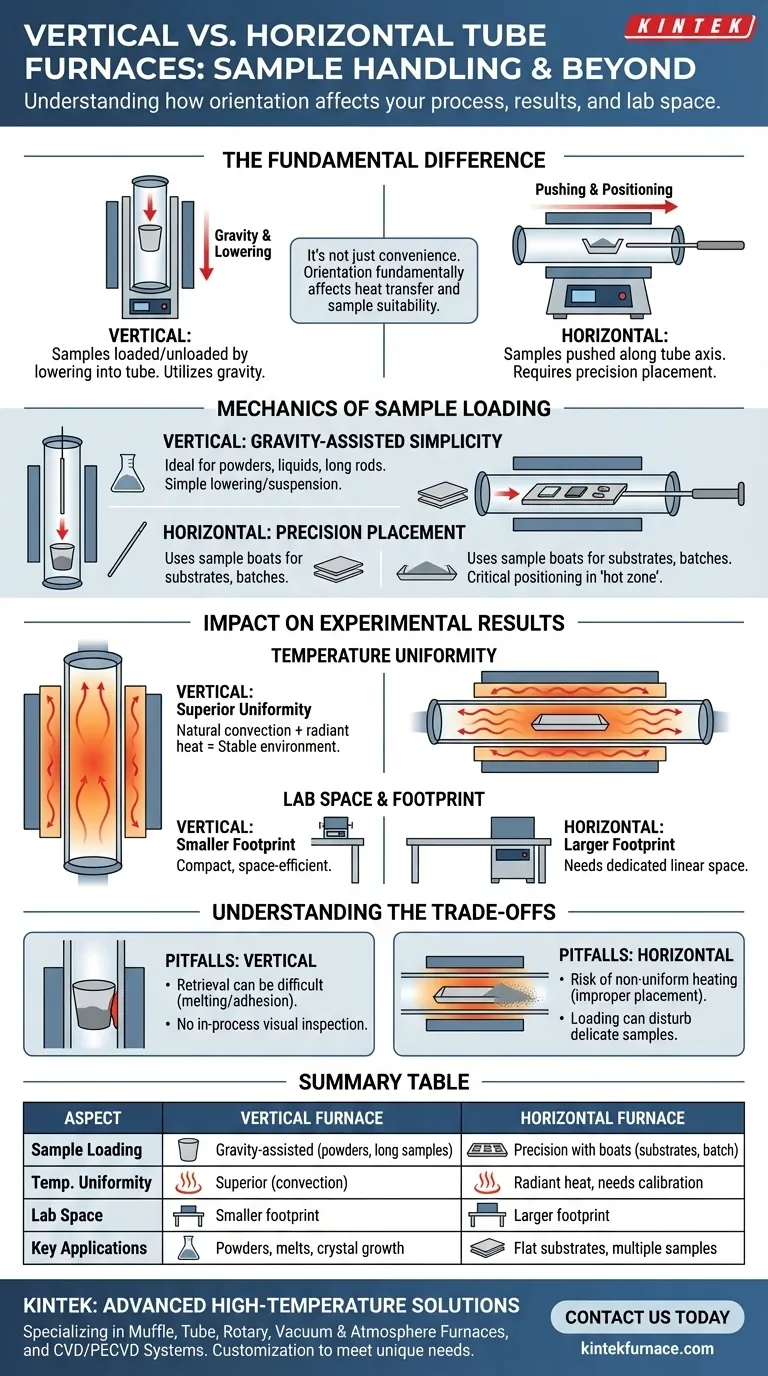
The fundamental difference in sample handling lies in the orientation and the forces at play. In a vertical furnace, samples are typically loaded and unloaded by lowering or dropping them into the processing tube, utilizing gravity for placement. Conversely, a horizontal furnace requires the sample to be pushed or placed along the tube's axis, demanding more careful positioning to ensure it resides in the optimal thermal zone.
