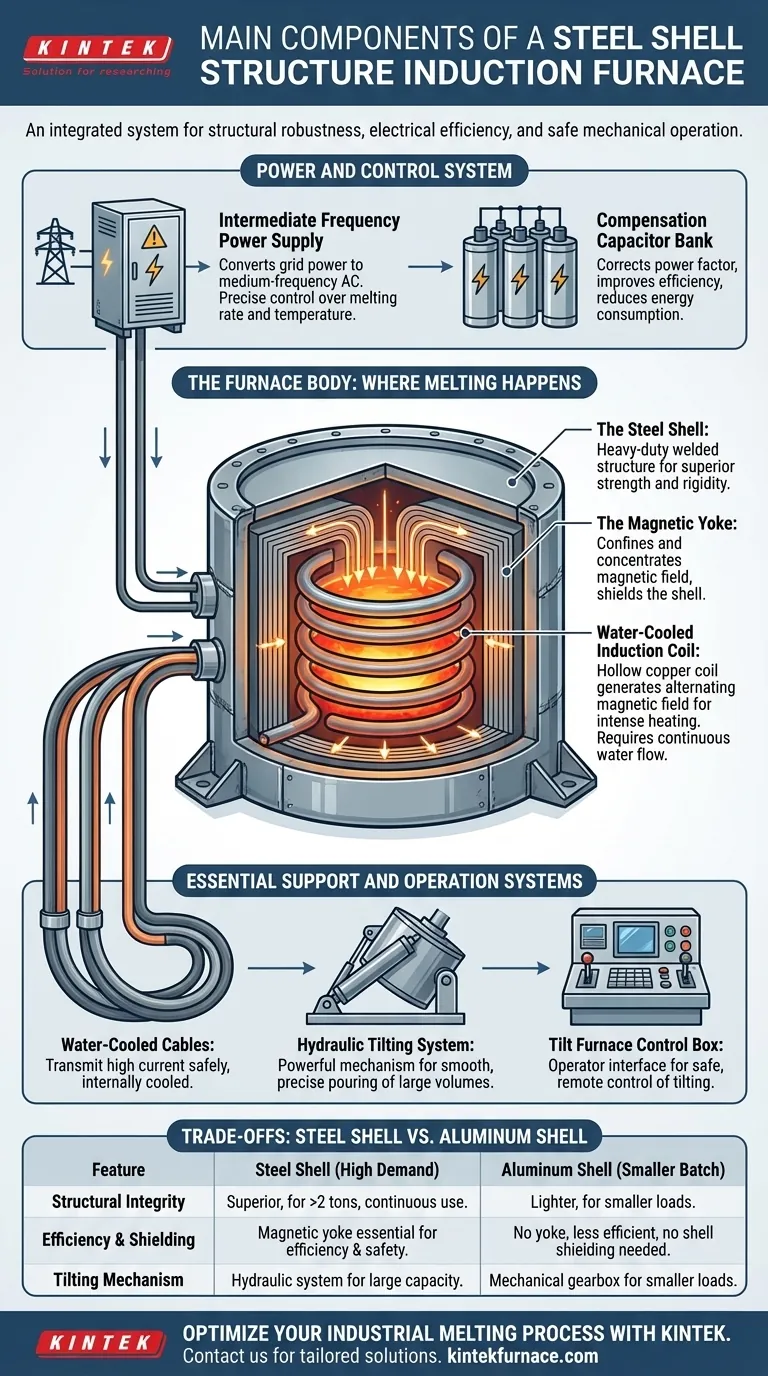
At its core, a steel shell induction furnace is an integrated system combining a power source, a robust furnace body, and hydraulic controls. The main components are the intermediate frequency power supply, a compensation capacitor bank, the steel shell furnace body which houses the induction coil and is supported by a magnetic yoke, water-cooled cables, a hydraulic station, and a control box for tilting.
A steel shell furnace is not merely a container for melting metal; it is an engineered system where each component is designed for structural robustness, electrical efficiency, and safe mechanical operation, making it the standard for high-demand industrial applications.

The Power and Control System
The efficiency and operation of the furnace begin with its electrical system. This is the heart of the induction process, converting grid power into the high-frequency energy required for melting.
Intermediate Frequency Power Supply
The power supply cabinet is the brain of the furnace. It takes standard three-phase AC power from the electrical grid and converts it into the single-phase, medium-frequency power needed by the induction coil. The ability to control this power output precisely dictates the melting rate and temperature.
Compensation Capacitor Bank
The induction coil is a highly inductive load, which creates an inefficient power factor. The capacitor bank is connected in parallel with the coil to compensate for this inductance. This correction dramatically improves the system's electrical efficiency, reducing overall energy consumption and stress on the power supply.
The Furnace Body: Where Melting Happens
The furnace body is the physical structure that contains the intense heat and magnetic forces of the melting process. Its design is critical for both safety and performance.
