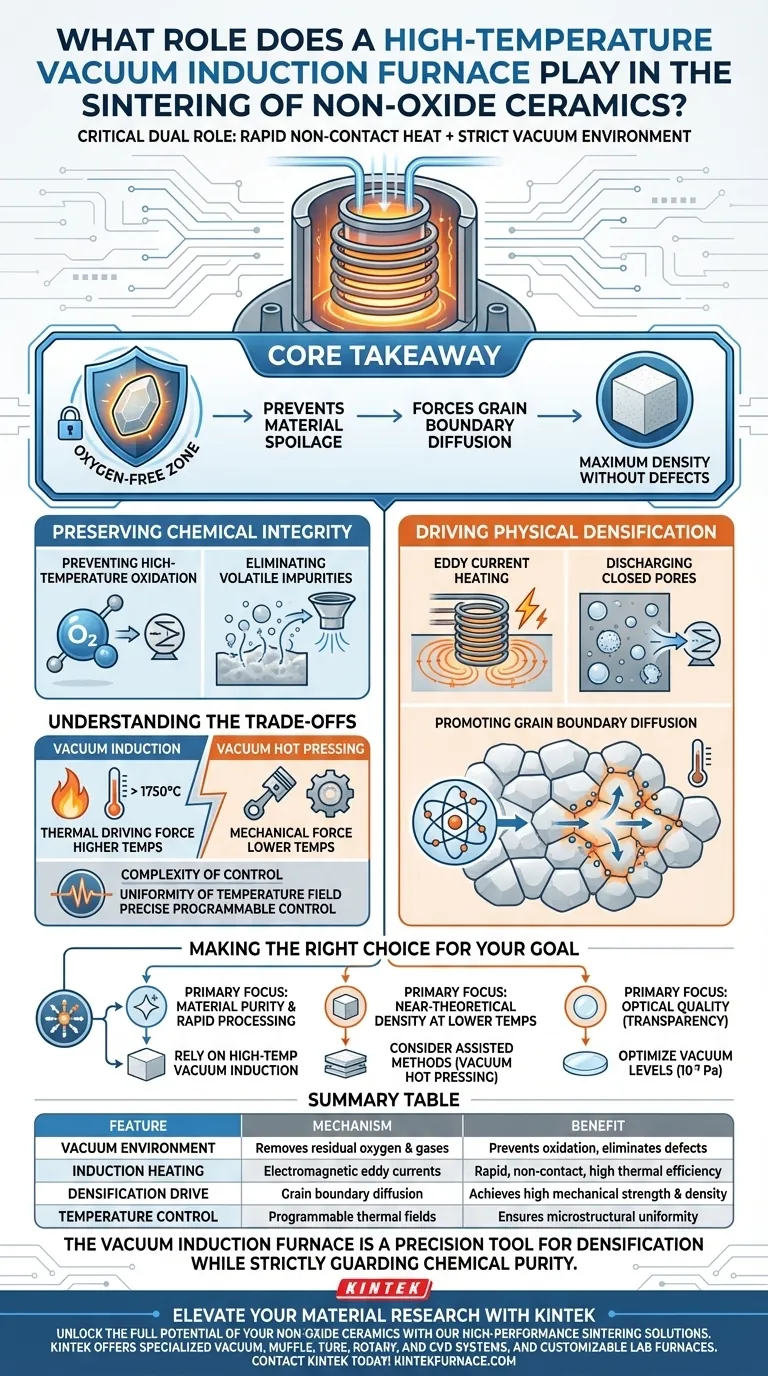
High-temperature vacuum induction furnaces play a critical dual role in processing non-oxide ceramics: they utilize electromagnetic induction to generate rapid, non-contact heat while maintaining a strict vacuum environment to prevent chemical degradation. By eliminating residual oxygen and volatile gases, these furnaces protect the raw material from oxidation while simultaneously driving the physical mechanisms required for high densification.
Core Takeaway The vacuum induction furnace is essential for non-oxide ceramics because it decouples heating from atmospheric interference. It creates an oxygen-free zone that prevents material spoilage while utilizing high-speed induction heating to force grain boundary diffusion, ensuring the final product achieves maximum density without chemical defects.

Preserving Chemical Integrity
The primary challenge in sintering non-oxide ceramics is their susceptibility to reacting with oxygen at elevated temperatures. The vacuum induction furnace addresses this through strict environmental control.
Preventing High-Temperature Oxidation
Non-oxide materials are highly sensitive to oxygen. During the heating process, the furnace creates a high-vacuum environment that effectively excludes residual oxygen.
