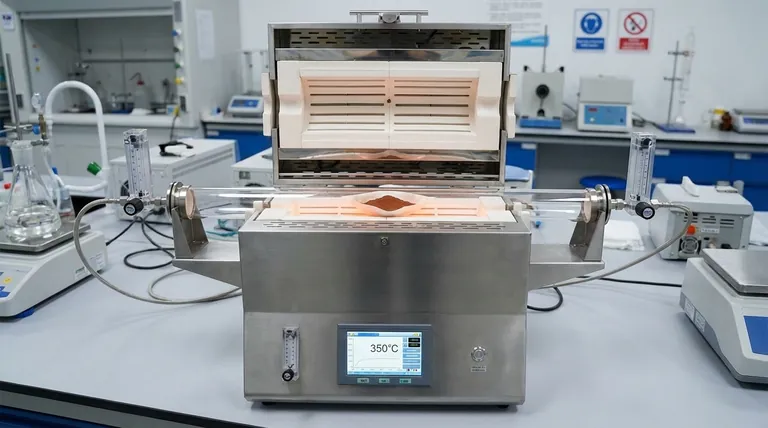
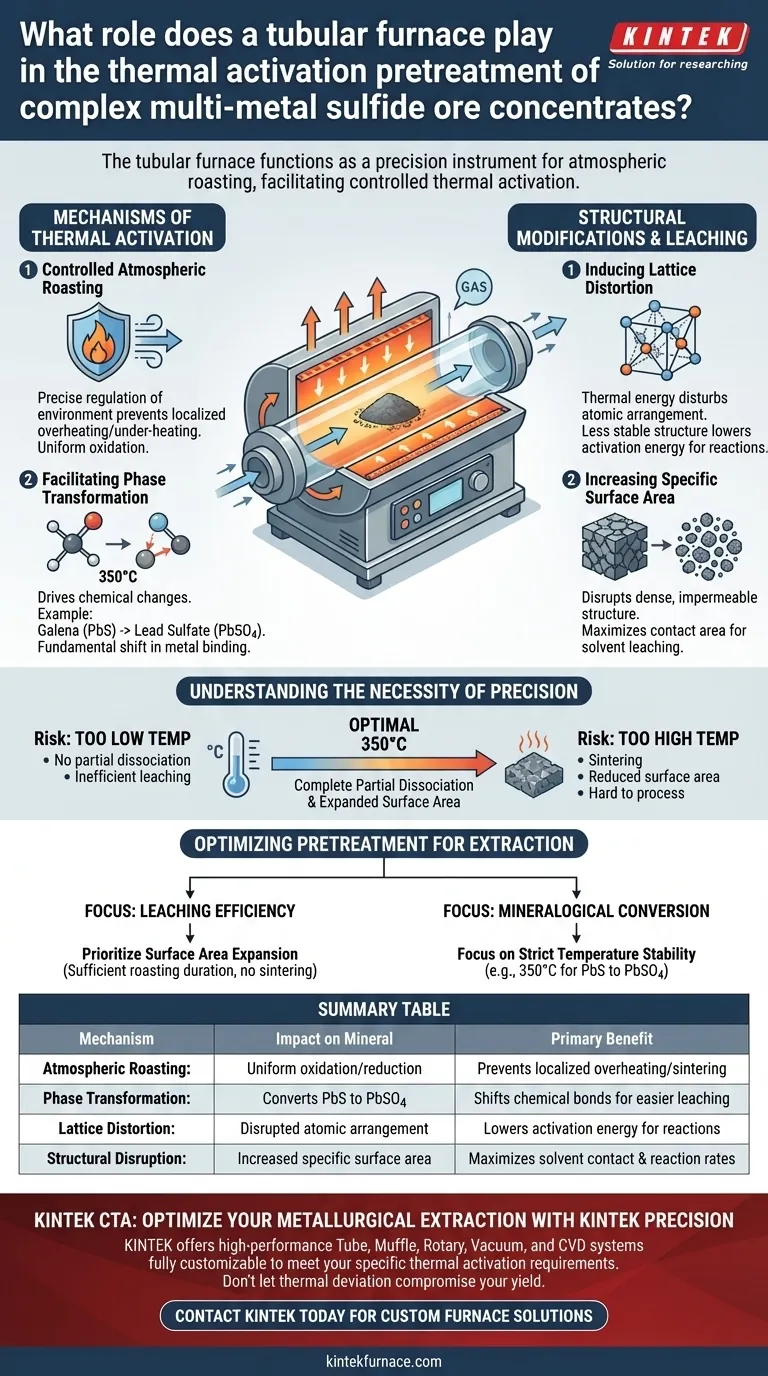
The tubular furnace functions as a precision instrument for atmospheric roasting, facilitating the controlled thermal activation of complex multi-metal sulfide ore concentrates. It provides the exact temperature profile and atmospheric conditions required to chemically alter stable minerals, preparing them for efficient metal extraction.