The choice between a vertical and horizontal tube furnace is not merely about loading convenience. It is a critical decision driven by how the furnace's orientation fundamentally affects heat transfer, temperature uniformity, and suitability for your specific sample type and process.

The Mechanics of Sample Loading
The physical act of introducing a sample into the furnace is the most immediate difference between the two configurations. Each design is optimized for different types of materials and containers.
Vertical Furnaces: Gravity-Assisted Simplicity
Samples are inserted vertically into the tube, which is ideal for processes that benefit from gravity. This method is exceptionally straightforward for powders, granulated materials, or liquids held in crucibles.
This orientation also excels with long, thin samples, such as wires or rods, that need to be suspended along the vertical axis for uniform heating. Loading and unloading are often as simple as lowering the sample with a wire or placing it on a support rod.
Horizontal Furnaces: Precision Placement
In a horizontal furnace, samples are typically placed in a long, shallow container called a sample boat. This boat is then carefully pushed into the center of the tube using a long rod.
This method is necessary for processing multiple small samples at once or for materials that must remain in a fixed, stable position, such as substrates or silicon wafers. Achieving correct placement in the furnace's central "hot zone" is critical and may require more complex positioning mechanisms.
How Orientation Impacts Experimental Results
Beyond simple loading, the furnace's orientation has profound implications for temperature control and the types of processes you can run effectively. The choice impacts the reliability and consistency of your results.
Temperature Uniformity and Heat Transfer
Vertical furnaces often achieve superior temperature uniformity. As heat rises, natural convection currents work in concert with radiant heat from the surrounding elements, creating an exceptionally stable thermal environment along the sample's length.
Horizontal furnaces rely primarily on radiant heat. While highly effective, this can sometimes lead to slight temperature variations along the length of the processing tube. Careful calibration is required to ensure the entire sample experiences the target temperature.
Footprint and Lab Space
The physical space required is a practical but critical factor. Vertical furnaces possess a much smaller footprint, making them an excellent choice for crowded labs or facilities where benchtop space is at a premium.
Horizontal furnaces, by their nature, are longer and require more dedicated linear space. This can necessitate placement on a dedicated, larger bench or even require custom infrastructure.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither design is universally superior. Acknowledging the inherent limitations of each is key to avoiding failed experiments and making a sound investment.
Pitfalls of Vertical Furnaces
While loading is simple, sample retrieval can sometimes be difficult, especially if a material melts and adheres to the crucible or tube wall. The top-down view also makes in-process visual inspection of the sample nearly impossible.
Pitfalls of Horizontal Furnaces
The primary risk in a horizontal furnace is non-uniform heating. If a sample boat is too long or improperly placed, parts of the sample may fall outside the optimal hot zone, leading to inconsistent results across a batch. The act of pushing the sample in can also disturb delicate powders or coatings.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your decision should be guided by the primary goal of your thermal process.
- If your primary focus is maximum temperature uniformity for powders, melts, or crystal growth: A vertical furnace is typically the superior choice due to the benefits of natural convection.
- If your primary focus is batch processing flat substrates or multiple solid samples: A horizontal furnace provides the practical layout needed to arrange samples in a boat for simultaneous processing.
- If your primary focus is conserving laboratory space: A vertical furnace offers a significantly more compact footprint for its processing volume.
By understanding how orientation dictates both handling and heating, you can confidently select the furnace that ensures the integrity and success of your work.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Vertical Furnace | Horizontal Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Sample Loading | Gravity-assisted, ideal for powders, liquids, and long samples | Precision placement with sample boats, suited for substrates and batch processing |
| Temperature Uniformity | Superior due to natural convection | Relies on radiant heat, may require calibration |
| Lab Space | Smaller footprint, space-efficient | Larger footprint, needs more linear space |
| Key Applications | Powders, melts, crystal growth | Flat substrates, multiple solid samples |
Struggling to choose the right tube furnace for your lab? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can enhance your process efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide



















