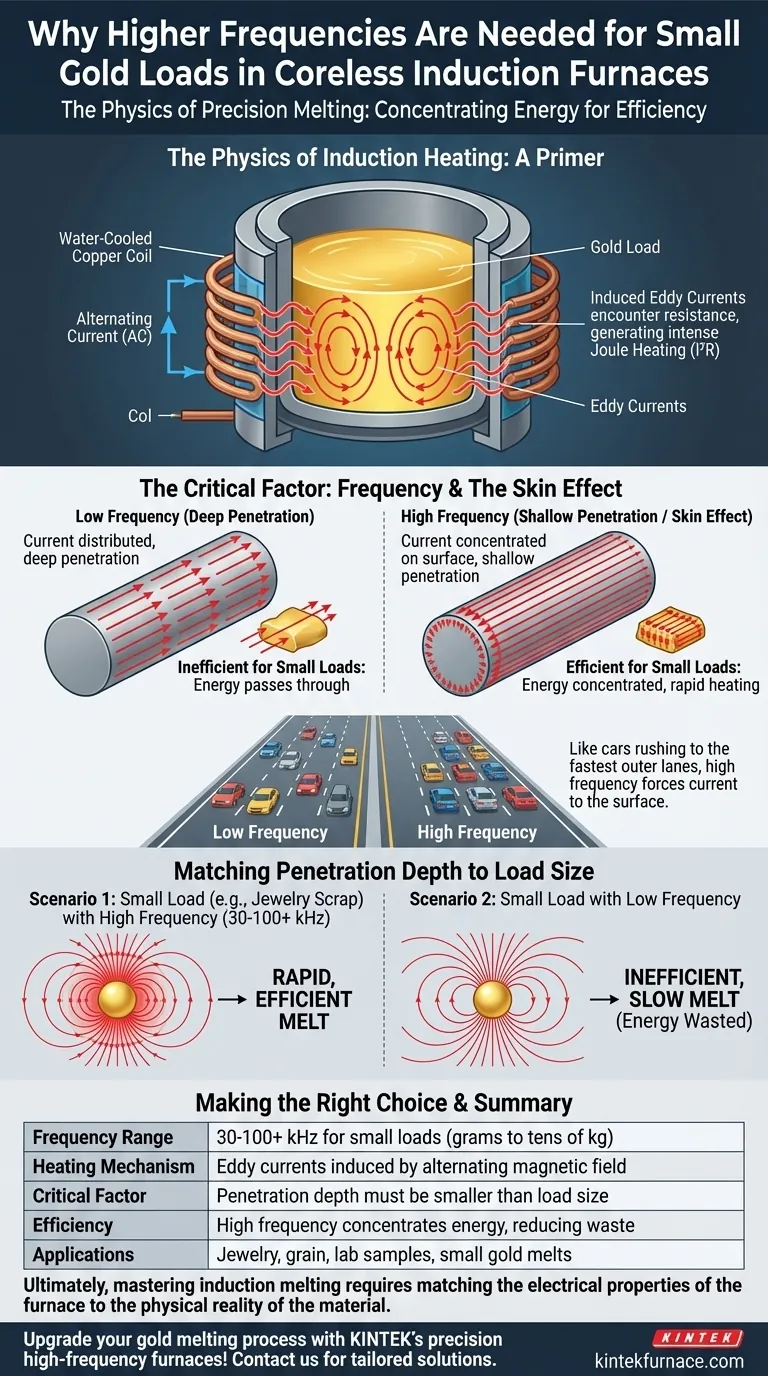
At its core, the need for higher frequencies when melting small loads of gold comes down to physics. To heat a small object efficiently with induction, you must concentrate the energy precisely where it's needed. High-frequency alternating currents create a phenomenon that forces the heating energy to the surface of the gold, a perfect match for the small dimensions of jewelry, grain, or lab samples.
The efficiency of any induction furnace is determined by matching the electrical frequency to the physical size of the metal being melted. For small gold loads, a high frequency is not just an improvement—it is a fundamental requirement for the process to work effectively.
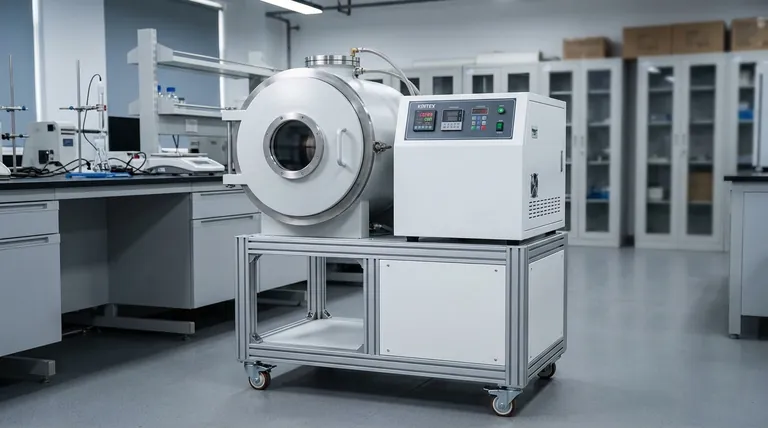

The Physics of Induction Heating: A Primer
To understand the role of frequency, we must first review how an induction furnace generates heat. The process relies on converting electrical energy into a powerful, oscillating magnetic field.
