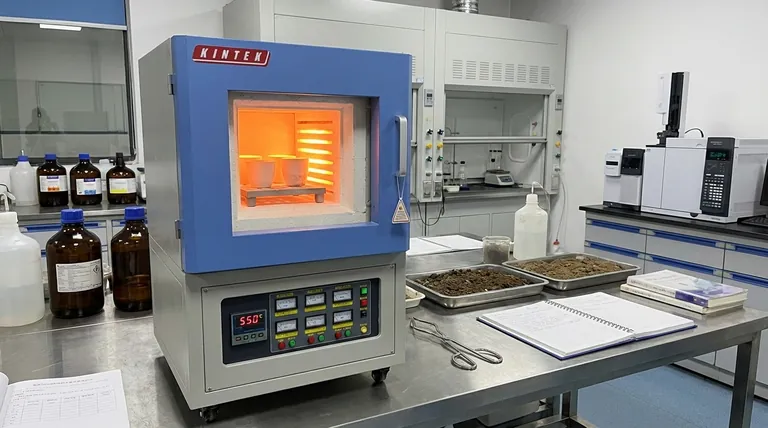
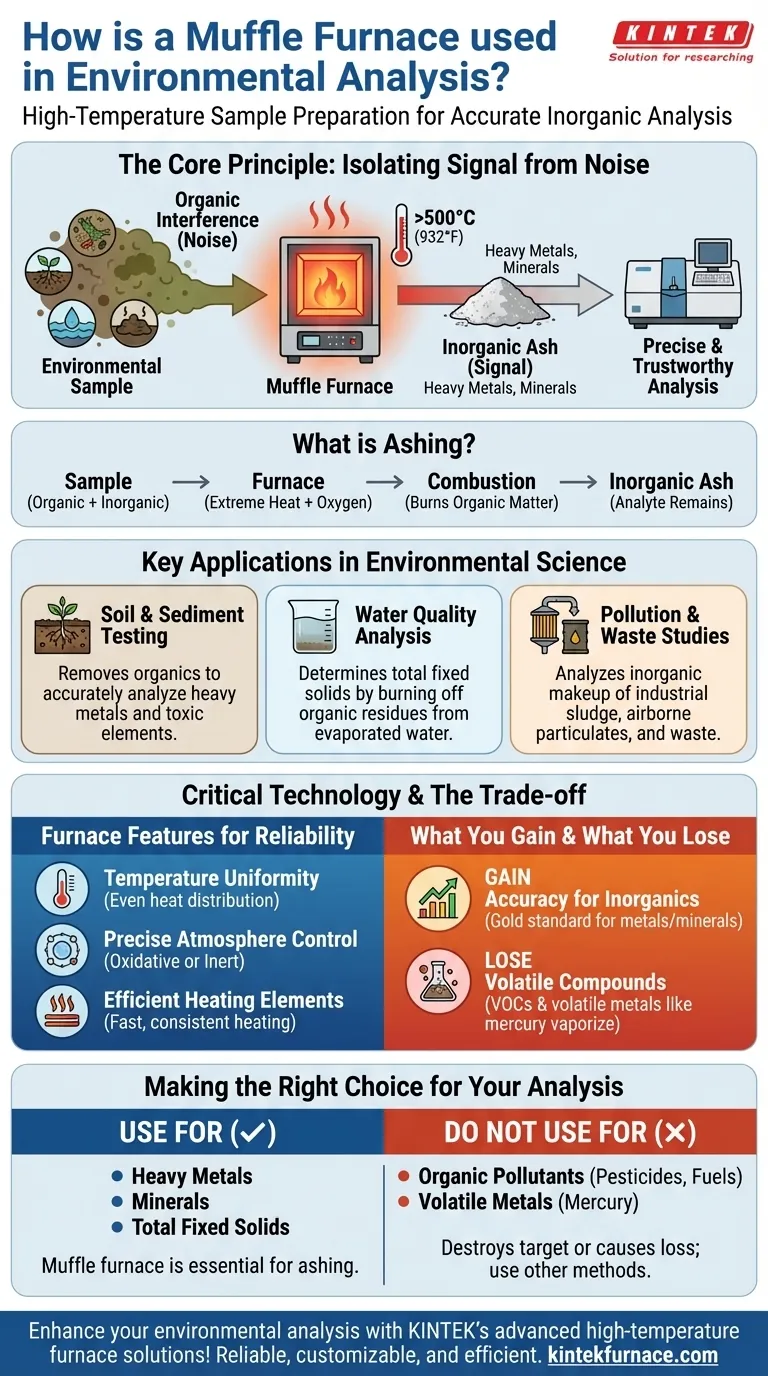
In environmental analysis, the muffle furnace serves one critical purpose: high-temperature sample preparation. It is used to systematically burn away organic matter from environmental samples like soil, water residue, or industrial sludge. This process, known as ashing, cleanly isolates the inorganic components, such as heavy metals or minerals, allowing for highly accurate and reliable measurement.
