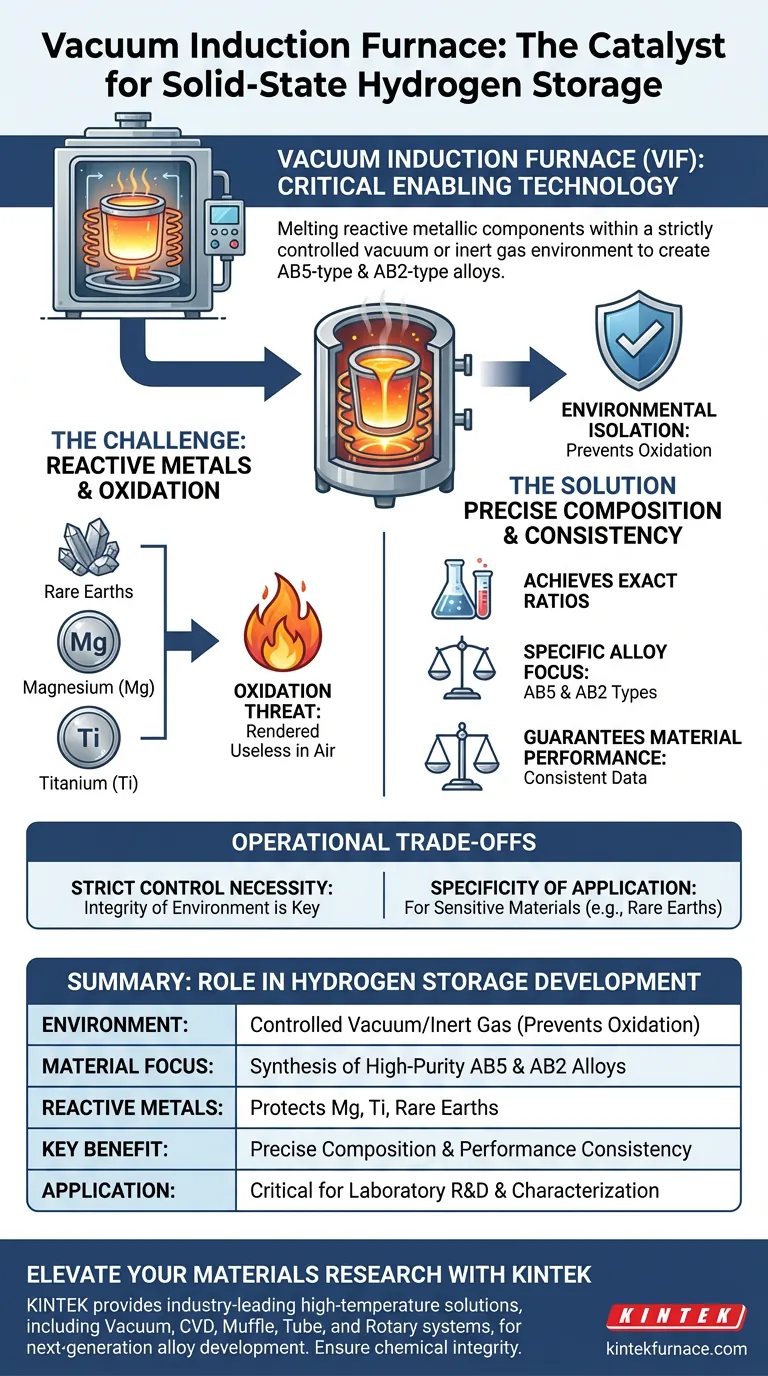
The Vacuum Induction Furnace (VIF) is the critical enabling technology for synthesizing high-purity solid-state hydrogen storage materials in the laboratory. It functions by melting reactive metallic components within a strictly controlled vacuum or inert gas environment, specifically to create AB5-type and AB2-type alloys. This isolation is the only reliable way to prevent the oxidation of volatile elements during the high-temperature melting process.
By eliminating oxygen from the melting environment, the Vacuum Induction Furnace ensures that highly reactive inputs like magnesium and titanium retain their chemical integrity, guaranteeing the precise composition ratios necessary for consistent hydrogen storage performance.
The Critical Challenge of Reactive Metals
Handling Active Metallic Components
Developing solid-state hydrogen storage materials often requires the use of active metallic components.