Creating Heat from Magnetism
An induction furnace uses a water-cooled copper coil through which a powerful alternating current (AC) flows. This AC generates a rapidly changing magnetic field in the space within the coil, where the crucible containing the gold is placed.
The Role of Eddy Currents
This oscillating magnetic field penetrates the gold, inducing circular electrical currents within the metal itself. These are known as eddy currents.
As these eddy currents swirl through the gold, they encounter the metal's natural electrical resistance. This resistance causes intense heat to be generated (known as Joule or I²R heating), quickly raising the gold's temperature to its melting point.
Why Frequency is the Critical Factor for Small Melts
The frequency of the alternating current is the single most important variable that determines where and how effectively these eddy currents form, especially in relation to the size of the load.
Introducing the "Skin Effect"
As the frequency of an alternating current increases, it has a tendency to flow near the outer surface of a conductor. This fundamental principle is known as the skin effect.
Think of it like cars on a multi-lane highway. At a slow, steady pace (low frequency), cars are distributed across all lanes. In a sudden, high-speed rush (high frequency), they tend to cluster in the fastest outer lanes, leaving the inner lanes underutilized. The electrical current in the gold behaves similarly.
Understanding Penetration Depth
The skin effect is quantified by a measurement called penetration depth. This is the effective depth from the surface where the vast majority of the heating occurs.
A high frequency creates a very shallow penetration depth. A low frequency results in a deep penetration depth. This relationship is the key to the entire process.
Matching Penetration Depth to Load Size
For efficient heating, the penetration depth must be significantly smaller than the diameter or thickness of the metal being heated.
If you use a low-frequency current (deep penetration depth) on a small piece of gold, the induced energy field is larger than the gold itself. Much of the energy "passes through" the target without being effectively converted to heat, resulting in a failed or painfully slow melt.
Conversely, a high-frequency current (shallow penetration depth) concentrates the eddy currents right within the small volume of the gold. This ensures a rapid, efficient, and complete energy transfer, leading to a fast and uniform melt.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the wrong frequency for a given load size leads directly to inefficiency and poor performance. The goal is always to match the technology to the task.
The Problem with Low Frequencies for Small Loads
Using a low- or medium-frequency furnace for small quantities of gold is highly inefficient. The magnetic coupling is poor, a significant portion of the electrical energy is wasted, and the furnace may struggle to even reach the required melting temperature.
The Problem with High Frequencies for Large Loads
On the other hand, using a very high-frequency furnace to melt a large ingot of gold is also inefficient. The shallow penetration depth would only heat the outer "skin" of the ingot, leading to a slow melt-down from the outside-in and poor magnetic stirring, which is necessary for creating a homogeneous final alloy.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The relationship between frequency and load size dictates your equipment choice. Always prioritize the frequency that matches your most common application.
- If your primary focus is melting small loads (e.g., a few grams to tens of kilograms of jewelry scrap, grain, or lab samples): A high-frequency (30-100+ kHz) induction furnace is essential for efficient and rapid heating.
- If your primary focus is melting larger ingots or bulk scrap (e.g., hundreds of kilograms): A medium- or low-frequency (0.5-10 kHz) furnace will provide the deep penetration depth needed for efficient coupling and a strong stirring action.
- If your goal is to select a single, versatile furnace: You must base your decision on the smallest load you intend to melt efficiently, as a high-frequency system can still melt larger loads (albeit more slowly), but a low-frequency system simply cannot melt small loads effectively.
Ultimately, mastering induction melting requires matching the electrical properties of the furnace to the physical reality of the material in the crucible.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Frequency Range | 30-100+ kHz for small loads (grams to tens of kg) |
| Heating Mechanism | Eddy currents induced by alternating magnetic field |
| Critical Factor | Penetration depth must be smaller than load size |
| Efficiency | High frequency concentrates energy, reducing waste |
| Applications | Jewelry, grain, lab samples, and small gold melts |
Upgrade your gold melting process with KINTEK's precision high-frequency furnaces! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with advanced solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures your unique experimental needs are met for efficient, uniform heating of small gold loads. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored furnace solutions can enhance your efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of vacuum melting, casting and re-melting equipment? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- What is vacuum induction melting technology and why is it important? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- What are the common applications of Vacuum Induction Melting? Essential for High-Performance Metals and Alloys
- How does vacuum melting technology contribute to sustainability? Boost Durability and Recycling Efficiency
- What are the core functions of the High Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace? Optimize DD5 Superalloy Purification



















