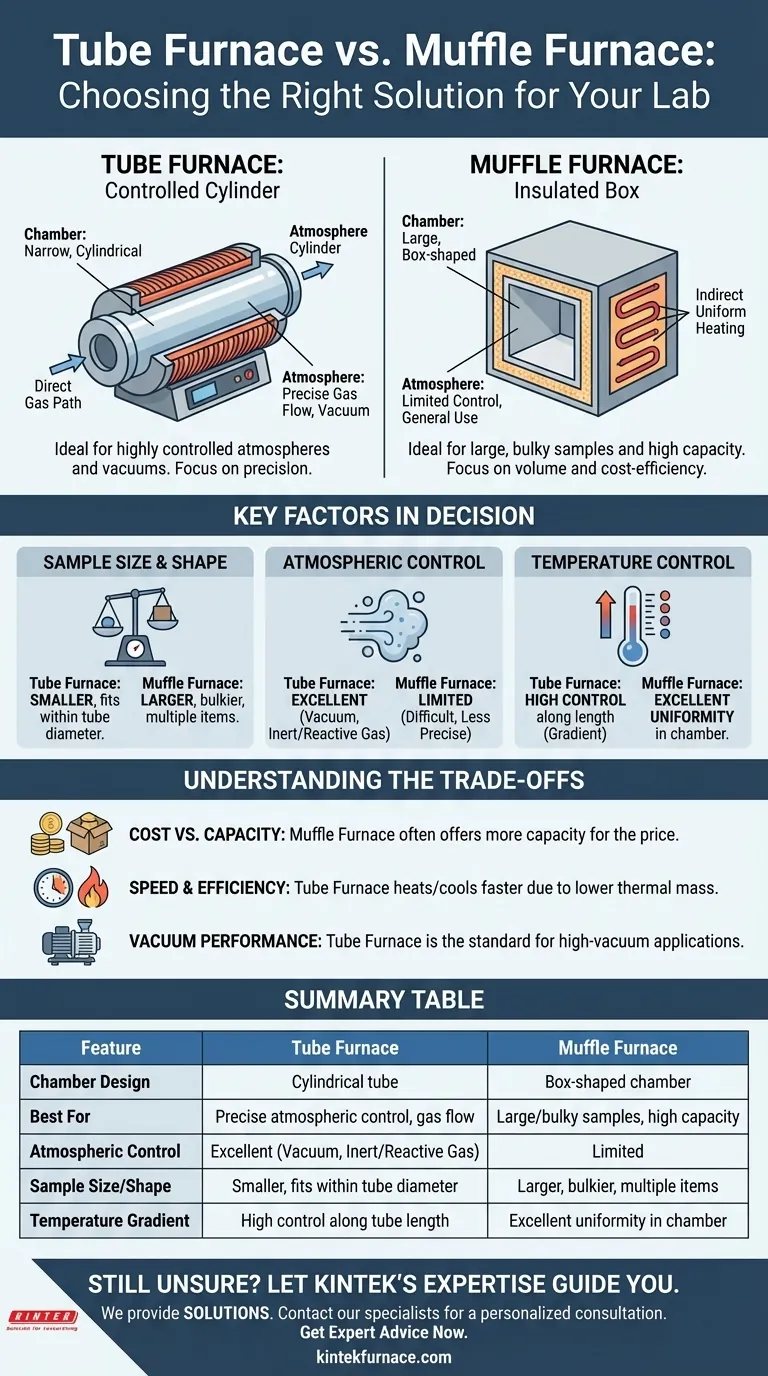
At its core, the difference between a tube furnace and a muffle furnace comes down to chamber geometry and its resulting impact on atmospheric control. A tube furnace uses a narrow, cylindrical chamber ideal for precise control over gas flow and temperature gradients, while a muffle furnace uses a larger, box-shaped chamber designed for heating bigger samples or multiple items at once.
The decision hinges on a fundamental trade-off. Choose a tube furnace for processes requiring highly controlled atmospheres or vacuums. Choose a muffle furnace when you need to process larger, bulkier samples or prioritize capacity and cost-effectiveness over atmospheric purity.

The Fundamental Design Difference
The names themselves hint at their construction. One is a tube, the other is a box. This core difference in shape dictates their ideal applications, advantages, and limitations.
