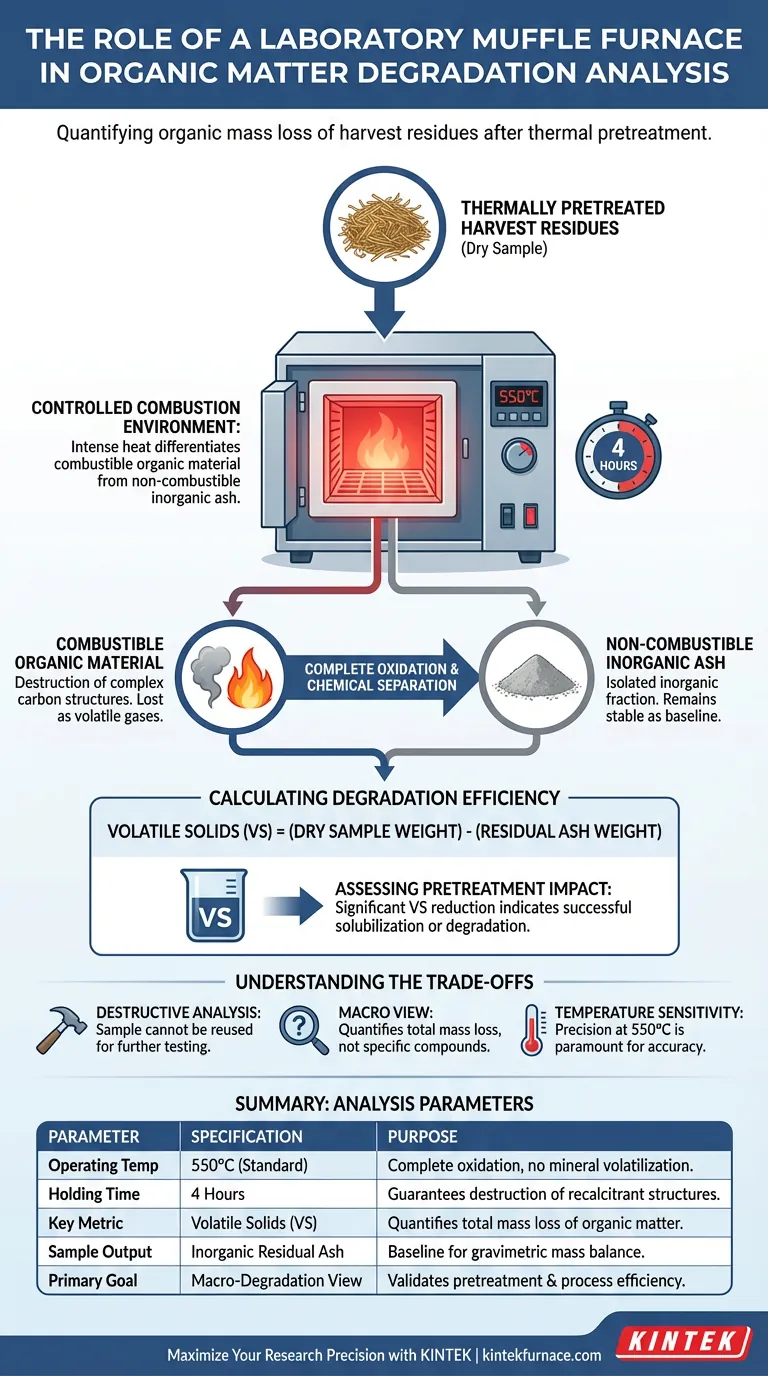
A laboratory muffle furnace acts as the primary instrument for quantifying organic mass loss by creating a controlled environment for complete combustion. Specifically, it subjects thermally pretreated harvest residues to intense heat to differentiate between combustible organic material and non-combustible inorganic ash. This separation provides the raw data necessary to calculate the Volatile Solids (VS) content, which is the definitive metric for assessing organic degradation.
The muffle furnace facilitates the precise calculation of organic degradation by maintaining a constant 550°C environment for four hours. This protocol ensures the total oxidation of organic components, leaving only residual ash to serve as a baseline for quantitative analysis.

The Mechanism of Quantitative Analysis
To understand the role of the furnace, one must look beyond the equipment itself and focus on the chemical separation it forces within the sample.
Controlled Oxidation
The primary function of the muffle furnace is to facilitate the complete oxidation of organic components. Unlike standard ovens, which are used for drying, a muffle furnace operates at temperatures high enough to break down complex carbon structures.