According to laboratory standards, these critical ingredients typically include rare earth elements, magnesium, and titanium.
The Threat of Oxidation
These metals share a common vulnerability: they are highly susceptible to oxidation.
At the high temperatures required for melting, exposure to standard air would cause these elements to react immediately with oxygen, rendering them useless for hydrogen storage.
The Solution: Environmental Isolation
The VIF solves this by creating a strictly controlled environment.
By operating under a vacuum or using an inert gas atmosphere, the furnace physically prevents oxygen from coming into contact with the molten metal.
Ensuring Precision and Consistency
Achieving Exact Composition Ratios
In alloy development, the ratio of ingredients determines the material's properties.
Because the VIF prevents material loss through oxidation, it ensures precision in alloy composition ratios. The elemental mix you calculate is exactly what ends up in the final alloy.
Focusing on Specific Alloy Types
The VIF is the primary tool used to prepare specific classes of storage materials.
It is specifically essential for the creation of high-purity AB5-type and AB2-type hydrogen storage alloys.
Guaranteeing Material Performance
Reliable research data depends on material consistency.
By protecting the active metals during synthesis, the VIF ensures the consistency of the resulting material performance, allowing researchers to accurately test hydrogen absorption and desorption capabilities.
Understanding the Operational Trade-offs
Necessity of Strict Control
The effectiveness of the VIF is entirely dependent on the integrity of the environment.
The reference emphasizes a "strictly controlled" vacuum or inert gas setup; any deviation or leak immediately compromises the purity of the active metals.
Specificity of Application
This is a specialized tool designed for specific material sensitivities.
Its primary value lies in processing materials that cannot survive open-air melting, such as rare earths and magnesium, rather than general-purpose metallurgy.
Making the Right Choice for Your Research
To determine if a Vacuum Induction Furnace is required for your specific workflow, consider the following:
- If your primary focus is synthesizing AB5 or AB2 alloys: You require a VIF to handle the high reactivity of rare earth elements and titanium without degradation.
- If your primary focus is experimental consistency: The VIF is essential to ensure that your composition ratios are precise and that oxidation does not skew your performance data.
The Vacuum Induction Furnace effectively acts as a shield, preserving the chemical potential of reactive metals to create stable, high-performance hydrogen storage alloys.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role in Hydrogen Storage Development |
|---|---|
| Environment | Strictly controlled vacuum or inert gas to prevent oxidation |
| Material Focus | Synthesis of high-purity AB5-type and AB2-type alloys |
| Reactive Metals | Protects magnesium, titanium, and rare earth elements |
| Key Benefit | Ensures precise composition ratios and performance consistency |
| Application | Critical for laboratory-scale R&D and material characterization |
Elevate Your Materials Research with KINTEK
Precise control over your melting environment is the difference between a breakthrough and a failed experiment. KINTEK provides industry-leading high-temperature solutions, including Vacuum, CVD, Muffle, Tube, and Rotary systems, all backed by expert R&D and precision manufacturing. Whether you are developing next-generation AB5/AB2 alloys or exploring new solid-state storage frontiers, our customizable laboratory furnaces ensure the chemical integrity of your most reactive materials.
Ready to achieve superior alloy purity? Contact our technical experts today to find your custom solution.
Visual Guide
References
- Yaohui Xu, Zhao Ding. Research Progress and Application Prospects of Solid-State Hydrogen Storage Technology. DOI: 10.3390/molecules29081767
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the function of vacuum induction melting and casting equipment in high manganese steel? Unlock Superior Purity
- What are the main components of a steel shell structure induction furnace? An In-Depth System Breakdown
- How does electromagnetic induction contribute to the heating process in an induction melting furnace? Achieve Superior Metal Melting Efficiency
- Why are multiple repeated melting cycles necessary in the production of Ni-Ti-Hf-La alloys? Ensuring Homogenization
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum induction furnace play in the sintering of non-oxide ceramics?
- Why are vacuum casting furnaces considered vital for modern manufacturing? Unlock Purity and Performance
- How are induction furnaces used in investment casting? Achieve Precision Melting for High-Quality Cast Parts
- What are the advantages of vacuum casting? Ideal for High-Fidelity Prototypes and Low-Volume Production



















