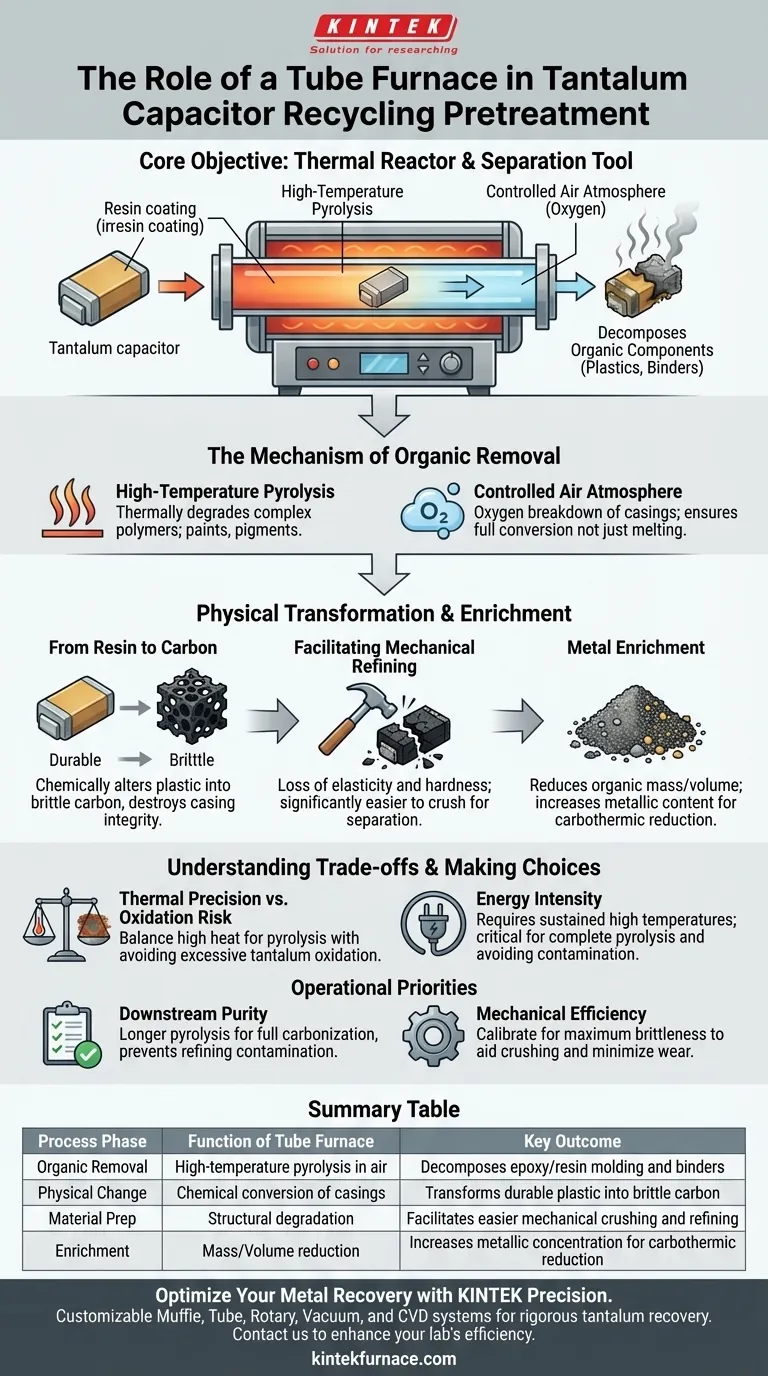
In the pretreatment phase of tantalum capacitor recycling, the tube furnace functions as a specialized thermal reactor designed to strip away non-metallic casing materials. It operates by subjecting the capacitors to high-temperature pyrolysis in an air atmosphere, effectively decomposing organic components like plastic packaging and binders into carbon to expose the valuable metals within.
The Core Objective The tube furnace is not merely a heating element; it is a separation tool. By converting durable resin casings into brittle carbon, it transforms composite electronic waste into a friable, metal-enriched feedstock ready for mechanical crushing and subsequent carbothermic reduction.

The Mechanism of Organic Removal
High-Temperature Pyrolysis
The primary technical challenge in recycling tantalum capacitors is the durable epoxy or resin molding that encapsulates the metal. The tube furnace addresses this by initiating pyrolysis.
