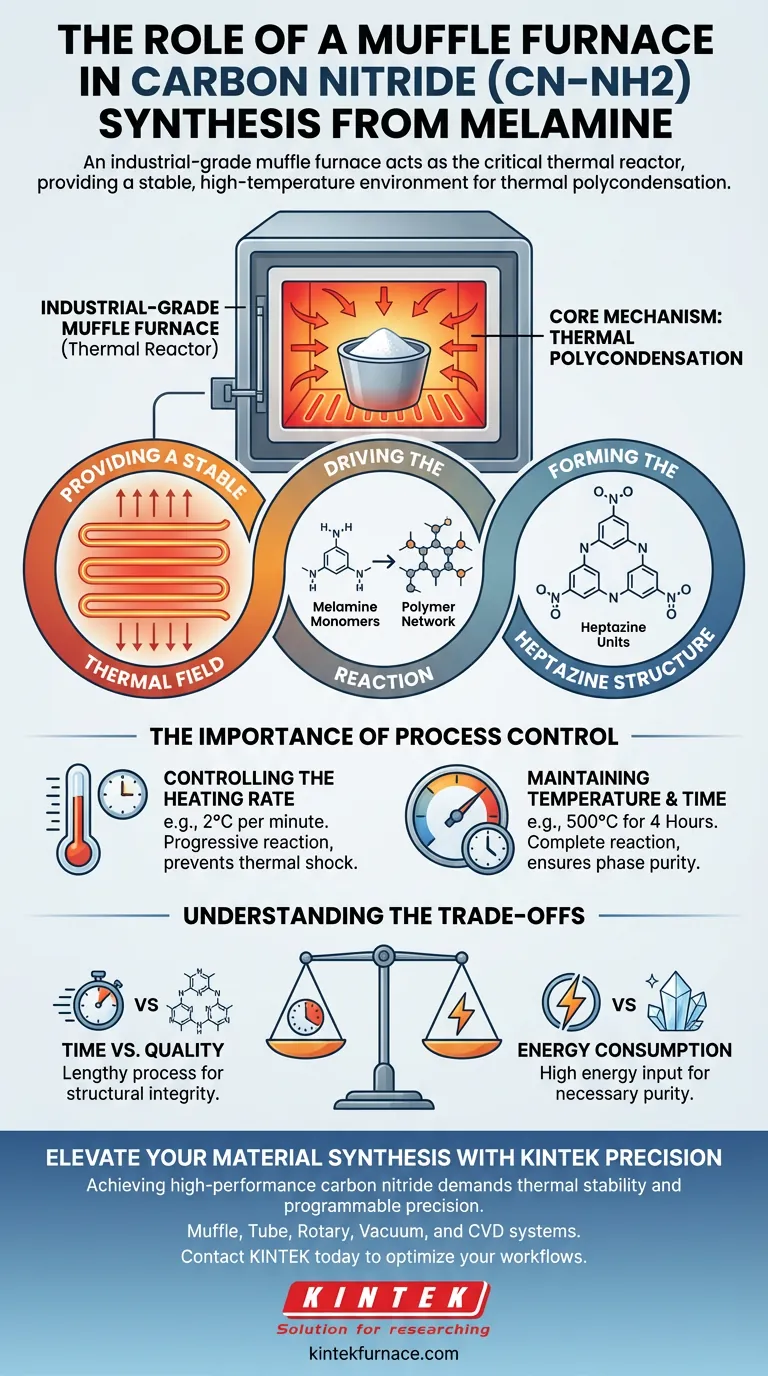
An industrial-grade muffle furnace acts as the critical thermal reactor in the synthesis of carbon nitride (CN–NH2) from melamine. Its primary function is to provide a stable, high-temperature environment that drives the thermal polycondensation of monomers into a cohesive polymer structure.
The muffle furnace does not simply heat the material; it creates a precisely controlled thermal field that ensures the complete reaction of precursors into stable heptazine units.

The Core Mechanism: Thermal Polycondensation
Providing a Stable Thermal Field
The fundamental requirement for synthesizing carbon nitride is a stable high-temperature thermal field.
The muffle furnace isolates the reaction environment, ensuring uniform heat distribution. This stability is essential for initiating the chemical changes required to transform the raw material.
