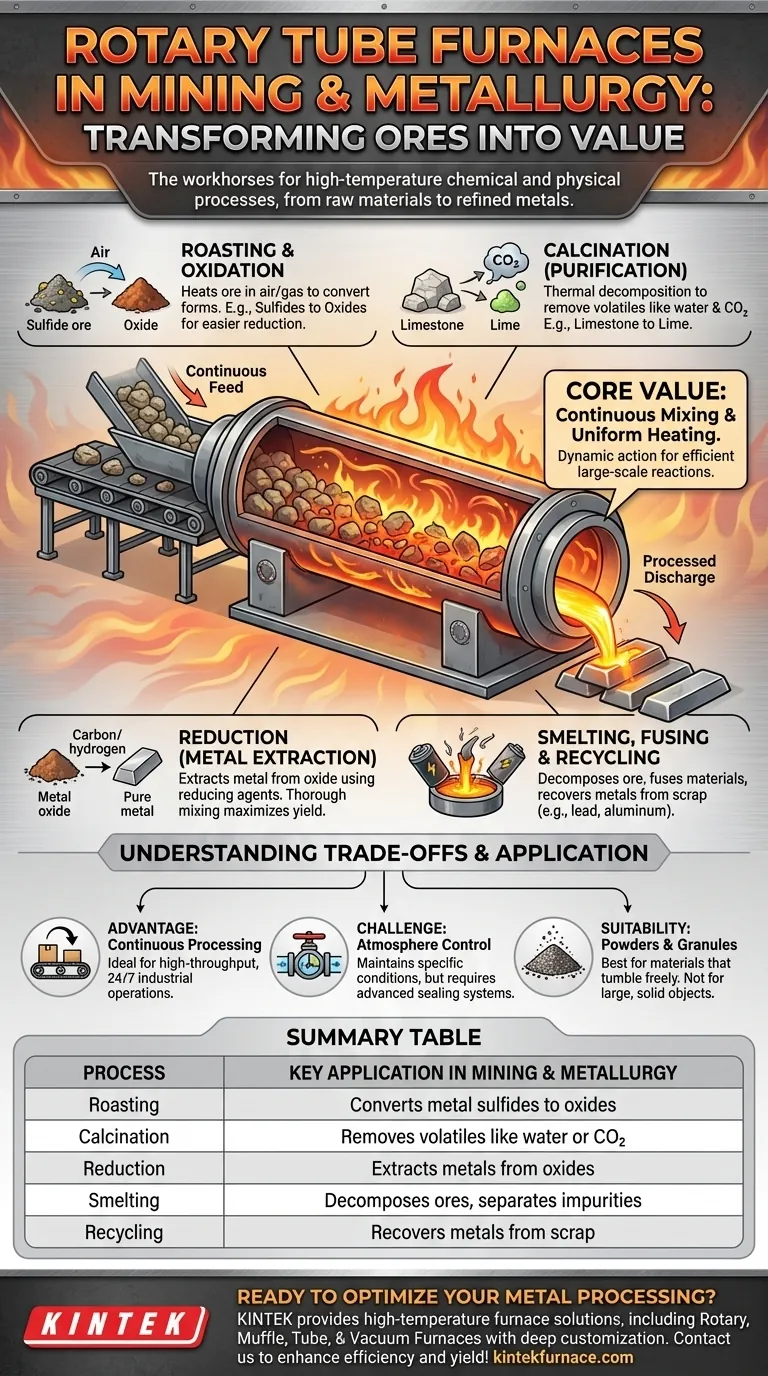
In mining and metallurgy, rotary tube furnaces are the workhorses for transforming raw ores and materials into valuable metals through high-temperature chemical and physical processes. They are used for a range of thermal treatments including roasting, calcination, reduction, and smelting, which are the fundamental steps in extracting, purifying, and recycling metals.
The core value of a rotary tube furnace is its ability to continuously mix and uniformly heat granular or powdered materials. This dynamic action makes it exceptionally efficient for the large-scale chemical reactions required to liberate and refine metals from their native ores.

The Core Function: Transforming Ores into Metals
A rotary tube furnace's primary role is to induce specific chemical and physical changes in materials using controlled heat and atmosphere. The rotation of the furnace tube is the key design feature that enables these transformations on an industrial scale.
Roasting and Oxidation
Roasting is a process that heats an ore in the presence of air or a specific gas. This is often done to convert metal sulfides into more easily reducible oxides.