Isolating Inorganic Material
By burning off all organic matter, the furnace isolates the inorganic fraction of the harvest residue. This residue, known as ash, remains stable even at high temperatures and serves as the constant against which organic loss is measured.
The Standardized Procedure
Reliable analysis depends on strict adherence to a specific thermal protocol. This standardization ensures that results are comparable across different pretreatment batches.
The 550°C Standard
The analysis requires the furnace to maintain a high temperature, specifically 550°C. This temperature is the industry standard for biomass combustion, ensuring that organic matter is destroyed without volatilizing the inorganic mineral salts.
Duration of Exposure
The samples must be held at this temperature for a duration of 4 hours. This time frame guarantees that even the most recalcitrant organic structures within the harvest residues are fully oxidized.
Calculating Degradation Efficiency
The physical operation of the furnace yields data that must be mathematically interpreted to evaluate the thermal pretreatment.
Determining Volatile Solids (VS)
The key metric derived from this process is Volatile Solids (VS). Researchers calculate VS by measuring the weight of the residual ash and subtracting it from the dry weight of the original sample.
Assessing Pretreatment Impact
By comparing the VS content before and after the thermal pretreatment of the harvest residues, researchers can quantify the degradation. A significant reduction in VS indicates that the pretreatment successfully solubilized or degraded the organic structure of the biomass.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While the muffle furnace is essential for gravimetric analysis, researchers must recognize the inherent limitations of this method to ensure data accuracy.
Destructive Analysis
This process is inherently destructive. Because the organic matter is combusted, the specific sample used for this analysis cannot be used for further chemical or structural testing.
Total vs. Specific Degradation
The muffle furnace provides a "macro" view of degradation. It quantifies the total mass of organic matter lost but does not identify which specific organic compounds (e.g., lignin vs. cellulose) were degraded.
Sensitivity to Temperature Fluctuations
Precision is paramount. If the furnace temperature drops below 550°C, combustion may be incomplete, artificially inflating the organic content readings. Conversely, excessive temperatures could volatilize certain minerals, skewing the ash calculations.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When analyzing harvest residues, how you utilize the muffle furnace data depends on your specific research objective.
- If your primary focus is process efficiency: Concentrate on the delta in Volatile Solids (VS); a larger drop in VS correlates directly to a more effective thermal pretreatment.
- If your primary focus is byproduct management: Focus on the Residual Ash Content, as this dictates the volume of inorganic waste that will remain after the organic matter is processed.
The muffle furnace provides the fundamental gravimetric truth required to validate any claim regarding the biological or thermal degradation of biomass.
Summary Table:
| Analysis Parameter | Specification / Protocol | Purpose in Degradation Study |
|---|---|---|
| Operating Temp | 550°C (Industry Standard) | Ensures complete oxidation without mineral volatilization |
| Holding Time | 4 Hours | Guarantees destruction of recalcitrant organic structures |
| Key Metric | Volatile Solids (VS) | Quantifies the total mass loss of organic matter |
| Sample Output | Inorganic Residual Ash | Serves as a baseline for gravimetric mass balance |
| Primary Goal | Macro-Degradation View | Validates thermal pretreatment and process efficiency |
Maximize Your Research Precision with KINTEK
Ensure the accuracy of your biomass degradation studies with high-performance heating solutions. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-precision Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, along with other specialized lab high-temp furnaces. Whether you are analyzing harvest residues or developing advanced materials, our systems are fully customizable to meet your unique thermal protocol needs.
Ready to upgrade your laboratory capabilities? Contact us today to find your custom solution!
Visual Guide
References
- Đurđica Kovačić, Mladen Jurišić. Influence of Thermal Pretreatment on Lignin Destabilization in Harvest Residues: An Ensemble Machine Learning Approach. DOI: 10.3390/agriengineering6010011
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the environmental conditions for a muffle furnace? Ensure Safe, Accurate High-Temperature Operations
- Why is a high-temperature muffle furnace required for U3O8 preparation? Achieving Phase Purity and Stability
- What safety features should a muffle furnace have? Essential Protections for Your Lab's Safety
- Which industries utilize Box Furnaces? The Essential Tool for Industrial Heat Treatment
- How does the calcination process in a precision muffle furnace affect CuO nanoparticles? Optimize Your Synthesis.
- Why is a precise muffle furnace required for Pt/Al2O3 catalyst calcination? Ensure High Activity and Dispersion
- Which types of labs commonly use vacuum muffle furnaces? Essential for High-Purity Heat Treatment
- Why is precise temperature control important in a muffle furnace? Ensure Reliable Results in Heat Treatment



