The core challenge in environmental testing is isolating the specific pollutants you need to measure from a complex sample matrix. A muffle furnace provides the controlled, high-heat environment necessary to remove this organic interference, ensuring that subsequent analysis of inorganic compounds is both precise and trustworthy.

The Core Principle: Isolating Signal from Noise
The fundamental goal of using a muffle furnace is to "clean up" a sample before it undergoes chemical analysis. Environmental samples are rarely pure; they are a mix of organic and inorganic materials.
What is Ashing?
Ashing is the process of using extreme heat, typically in the presence of oxygen, to incinerate all organic (carbon-based) substances in a sample.
The material left behind is a small amount of non-combustible ash containing the inorganic compounds. This ash is what is then analyzed.
Why Remove Organic Matter?
Organic compounds present in soil, water, or waste can interfere with the analytical instruments used to detect and quantify inorganic pollutants like lead, cadmium, or arsenic.
By removing this organic "noise," you effectively unmask the target substances. This dramatically increases the purity of the sample and the accuracy of the final test results.
The Role of High Temperature
Muffle furnaces operate at temperatures above 500°C (932°F) for this process. This intense heat ensures the complete and efficient combustion of all organic material, leaving only the stable, inorganic mineral ash for analysis.
Key Applications in Environmental Science
The muffle furnace is a workhorse in environmental labs, used across several critical testing domains.
Soil and Sediment Testing
Before testing soil for contamination with heavy metals, samples are ashed in a muffle furnace. This removes the humus, roots, and other biological matter, leaving behind a mineral sample that can be accurately analyzed for toxic elements.
Water Quality Analysis
When analyzing the total fixed solids in a water or wastewater sample, the water is first evaporated. The remaining solid residue is then placed in a muffle furnace to burn off any organic solids, leaving only the inorganic mineral content to be weighed.
Pollution and Waste Studies
Industrial sludge, airborne particulates captured on filters, and other waste materials are processed in a muffle furnace to determine their inorganic makeup. This provides strong data support for pollution analysis and environmental protection efforts.
Understanding the Critical Technology
Not all furnaces are equal. The reliability of environmental data depends on key furnace features that ensure the ashing process is consistent and complete.
Temperature Uniformity
Ensuring an even temperature distribution throughout the furnace chamber is vital. Localized "cold spots" can result in incomplete ashing, leaving behind residual organic matter that will skew analysis results.
Precise Atmosphere Control
Most ashing is done in an oxidative atmosphere (air). However, some analyses require an inert atmosphere (like nitrogen) to prevent the target inorganic compounds from reacting with oxygen at high temperatures, which would alter their chemical form and ruin the test.
Efficient Heating Elements
Modern heating elements reduce the time it takes to reach the target temperature. In a production laboratory, this directly translates to higher sample throughput and improved overall efficiency.
The Trade-off: What You Gain and What You Lose
Using a muffle furnace is a deliberate choice with clear consequences for your sample. Understanding this trade-off is key to its proper application.
Gaining Accuracy for Inorganics
The primary benefit is undeniable: you achieve exceptionally accurate and defensible data for inorganic analytes like toxic metals and essential minerals. This is the gold standard for this type of analysis.
Losing Volatile Compounds
The major limitation is that this destructive process completely eliminates all volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and can also vaporize certain volatile metals like mercury. A muffle furnace is therefore never used when these volatile substances are the target of the analysis.
Making the Right Choice for Your Analysis
Applying this technique correctly depends entirely on your analytical goal.
- If your primary focus is heavy metals, minerals, or total fixed solids: A muffle furnace is the essential and correct tool for preparing your samples via ashing.
- If your primary focus is organic pollutants (like pesticides or fuels): Do not use a muffle furnace, as this method will destroy your target compounds; different chemical extraction methods are required.
- If your primary focus is volatile metals like mercury: A muffle furnace is inappropriate; specialized, lower-temperature analytical techniques must be used to prevent the metal from being lost.
Ultimately, understanding when and why to use a muffle furnace is fundamental to producing accurate and defensible environmental data.
Summary Table:
| Application | Purpose | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Soil and Sediment Testing | Remove organic matter to analyze heavy metals | Accurate detection of contaminants |
| Water Quality Analysis | Determine total fixed solids by ashing residue | Reliable measurement of inorganic content |
| Pollution and Waste Studies | Process sludge and particulates for inorganic makeup | Strong data for environmental protection |
Enhance your environmental analysis with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with reliable muffle, tube, rotary, vacuum & atmosphere furnaces, and CVD/PECVD systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs, improving accuracy and efficiency in pollutant detection. Contact us today to discuss how our products can support your lab's goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis



















