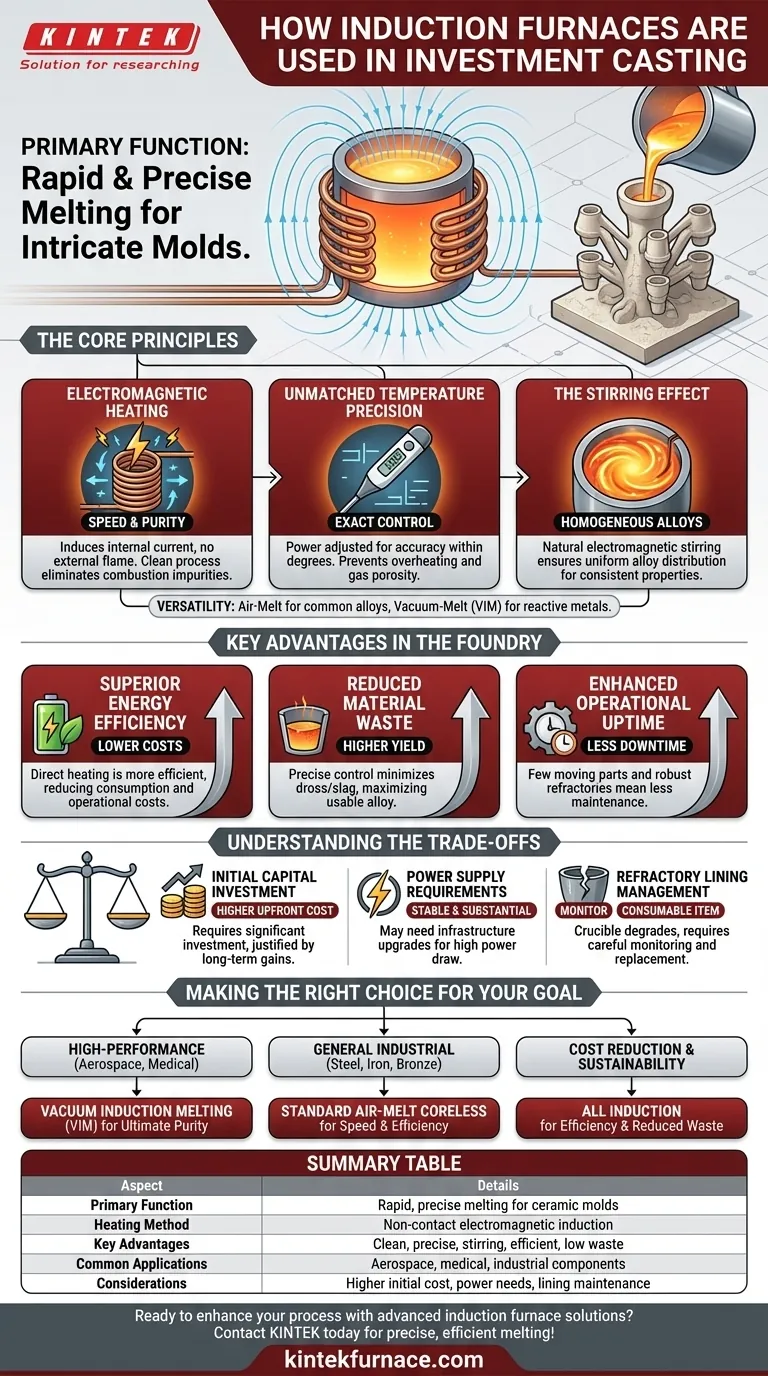
In investment casting, induction furnaces serve one primary, critical function: to rapidly and precisely melt metal alloys before they are poured into the ceramic investment mold. They use non-contact electromagnetic heating to turn solid metal into a liquid state with exceptional control over temperature and purity, which is essential for producing the intricate and high-quality parts characteristic of this process.
The core reason induction furnaces are standard in investment casting is their ability to deliver unparalleled control. By using electromagnetic fields, they provide rapid, clean, and highly uniform heat, which is essential for producing the complex, high-integrity parts that investment casting is known for.
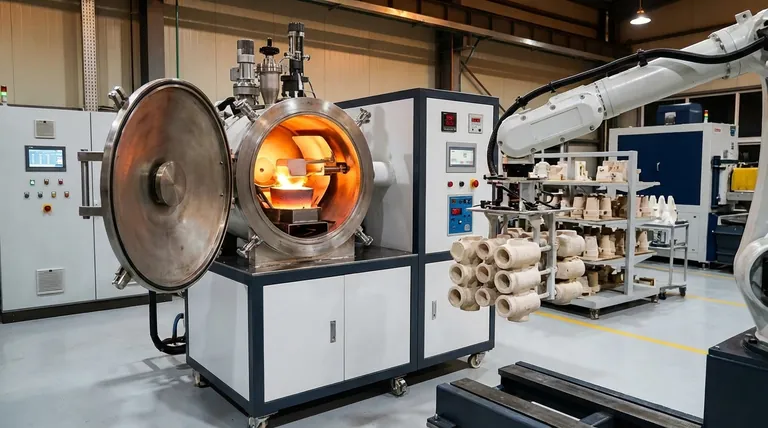

The Core Principles: Why Induction Excels
Induction technology is not just another way to heat metal; its fundamental principles directly address the core requirements of high-quality investment casting.