Muffle Furnace: The Insulated Box
A muffle furnace is essentially a front-loading oven with a chamber made of a high-temperature, non-contaminating material. The heating elements are positioned outside this chamber, or "muffle."
This design provides indirect heating. The sample is protected from direct contact with the heating elements, which ensures excellent temperature uniformity and prevents contamination. Its large, boxy chamber is its defining feature.
Tube Furnace: The Controlled Cylinder
A tube furnace features a cylindrical tube, typically made of quartz, alumina, or ceramic, surrounded by heating coils. The ends of the tube can be sealed.
This design is purpose-built for atmospheric control. The narrow, enclosed geometry makes it simple to create a vacuum or to introduce a precise flow of inert or reactive gases over a sample.
Key Factors in Your Decision
Choosing the right furnace requires you to weigh your priorities regarding sample size, atmosphere, and temperature precision.
Sample Size and Shape
This is the most straightforward differentiator. A muffle furnace is the clear choice for samples that are large, bulky, or oddly shaped. It is also ideal for processing many smaller samples simultaneously.
A tube furnace is limited by the diameter and length of its tube. It is only suitable for smaller samples that can fit comfortably inside.
Atmospheric Control
The tube furnace offers unparalleled atmospheric control. Its easily sealed ends and defined cylindrical path are perfect for creating high-vacuum conditions or for processes that depend on a specific gas flowing over the sample, such as chemical vapor deposition (CVD).
While some muffle furnaces can be fitted with gas ports, achieving a truly pure, controlled, and uniform atmosphere is significantly more difficult and less precise than in a tube furnace.
Temperature Uniformity and Control
Both furnace types offer precise temperature control. However, a tube furnace provides more granular control over the temperature gradient along its length, which is critical for certain material synthesis and crystal growth applications.
A muffle furnace delivers excellent temperature uniformity throughout its larger chamber, making it reliable for processes like ashing, sintering, or annealing where the entire sample must be held at a single, stable temperature.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither furnace is universally superior. The optimal choice depends on balancing performance needs with practical constraints.
Cost vs. Capacity
For a given price, a muffle furnace almost always offers more internal capacity. If your primary need is heating volume, the muffle furnace is the more cost-effective solution.
Speed and Efficiency
The large thermal mass of a muffle furnace means it is generally slower to heat up and cool down than a smaller tube furnace. This can impact your total processing time and throughput, especially for processes requiring multiple cycles.
Vacuum Performance
While both types can be configured for vacuum use, the tube furnace is the standard for high-vacuum, oxygen-free applications. Its simple, cylindrical geometry is far easier to seal reliably than the large front-loading door of a muffle furnace.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Evaluate your primary goal to make a clear decision.
- If your primary focus is precise atmospheric control for processes like CVD or creating specific gas environments: The tube furnace is the superior choice due to its easily sealed cylindrical design.
- If your primary focus is processing larger items, multiple samples at once, or general-purpose heat treatment: The muffle furnace offers greater capacity and versatility, often at a lower cost per unit of volume.
- If your process requires a specific, controlled flow of gas directly across a sample: The tube furnace's defined inlet and outlet points make it the only practical option.
Ultimately, your decision rests on whether your process demands the specialized atmospheric precision of a tube furnace or the general-purpose capacity of a muffle furnace.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Tube Furnace | Muffle Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Chamber Design | Cylindrical tube | Box-shaped chamber |
| Best For | Precise atmospheric control, gas flow | Large/bulky samples, high capacity |
| Atmospheric Control | Excellent (Vacuum, Inert/Reactive Gas) | Limited |
| Sample Size/Shape | Smaller, fits within tube diameter | Larger, bulkier, multiple items |
| Temperature Gradient | High control along tube length | Excellent uniformity in chamber |
Still Unsure Which Furnace is Right for Your Application?
Let KINTEK's expertise guide you. Choosing between a tube and muffle furnace is a critical decision that impacts your research outcomes and efficiency.
We don't just sell furnaces; we provide solutions. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer a comprehensive product line—including Tube Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Rotary Furnaces, and advanced CVD/PECVD Systems—backed by deep customization capabilities to meet your unique experimental requirements perfectly.
Contact our thermal processing specialists today for a personalized consultation. We'll help you analyze your specific needs for sample size, atmosphere, and temperature control to recommend the optimal furnace solution.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab



