This process uses high heat to thermally degrade complex organic polymers—including binders, paints, and pigments.
Controlled Air Atmosphere
Unlike processes requiring inert environments to prevent oxidation, this specific pretreatment stage utilizes an air atmosphere.
Oxygen plays a role in the efficient breakdown of these organic casings, ensuring they are fully converted rather than merely melted or charred incompletely.
Physical Transformation and Enrichment
From Resin to Carbon
The furnace transforms the physical state of the waste material. The robust plastic packaging is chemically altered into a porous, brittle carbon structure.
This conversion is critical because it destroys the structural integrity of the capacitor's casing without melting the high-melting-point tantalum inside.
Facilitating Mechanical Refining
Once the organics are carbonized, the material loses its elasticity and hardness. This renders the capacitors significantly easier to crush.
This brittleness allows for efficient mechanical separation, ensuring that the subsequent refining steps are not hindered by gummy or durable plastics.
Metal Enrichment
By reducing the mass and volume of the organic components, the furnace effectively enriches the metallic content of the batch.
This yields a high-quality mixed material that serves as the ideal precursor for the next critical phase: carbothermic reduction reactions.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Thermal Precision vs. Oxidation Risk
While the primary reference highlights the use of an air atmosphere, operating a tube furnace requires a delicate balance.
You must maintain temperatures high enough to fully pyrolyze the organics, yet controlled enough to avoid excessive, unwanted oxidation of the tantalum metal itself before the reduction phase.
Energy Intensity
This pretreatment is an energy-intensive step. It requires sustaining high temperatures for specific durations to ensure the heat penetrates the core of the capacitor batch.
Cutting corners on heating time or temperature can result in incomplete pyrolysis, leaving behind residual plastics that will contaminate downstream chemical processes.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the efficacy of your recycling line, consider the following operational priorities:
- If your primary focus is Downstream Purity: Ensure the pyrolysis cycle is long enough to fully carbonize all binders and pigments, preventing organic contamination in the chemical refining stage.
- If your primary focus is Mechanical Efficiency: Calibrate the furnace to maximize the brittleness of the output, ensuring the material crushes effortlessly with minimal wear on your grinding equipment.
The tube furnace is the gateway to efficient recycling; it turns a composite waste product into a manageable, chemically simple raw material.
Summary Table:
| Process Phase | Function of Tube Furnace | Key Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Organic Removal | High-temperature pyrolysis in air | Decomposes epoxy/resin molding and binders |
| Physical Change | Chemical conversion of casings | Transforms durable plastic into brittle carbon |
| Material Prep | Structural degradation | Facilitates easier mechanical crushing and refining |
| Enrichment | Mass/Volume reduction | Increases metallic concentration for carbothermic reduction |
Optimize Your Metal Recovery with KINTEK Precision
Maximize the efficiency of your recycling processes with KINTEK’s high-performance thermal solutions. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK offers customizable Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems specifically engineered to handle the rigorous demands of tantalum recovery and lab high-temp applications.
Whether you need precise atmosphere control for pyrolysis or high-throughput systems for metal enrichment, our technical experts are ready to design a solution tailored to your unique needs. Contact us today to enhance your lab’s efficiency!
Visual Guide
References
- Ansan Pokharel, Terence Musho. Microwave-assisted recycling of tantalum and manganese from end-of-life tantalum capacitors. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-96574-7
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a horizontal tube furnace differ from a vertical tube furnace? Choose the Right Furnace for Your Lab
- How does the heating rate control of a tube furnace affect g-C3N4? Master Precise Thermal Polycondensation
- Why is maintenance important for split tube furnaces? Ensure Precision, Safety, and Efficiency
- Why is vacuum-sealed quartz tube encapsulation necessary? Ensure High-Purity Liquid Metal Spectral Analysis
- How can tube furnaces be configured for different laboratory needs? Optimize Your Lab's Thermal Processes
- What is the advantage of a three-zone tube furnace? Achieve Larger, More Uniform Heating for Your Processes
- What is the function of a double-temperature zone tube furnace in CVD synthesis of 2D epsilon-Fe2O3 nanosheets?
- Why is a high-temperature tube furnace used for silicon wafer oxidation? Optimize Your Cobalt Nanoparticle Production



















