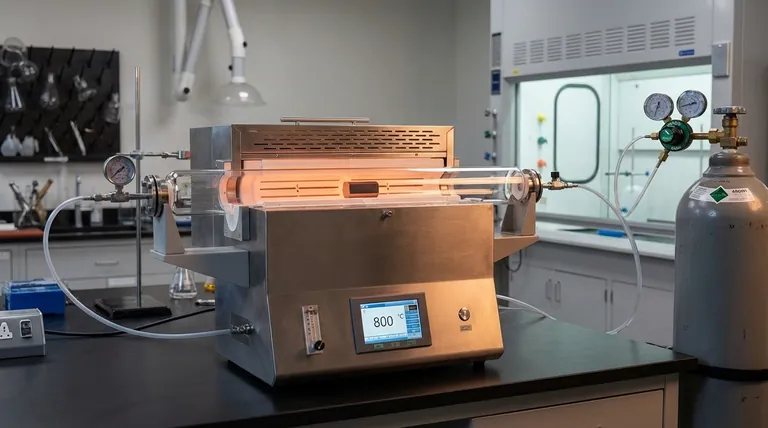
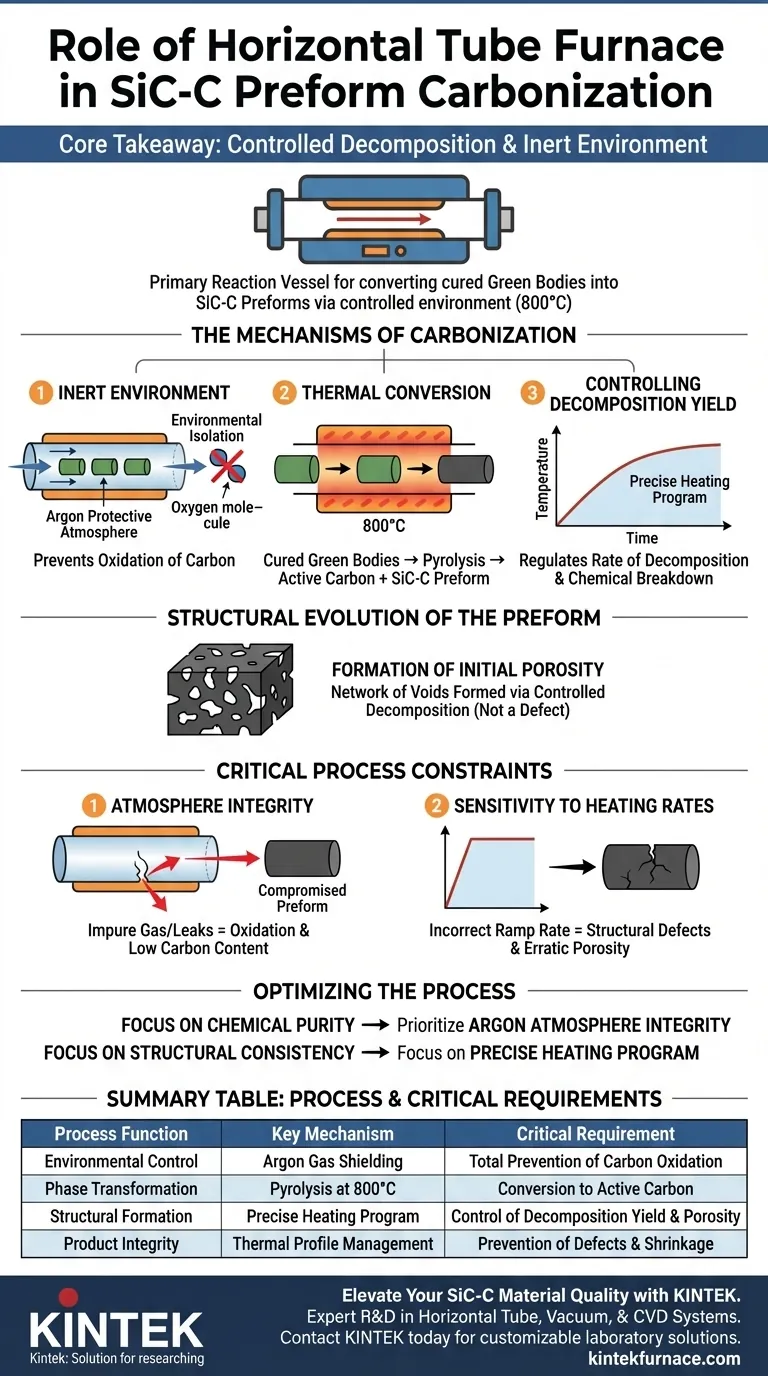
A horizontal tube furnace acts as the primary reaction vessel for converting cured "green bodies" into silicon carbide-carbon (SiC-C) preforms. By strictly controlling the environment and temperature—typically reaching 800 °C—it facilitates the carbonization process required to generate active carbon without damaging the material through oxidation.
