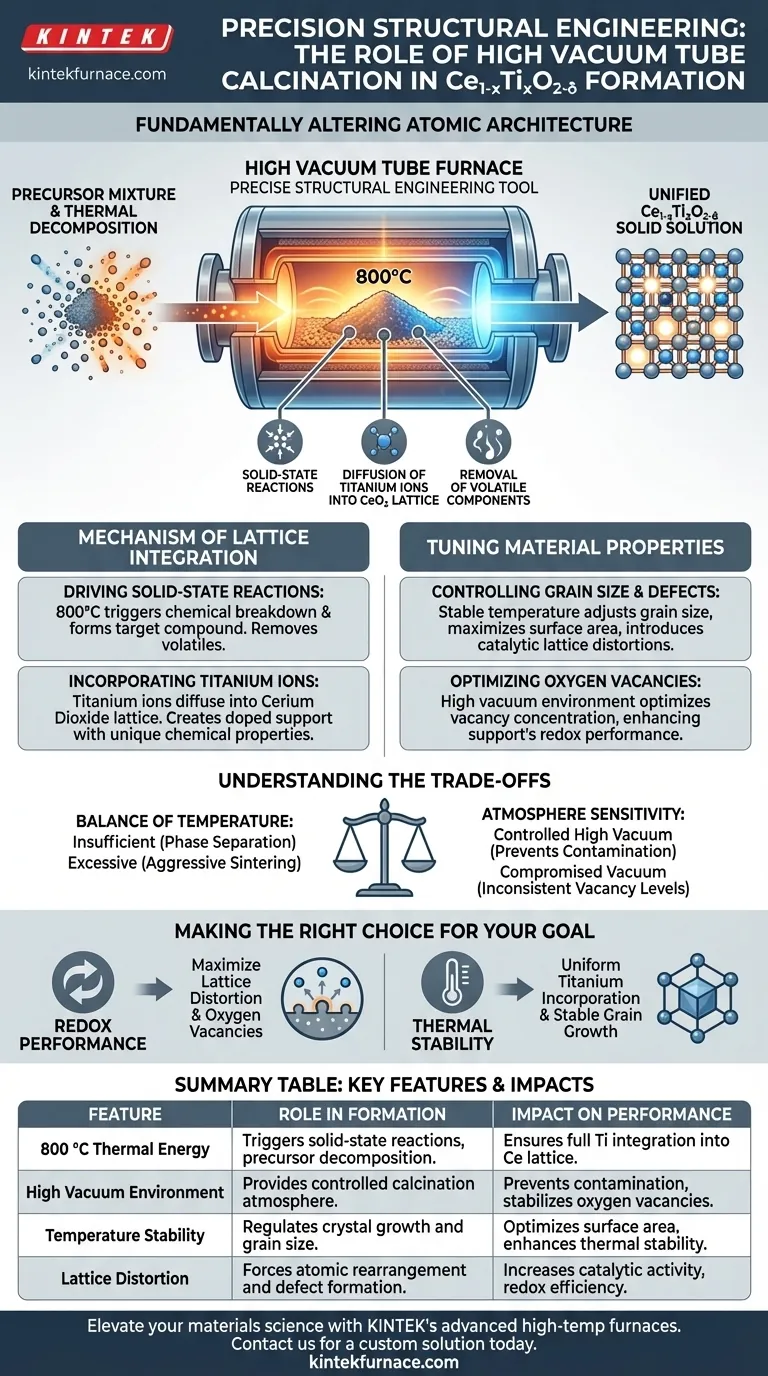
The role of the high vacuum tube furnace is to act as a precise structural engineering tool, fundamentally altering the atomic architecture of Ce1-xTixO2-δ supports. Operating at approximately 800 °C, the furnace drives the thermal decomposition of precursors and initiates solid-state reactions. This thermal energy forces titanium ions to integrate directly into the cerium dioxide lattice, transforming a mixture of elements into a unified, functional solid solution.
The high vacuum environment and stable temperature field allow for the precise manipulation of atomic defects. By controlling lattice distortion and oxygen vacancy concentration, the calcination process directly dictates the material's final redox efficiency and thermal stability.
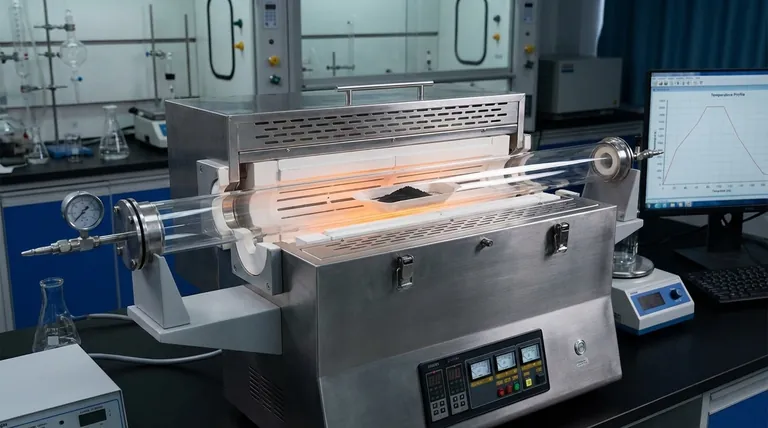

The Mechanism of Lattice Integration
Driving Solid-State Reactions
The core function of the furnace is to provide the activation energy required for solid-state reactions. Simple mixing of precursors is insufficient; the 800 °C environment triggers the chemical breakdown necessary to form the target compound. This thermal decomposition removes volatile components and sets the stage for atomic rearrangement.