The furnace's constant tumbling action ensures that every particle of the ore is uniformly exposed to the furnace atmosphere, promoting a complete and efficient chemical reaction. This is a critical preparatory step for subsequent extraction.
Calcination for Material Purification
Calcination is a thermal treatment process used to cause thermal decomposition or a phase transition. In metallurgy, it's used to remove volatile components like water or carbon dioxide from ores.
For example, calcination can be used to convert limestone (CaCO3) into lime (CaO), a crucial fluxing agent in many smelting operations. The furnace's efficient heat transfer to powders makes it ideal for driving off these impurities.
Reduction for Metal Extraction
Reduction is the central process for extracting metal from its oxide ore. This involves heating the ore in a reducing atmosphere (like carbon monoxide or hydrogen) to chemically strip oxygen atoms from the metal.
The rotary furnace excels here by ensuring intimate contact between the solid ore particles and the reducing agent, whether it's a gas or a solid like powdered carbon mixed into the feed. This thorough mixing accelerates the reaction and maximizes metal yield.
Beyond Extraction: Refining and Recycling
The versatility of rotary furnaces extends beyond primary metal extraction. They are also critical tools in secondary processes like creating alloys and recovering valuable materials from waste streams.
Smelting and Fusing Metals
Smelting uses heat and a chemical reducing agent to decompose the ore, driving off other elements as gases or slag and leaving the metal behind. Rotary furnaces can be configured to achieve the high temperatures needed for smelting.
They are also used to melt and fuse different metals and materials together, creating specialized alloys with desired properties.
Material Recovery and Recycling
Rotary furnaces are highly effective in recycling applications. A common example is the recovery of lead from scrap batteries.
The furnace heats the material to burn off plastic and other contaminants while melting the lead, which can then be collected for purification and reuse. This same principle applies to recovering other metals, like aluminum, from various industrial byproducts.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While highly effective, the choice to use a rotary tube furnace comes with specific operational considerations. Understanding these is key to its successful implementation.
The Advantage of Continuous Processing
Unlike static batch furnaces, the angled, rotating design of a rotary furnace allows for the continuous feeding of raw material at one end and the discharge of processed material at the other. This makes them exceptionally well-suited for high-throughput, 24/7 industrial operations.
The Challenge of Atmosphere Control
Maintaining a perfectly sealed, controlled atmosphere inside a rotating tube is a significant engineering challenge. While advanced sealing systems are effective, preventing any air ingress or process gas egress at the rotating joints requires careful design and maintenance.
Material Suitability
These furnaces are specifically designed to process powders, granules, and small, lumpy materials that can tumble freely. They are not suitable for processing large, solid objects or components that could be damaged by the tumbling action or that would not mix properly.
How to Apply This to Your Process
The decision to use a rotary tube furnace hinges on the specific transformation your material requires and the scale of your operation.
- If your primary focus is ore preparation: A rotary furnace is ideal for large-scale calcination to drive off volatiles or for roasting to convert mineral forms, such as turning sulfides into oxides.
- If your primary focus is direct metal extraction: It is the superior tool for reduction processes where powdered ore must be thoroughly and uniformly mixed with a reducing agent to achieve high yields.
- If your primary focus is recycling and recovery: Use a rotary furnace to efficiently separate valuable metals like lead or aluminum from scrap by burning off contaminants and melting the target material for collection.
Ultimately, the rotary tube furnace is a powerful and versatile tool, uniquely designed to ensure the uniform heat treatment and chemical reaction essential for modern metallurgy.
Summary Table:
| Process | Key Application in Mining & Metallurgy |
|---|---|
| Roasting | Converts metal sulfides to oxides for easier reduction |
| Calcination | Removes volatiles like water or CO₂ from ores |
| Reduction | Extracts metals from oxides using reducing agents |
| Smelting | Decomposes ores to separate metals from impurities |
| Recycling | Recovers metals (e.g., lead, aluminum) from scrap |
Ready to optimize your metal processing with advanced rotary tube furnaces? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for mining and metallurgy. Our product line, including Rotary Furnaces, Muffle, Tube, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental and production needs. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your efficiency and yield!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
People Also Ask
- What are the main structural components of a rotary furnace? Explore Key Parts for Efficient Material Processing
- What are the common approaches to mixing in rotary furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- What is the purpose of the rotation mechanism in a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating and Enhanced Process Control
- What materials can be used to make the rotating tube assembly of these furnaces? Choose the Best for Your High-Temp Needs
- What supplementary features can enhance rotary tube furnace performance? Boost Efficiency with Precision Control



