Driving the Reaction
The process relies on thermal polycondensation.
Through applied heat, the furnace forces the melamine monomers to link together. This drives the transition from simple distinct molecules into a complex, connected polymeric network.
Forming the Heptazine Structure
The ultimate goal of this thermal treatment is the formation of the heptazine unit structure.
This structural unit dictates the properties of the final carbon nitride material. The muffle furnace ensures the energy input is sufficient to create these specific molecular bonds.
The Importance of Process Control
Controlling the Heating Rate
Precision is more critical than raw heat. The primary reference highlights a controlled heating rate, such as 2 °C per minute.
A slow, steady ramp-up allows the material to react progressively. This prevents thermal shock or rapid volatilization that could disrupt the formation of the ordered structure.
Maintaining Temperature and Time
Once the target temperature is reached, it must be held strictly constant.
For carbon nitride, a typical protocol involves maintaining 500 °C for 4 hours. This "soak time" ensures that every portion of the precursor undergoes the complete reaction, leaving no unreacted monomers behind.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Time vs. Quality
The specific parameters required for this synthesis (e.g., 2 °C/min) result in a lengthy process.
Attempting to accelerate the synthesis by increasing the heating rate can compromise the material's integrity. You trade production speed for the completeness of the reaction and the stability of the final heptazine structure.
Energy Consumption
Maintaing a high temperature (500 °C) for extended periods (4 hours) requires significant energy input.
However, this energy expenditure is non-negotiable for achieving the necessary phase purity. Cutting the holding time short to save energy often results in an unstable or impure product.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the quality of your carbon nitride synthesis, prioritize the furnace's programmable control features.
- If your primary focus is Structural Stability: Prioritize a slow, controlled heating rate (e.g., 2 °C/min) to ensure the proper formation of heptazine units without thermal shock.
- If your primary focus is Reaction Completeness: Ensure the furnace can maintain the target temperature (e.g., 500 °C) without fluctuation for the full duration (e.g., 4 hours).
Precise thermal regulation is the difference between a loose aggregate of monomers and a high-performance carbon nitride polymer.
Summary Table:
| Process Parameter | Role in Synthesis | Impact on Final Product |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Rate (e.g., 2°C/min) | Progressive reaction | Prevents thermal shock; ensures ordered structure |
| Peak Temp (e.g., 500°C) | Thermal Polycondensation | Drives melamine monomer linkage into polymers |
| Soak Time (e.g., 4 Hours) | Reaction Completeness | Eliminates unreacted monomers for phase purity |
| Thermal Field | Uniform Distribution | Creates stable heptazine units throughout material |
Elevate Your Material Synthesis with KINTEK Precision
Achieving high-performance carbon nitride requires more than just heat; it demands the absolute thermal stability and programmable precision that only expert-engineered equipment can provide.
KINTEK empowers your research and production with a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems. Backed by industry-leading R&D and manufacturing, our furnaces are fully customizable to meet the rigorous demands of thermal polycondensation and complex material synthesis.
Don’t compromise on structural integrity. Contact KINTEK today to discover how our high-temperature solutions can optimize your laboratory workflows and ensure superior reaction completeness.
Visual Guide
References
- Debin Zeng, Yuzheng Guo. CO<sub>2</sub> chemisorption and activation on carbon nitride with less amino groups boost CO<sub>2</sub> photoreduction. DOI: 10.1039/d3cy01585h
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why is a constant temperature oven better than a heating plate for annealing Cs3Cu2I5:Tb films? Expert Comparison
- How is a box muffle furnace used in chemical experiments? Unlock Precise High-Temperature Processing
- What is the significance of high-temperature furnace equipment in electrode testing? Ensure Industrial Peak Performance
- Why is a muffle furnace utilized for Boehmite treatment? Optimize Your Catalyst Preparation
- What are the benefits of custom muffle furnaces? Tailored Solutions for Superior Materials Processing
- What safety precautions should be taken when using a Muffle furnace? Ensure Lab Safety with Expert Guidelines
- How is a muffle furnace used in environmental analysis? Achieve Accurate Sample Preparation for Pollutants
- What should be considered regarding the controller when purchasing a muffle furnace? Choose the Right Controller for Precision



