Electromagnetic Heating for Speed and Purity
An induction furnace works by generating a powerful alternating magnetic field. This field induces strong electrical currents directly within the metal, causing it to heat up rapidly from the inside out.
Because there is no external flame or heating element, the risk of introducing impurities from combustion byproducts is eliminated. This clean melting process is vital for producing metallurgically sound castings.
Unmatched Temperature Precision
The power supplied to the induction coil can be adjusted with extreme accuracy. This gives operators precise control over the metal's temperature, often within a few degrees.
This precision prevents overheating, which can lead to gas porosity and the loss of valuable alloying elements. It also ensures the metal is at the optimal pouring temperature to perfectly fill the intricate details of the investment mold.
The Stirring Effect for Homogeneous Alloys
A unique benefit of induction melting is the natural electromagnetic stirring that occurs within the molten bath. The magnetic fields create a gentle, continuous mixing action.
This ensures that all alloying elements are distributed evenly throughout the melt, resulting in a perfectly homogeneous alloy. For high-performance components, this chemical uniformity is non-negotiable for consistent mechanical properties.
Versatility Across Metals and Atmospheres
Induction furnaces are available in many configurations, including air-melt and vacuum-melt systems.
Air-melt furnaces are workhorses for common alloys like steel, iron, and copper. Vacuum induction melting (VIM) furnaces allow for the processing of highly reactive metals like titanium and superalloys in a controlled atmosphere, preventing oxidation and ensuring ultimate purity.
Key Advantages in the Foundry
The principles of induction melting translate directly into tangible operational and financial benefits for the investment casting foundry.
Superior Energy Efficiency
By heating the metal directly, induction furnaces are significantly more energy-efficient than fuel-fired or resistance furnaces, where a large amount of energy is lost heating the furnace structure and the surrounding air. This translates to lower energy consumption and reduced operational costs.
Reduced Material Waste
Precise temperature control minimizes the formation of dross and slag (impurities that float on top of the melt), meaning more of the expensive alloy ends up in the final casting. This accuracy reduces material waste and improves yield.
Enhanced Operational Uptime
Induction furnaces have few moving parts and their linings (refractories) are robust. This inherent durability and minimal maintenance requirement means less downtime for repairs and more time spent in production, reducing long-term operational costs.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, induction technology is not without its considerations. A trusted advisor must acknowledge the full picture.
Initial Capital Investment
The upfront cost of an induction melting system, including the power supply and installation, is typically higher than that of a conventional fuel-fired furnace. This represents a significant capital expenditure that must be justified by long-term efficiency gains.
Power Supply Requirements
These furnaces demand a substantial and stable electrical power supply. Facilities may need to upgrade their electrical infrastructure to support the high power draw, which can add to the initial project cost and complexity.
Refractory Lining Management
The crucible or refractory lining that holds the molten metal is a consumable item. It degrades over time and must be carefully monitored and periodically replaced. Improper management can lead to furnace failure and costly production delays.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a specific type of induction furnace should be driven by the final application of the cast part.
- If your primary focus is high-performance aerospace or medical parts: A vacuum induction melting (VIM) furnace is non-negotiable for its ability to handle reactive alloys and ensure ultimate purity.
- If your primary focus is general industrial components (steel, iron, bronze): A standard air-melt coreless induction furnace provides the best balance of speed, efficiency, and cost for a wide range of common alloys.
- If your primary focus is cost reduction and sustainability: The inherent energy efficiency and reduced material waste of all induction technologies directly support lower operational costs and a smaller environmental footprint.
Ultimately, adopting induction technology is about gaining precise control over the most critical variable in the casting process: the metal itself.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Rapid and precise melting of metal alloys for pouring into ceramic molds |
| Heating Method | Non-contact electromagnetic induction for internal heating |
| Key Advantages | Clean melting, precise temperature control, electromagnetic stirring for homogeneity, energy efficiency, reduced waste |
| Common Applications | Aerospace, medical, and industrial components using metals like steel, titanium, and superalloys |
| Considerations | Higher initial cost, need for stable power supply, refractory lining maintenance |
Ready to enhance your investment casting process with advanced induction furnace solutions? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide high-temperature furnaces tailored for diverse laboratory needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by deep customization capabilities to meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how we can deliver precise, efficient melting for your high-quality cast parts!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the core functions of the High Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace? Optimize DD5 Superalloy Purification
- What are the common applications of Vacuum Induction Melting? Essential for High-Performance Metals and Alloys
- What is vacuum induction melting technology and why is it important? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- How does vacuum melting technology contribute to sustainability? Boost Durability and Recycling Efficiency
- What are some common applications of vacuum induction melting and casting (VIM&C)? Essential for Aerospace, Medical, and Nuclear Industries



