The core value of the tubular furnace lies in structural disruption. By maintaining strict thermal parameters, it forces the partial dissociation of dense sulfide minerals, distorting their crystal lattice and drastically increasing the surface area available for subsequent chemical leaching.

Mechanisms of Thermal Activation
Controlled Atmospheric Roasting
The primary role of the tubular furnace is to provide a stable, controlled atmosphere for roasting. Unlike open-air heating, a tubular design allows for precise regulation of the environment surrounding the ore concentrate.
This control ensures that the oxidation or roasting process occurs uniformly across the sample. It prevents localized overheating or under-heating, which is critical for complex multi-metal ores.
Facilitating Phase Transformation
Within the furnace, specific thermal conditions drive chemical changes. For example, when operating at 350°C for a set duration, the furnace enables the partial dissociation of specific minerals.
A key transformation involves converting galena (PbS) into lead sulfate (PbSO4). This conversion is not merely a change in composition; it represents a fundamental shift in how the metal is bound within the rock.
Structural Modifications and Leaching
Inducing Lattice Distortion
The thermal energy applied by the furnace acts directly on the mineral crystal structure. As the phase transformation occurs, the atomic arrangement within the mineral is disturbed.
This process creates lattice distortion, rendering the mineral structure less stable. This instability is desirable because it lowers the activation energy required for downstream chemical reactions.
Increasing Specific Surface Area
Raw sulfide ore concentrates often possess a dense, impermeable structure that resists chemical attack. The thermal activation process effectively disrupts this density.
By breaking down the dense structure, the furnace treatment significantly increases the ore's specific surface area. This maximizes the contact area between the ore and the solvent during the subsequent leaching stage, creating ideal physicochemical conditions for extraction.
Understanding the Necessity of Precision
The Risk of Thermal deviation
The effectiveness of this pretreatment relies entirely on precision. The tubular furnace is chosen because it can maintain the temperature exactly at the required set point (e.g., 350°C).
If the temperature is too low, the partial dissociation of galena will not occur, and the lattice remains too stable for efficient leaching.
Conversely, excessive heat can lead to unwanted sintering or the formation of refractory compounds. This would reduce the surface area and negate the benefits of the pretreatment, making the ore harder to process than before.
Optimizing Pretreatment for Extraction
To maximize the utility of a tubular furnace in your metallurgical workflow, consider your specific processing goals:
- If your primary focus is leaching efficiency: Prioritize the expansion of surface area by ensuring the roasting duration is sufficient to disrupt the dense mineral structure without sintering.
- If your primary focus is mineralogical conversion: Focus on strict temperature stability (e.g., maintaining 350°C) to ensure the complete partial dissociation of PbS to PbSO4 without triggering unwanted side reactions.
By leveraging the precise control of a tubular furnace, you transform a resistant, dense mineral into a reactive material primed for high-yield extraction.
Summary Table:
| Mechanism | Impact on Mineral | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Atmospheric Roasting | Uniform oxidation/reduction | Prevents localized overheating/sintering |
| Phase Transformation | Converts PbS to PbSO4 | Shifts chemical bonds for easier leaching |
| Lattice Distortion | Disrupted atomic arrangement | Lowers activation energy for reactions |
| Structural Disruption | Increased specific surface area | Maximizes solvent contact & reaction rates |
Optimize Your Metallurgical Extraction with KINTEK Precision
Is your mineral extraction process hindered by dense, impermeable sulfide structures? Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to meet your specific thermal activation requirements.
Our advanced tubular furnaces provide the strict atmospheric control and temperature stability necessary to induce lattice distortion and maximize the surface area of complex multi-metal ores. Don't let thermal deviation compromise your yield.
Contact KINTEK Today to discuss your unique laboratory needs and custom furnace solutions.
Visual Guide
References
- Yueqiang Wu, J. Li. Behavior and Study of the Kinetics Aspects of Hydrothermal Leaching Conducted on Thermal Activated Products of Complex Polymetallic Secondary Sulfide Concentrate. DOI: 10.24425/amm.2025.153476
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
People Also Ask
- Why is heat treatment in a tube furnace or muffle furnace required after synthesizing magnesium hydroxide nano-precursors via electrochemical methods? Unlock the Full Potential of Your MgO Nanomaterials
- What are the primary applications of vacuum tube furnaces in materials science? Unlock Precision in Material Synthesis and Heat Treatment
- What is the primary role of a tube furnace in the evaluation of cable material smoke acidity? Achieve Precise Testing
- What is the function of an electric tubular furnace in the carbon fiber recovery process? Master CFRP Recycling
- What conditions does a tubular reactor provide for catalyst reduction? Master Platinum, Copper, and Nickel Activation
- What role does a high-temperature tube furnace play in Nb2O5 nanogrids? Achieve 550°C Precision for Synthesis
- What are the main characteristics of vertical tube furnaces? Optimize Your Lab with Space-Saving, Uniform Heating
- What is the necessity of using high-temperature tube furnaces for annealing? Master Quantum Emitter Fabrication



