Eliminating Volatile Impurities
Beyond oxygen, raw materials often contain adsorbed gases or generate volatile byproducts during the reaction. The vacuum environment facilitates the removal of these gases, preventing them from becoming trapped defects within the ceramic structure.
Driving Physical Densification
Once the chemical stability is secured, the furnace utilizes specific thermal mechanisms to transform the loose "green body" into a solid, dense ceramic.
Eddy Current Heating
Unlike conventional electric heaters, this furnace employs an alternating magnetic field to generate eddy currents directly within the conductor. This method allows for non-contact heating with exceptionally high heating rates, reducing the total cycle time.
Discharging Closed Pores
Achieving high density requires the elimination of microscopic voids between particles. The vacuum condition assists in discharging internal closed pores, effectively pulling gas out of the material as the ceramic grains merge.
Promoting Grain Boundary Diffusion
The combination of high temperature and vacuum promotes grain boundary diffusion. This is the fundamental atomic movement where grains merge and grow, leading to the high densification of the material and the development of its final mechanical strength.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While vacuum induction sintering is powerful, it is distinct from other methods like vacuum hot pressing. It is important to understand the operational differences.
Thermal Force vs. Mechanical Force
Vacuum induction relies primarily on thermal driving force to achieve density. This often requires higher temperatures (potentially exceeding 1750°C) compared to hot-press methods, which use mechanical pressure to lower the required sintering temperature.
Complexity of Control
The quality of the final ceramic—including its density and microstructure—is directly determined by the uniformity of the temperature field. Because induction heating is rapid, precise programmable control is necessary to prevent thermal gradients that could lead to uneven sintering or structural stress.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The selection of sintering equipment defines the final properties of your ceramic component.
- If your primary focus is material purity and rapid processing: Rely on high-temperature vacuum induction, as the non-contact heating prevents contamination and the vacuum strictly prevents oxidation.
- If your primary focus is achieving near-theoretical density at lower temperatures: Consider assisted methods like vacuum hot pressing, which utilizes mechanical pressure to aid particle rearrangement when thermal force alone is insufficient.
- If your primary focus is optical quality (transparency): Ensure your vacuum levels are optimized ($10^{-3}$ Pa range), as the complete removal of micropores is the deciding factor in transforming opaque ceramics into transparent ones.
The vacuum induction furnace is not just a heat source; it is a precision tool that forces material densification while strictly guarding its chemical purity.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Mechanism | Benefit for Non-Oxide Ceramics |
|---|---|---|
| Vacuum Environment | Removes residual oxygen and gases | Prevents oxidation and eliminates internal defects/pores |
| Induction Heating | Electromagnetic eddy currents | Rapid, non-contact heating with high thermal efficiency |
| Densification Drive | Grain boundary diffusion | Achieves high mechanical strength and material density |
| Temperature Control | Programmable thermal fields | Ensures microstructural uniformity and avoids stress |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK
Unlock the full potential of your non-oxide ceramics with our high-performance sintering solutions. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers specialized Vacuum, Muffle, Tube, Rotary, and CVD systems, as well as customizable lab high-temp furnaces designed to meet your unique density and purity requirements. Whether you are aiming for near-theoretical density or optical transparency, our systems provide the precision you need.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your custom furnace needs!
Visual Guide
References
- Zhanjiang Pei, Yanling Yu. The Enhancing Effect of Biochar Derived from Biogas Residues on the Anaerobic Digestion Process of Pig Manure Water. DOI: 10.3390/fermentation10120644
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the role of the control circuit in an induction heater? Unlock Precision and Efficiency in Your Heating Process
- Why is the precise addition of alloying elements in induction furnaces necessary for heavy-section ADI?
- Why are higher frequencies needed in coreless induction furnaces for melting small loads of gold? Achieve Efficient Melting for Jewelry and Lab Samples
- What role does a VIM furnace play in Fe-32Mn-11Al-1.4C-3Ni steel? Precision Purity and Oxidation Protection
- What are the maintenance benefits of using IGBT technology in induction melting? Maximize Uptime & Reduce Downtime
- What are the benefits of using induction furnaces for copper melting? Boost Quality, Efficiency & Safety
- Why is superior temperature control accuracy important in induction furnaces? Ensure Metallurgical Quality & Cost Control
- What are the energy efficiency advantages of induction melting furnaces? Achieve 30-80% Greater Energy Savings



