Incorporating Titanium Ions
The defining characteristic of Ce1-xTixO2-δ is the presence of titanium within the cerium structure. The furnace facilitates the diffusion of titanium ions into the cerium dioxide lattice. This is not merely a surface coating but a structural integration that creates a doped support material with unique chemical properties.
Tuning Material Properties
Controlling Grain Size and Defects
The stability of the temperature field within the tube furnace allows for the precise adjustment of grain size. By controlling how the crystals grow, engineers can maximize the surface area available for reactions. Furthermore, the process introduces controlled lattice distortions, which are essential for the material's catalytic activity.
Optimizing Oxygen Vacancies
One of the most critical outcomes of this specific calcination process is the manipulation of oxygen vacancy concentration. These vacancies (missing oxygen atoms in the lattice) act as active sites for chemical reactions. The furnace environment is tuned to optimize these vacancies, thereby enhancing the support's redox (reduction-oxidation) performance.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Balance of Temperature
While high temperature is necessary for lattice integration, precision is paramount. If the temperature is insufficient, the titanium ions may not fully incorporate, leading to phase separation rather than a solid solution. Conversely, excessive heat or lack of control can lead to aggressive sintering, destroying the specific surface area and reducing reactivity.
Atmosphere Sensitivity
The "high vacuum" aspect of the furnace plays a subtle but vital role. It ensures a controlled calcination atmosphere, preventing unwanted reactions with ambient gases. A compromised vacuum or unstable atmosphere can lead to inconsistent oxygen vacancy levels, rendering the material less effective for high-performance applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The calcination parameters should be adjusted based on the specific performance metrics you need to prioritize for your Ce1-xTixO2-δ supports.
- If your primary focus is Redox Performance: Prioritize parameters that maximize lattice distortion and oxygen vacancy concentration, as these defects serve as the active sites for chemical exchange.
- If your primary focus is Thermal Stability: Focus on the uniformity of titanium incorporation and stable grain growth to ensure the material can withstand operating stresses without degrading.
Ultimately, the high vacuum tube furnace is not just a heating device, but the instrument that defines the atomic-level "DNA" of your catalyst support.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role in Ce1-xTixO2-δ Formation | Impact on Material Performance |
|---|---|---|
| 800 °C Thermal Energy | Triggers solid-state reactions and precursor decomposition | Ensures full integration of Titanium into the Cerium lattice |
| High Vacuum Environment | Provides a controlled calcination atmosphere | Prevents contamination and stabilizes oxygen vacancy levels |
| Temperature Stability | Regulates crystal growth and grain size | Optimizes surface area and enhances thermal stability |
| Lattice Distortion | Forces atomic rearrangement and defect formation | Increases catalytic activity and redox efficiency |
Precision engineering of catalyst supports requires the highest standards of thermal control. KINTEK offers advanced Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to meet your exact R&D specifications. Backed by expert manufacturing, our high-temp furnaces are fully customizable to help you optimize lattice integration and oxygen vacancy concentration in your materials. Elevate your materials science—contact KINTEK today for a custom solution.
Visual Guide
References
- Jintao Miao, Jing Zhou. Effect of Ti dopants in Ce <sub> 1− <i>x</i> </sub> Ti <sub> <i>x</i> </sub> O <sub> 2− <i>δ</i> </sub> -supported Ni catalysts: structure, redox properties, and carbon resistance in DRM. DOI: 10.1039/d5cy00760g
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a multi-zone tube furnace achieve precise temperature gradient control? Master MoS2 Isotope Monolayer Synthesis
- How does the melt-diffusion process for Te1S7 use tube furnaces? Achieve High-Precision Molecular Confinement
- What are the common materials for reaction tubes in a tube furnace? A Guide to Alumina, Quartz, and More
- What are the main operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Ensure Precision and Safety in Your Experiments
- How are rotary tube furnaces used in the mining and metallurgy industry? Boost Efficiency in Metal Processing
- What functions does a high-temperature quartz tube furnace perform? Precise Synthesis of Doped Carbon Supports
- What is the function of a tube furnace for bond-coated substrates? Ensure TBC Durability with Controlled Pre-Oxidation
- How does a laboratory tube furnace contribute to the continuity and quality of Mn3O4 arrays? Master Atomic Stitching



