Core Takeaway Carbonization is not simply about heating; it is about controlled decomposition. The horizontal tube furnace provides a sealed, inert environment that protects the carbon source while establishing the material's initial porosity and chemical composition through a precise thermal profile.

The Mechanisms of Carbonization
To understand the role of the furnace, one must look beyond the generation of heat. The device serves three specific functions critical to the material science of SiC-C preforms.
Creating an Inert Environment
The most immediate function of the horizontal tube furnace is environmental isolation. The process requires an argon protective atmosphere.
Without this inert gas blanket, the carbon sources within the green body would react with oxygen at high temperatures. This would lead to oxidation, effectively burning away the carbon rather than converting it into the desired structural form.
Thermal Conversion of Green Bodies
The furnace drives the physical phase change of the material. It takes the "cured green bodies"—the initial, molded composite mixture—and subjects them to high heat, typically around 800 °C.
At this temperature, the organic components within the cured body undergo pyrolysis. This thermal degradation transforms the precursors into a SiC-C preform containing active carbon, which is essential for the material's final properties.
Controlling Decomposition Yield
The furnace allows for a "precise heating program." This is distinct from uncontrolled heating.
By regulating the rate at which the temperature rises, the furnace controls the decomposition yield of the components. This ensures that the chemical breakdown happens at a manageable rate, preventing structural defects that could arise from rapid gas evolution or uneven shrinkage.
Structural Evolution of the Preform
The physical structure of the final material is determined during this furnace stage.
Formation of Initial Porosity
As the components decompose and volatile elements are driven off, the material does not remain a solid block. The process creates a network of voids.
The furnace's heating program directly dictates the formation of initial porosity. This porous structure is not a defect; it is a critical feature that defines the density and potential for future infiltration or matrix formation in the final SiC-C composite.
Critical Process Constraints
While the horizontal tube furnace is the enabler of this process, reliance on it introduces specific variables that must be managed to avoid failure.
Atmosphere Integrity
The effectiveness of the process relies entirely on the purity of the argon atmosphere. Even minor leaks or impure gas sources within the tube furnace will compromise the prevention of oxidation, leading to a degraded preform with insufficient carbon content.
Sensitivity to Heating Rates
The reference emphasizes a "precise heating program." Deviating from the optimal ramp rate—heating too quickly or cooling too abruptly—can disrupt the decomposition yield. This mismatch can result in erratic pore structures or internal stresses that weaken the preform before it is ever put into use.
Optimizing the Carbonization Process
To ensure high-quality SiC-C preforms, your operation of the furnace must align with your specific material goals.
- If your primary focus is Chemical Purity: Prioritize the integrity of the argon atmosphere. Ensure the tube is perfectly sealed to prevent any oxidation of the carbon source.
- If your primary focus is Structural Consistency: Focus on the heating program. A strictly controlled temperature ramp is required to manage the decomposition yield and create uniform porosity.
The horizontal tube furnace is the gatekeeper of quality, determining whether a green body becomes a high-performance preform or defective waste.
Summary Table:
| Process Function | Key Mechanism | Critical Requirement |
|---|---|---|
| Environmental Control | Argon gas shielding | Total prevention of carbon oxidation |
| Phase Transformation | Pyrolysis at 800 °C | Conversion of cured bodies to active carbon |
| Structural Formation | Precise heating program | Control of decomposition yield and porosity |
| Product Integrity | Thermal profile management | Prevention of structural defects and shrinkage |
Elevate Your SiC-C Material Quality with KINTEK
Precise carbonization requires absolute control over atmosphere and thermal ramp rates. At KINTEK, we specialize in high-performance Horizontal Tube, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed for the rigorous demands of advanced material science. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, our customizable furnaces ensure the integrity of your inert environments and the precision of your heating programs.
Ready to optimize your carbonization process? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your unique laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
References
- Mingjun Zhang, Bo Wang. Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Effectiveness of Pure SiC–Ti3SiC2 Composites Fabricated by Reactive Melt Infiltration. DOI: 10.3390/ma18010157
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
People Also Ask
- What is the primary purpose of using a Quartz Tube Furnace for MoS2 annealing? Unlock High Electrical Performance
- What is the necessity of using high-temperature tube furnaces for annealing? Master Quantum Emitter Fabrication
- What is the primary purpose of using a tube reduction furnace? Achieve High-Purity Fe-Cu Sintering
- What are some common applications of tubular furnaces? Unlock Precision in High-Temperature Processing
- What is the function of a high-temperature tube furnace in the synthesis of SPC-Fe? Master Graphitic Carbon Production
- What conditions does a tubular reactor provide for catalyst reduction? Master Platinum, Copper, and Nickel Activation
- How are multi zone tube furnaces applied in biomedical research? Unlock Advanced Biomaterial Engineering
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace contribute to the pre-carbonization of biomass? Optimize Carbon Yield Today



