The Steel Shell
The defining feature of this furnace is its heavy-duty steel shell. This welded steel structure provides superior mechanical strength and rigidity. It securely supports the refractory lining and the induction coil, preventing deformation during tilting and under the stress of continuous operation.
The Magnetic Yoke
Laminated silicon steel sheets, known as the magnetic yoke, are fixed to the inside of the steel shell, surrounding the induction coil. The yoke serves two critical functions: it confines and concentrates the magnetic field onto the metal charge, increasing heating efficiency. It also shields the steel shell from stray magnetic flux, preventing the shell itself from heating up.
Water-Cooled Induction Coil
Though contained within the body, the hollow copper induction coil is the active component. High-frequency current flows through it, generating a powerful alternating magnetic field. This field induces eddy currents within the metal charge, generating the intense heat required for melting. Continuous water flow through the coil is essential to prevent it from melting.
Essential Support and Operation Systems
These components provide the necessary connections, movement, and operator control to make the furnace a functional industrial tool.
Water-Cooled Cables
These specialized, flexible cables transmit the high current from the power supply to the furnace's induction coil. They are internally water-cooled to handle the immense electrical load without overheating, ensuring both safety and system longevity.
Hydraulic Tilting System
Steel shell furnaces handle large volumes of molten metal, requiring a powerful and smooth tilting mechanism for pouring. A hydraulic station with rams provides this force, allowing for precise and safe control over the pouring process, which is essential for large-capacity operations.
Tilt Furnace Control Box
This is the operator's interface for the mechanical systems. It typically contains the controls for the hydraulic tilting mechanism, allowing the operator to safely and accurately pour the molten metal from a secure distance.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Steel Shell vs. Aluminum Shell
The choice of a steel shell is a deliberate engineering decision with clear advantages and differences compared to its lighter-duty counterpart, the aluminum shell furnace.
Structural Integrity and Scale
A steel shell offers superior structural rigidity and durability. This makes it the standard for furnace capacities above 2 tons and in demanding, continuous-use foundry environments. Aluminum shells are lighter and less expensive but are generally limited to smaller batch sizes and less frequent use.
Efficiency and Shielding
The magnetic yoke in a steel shell furnace is non-negotiable; it is essential for both efficiency and safety. Without it, the magnetic field would induce heat directly into the steel shell, wasting energy and creating a hazard. Non-magnetic aluminum shells do not have this issue, but they also lack the field-concentrating benefit of a well-designed yoke.
Tilting Mechanism
The use of a hydraulic system in steel shell furnaces corresponds to their larger capacity. It provides the power needed to safely tilt many tons of molten metal. Aluminum shell furnaces typically use a simpler and less powerful mechanical gearbox (reducer) for tilting, which is adequate for their smaller loads.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Understanding these components allows you to select a furnace based on your specific operational needs, not just on initial cost.
- If your primary focus is large-scale, continuous production: The robust steel shell, efficient magnetic yoke, and powerful hydraulic system are designed for the high durability and capacity you require.
- If your primary focus is smaller batch melting or research and development: An aluminum shell furnace may be a more cost-effective solution due to its simpler construction and lower capacity.
By understanding how each component contributes to the furnace's performance, you can confidently invest in the system that aligns precisely with your operational demands and long-term goals.
Summary Table:
| Component | Primary Function | Key Feature |
|---|---|---|
| Intermediate Frequency Power Supply | Converts grid power to medium-frequency AC | Precise control over melting rate and temperature |
| Compensation Capacitor Bank | Corrects power factor for efficiency | Reduces energy consumption and stress on the system |
| Steel Shell & Magnetic Yoke | Provides structural support and magnetic field concentration | Ensures durability and maximizes heating efficiency |
| Water-Cooled Induction Coil | Generates the magnetic field for induction heating | Hollow copper design requires continuous water cooling |
| Hydraulic Tilting System | Safely pours molten metal | Essential for handling large-capacity, heavy loads |
| Water-Cooled Cables & Control Box | Transmit power and provide operator control | Enable safe operation from a distance |
Optimize Your Industrial Melting Process with KINTEK
Understanding the robust engineering of a steel shell induction furnace is the first step. The next is implementing the right solution for your high-demand production. KINTEK's expertise in advanced thermal processing is exactly what you need to achieve superior results.
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories and foundries with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental and industrial requirements.
Let us help you build a more efficient, durable, and powerful melting operation.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss how our induction furnace solutions can be tailored to your specific capacity and performance goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the core functions of the High Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace? Optimize DD5 Superalloy Purification
- What are some common applications of vacuum induction melting and casting (VIM&C)? Essential for Aerospace, Medical, and Nuclear Industries
- Why is a Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace essential? Unlock Purity for Aerospace and Semiconductors
- How has vacuum smelting impacted the development of superalloys? Unlock Higher Strength and Purity
- What are the common applications of Vacuum Induction Melting? Essential for High-Performance Metals and Alloys



















