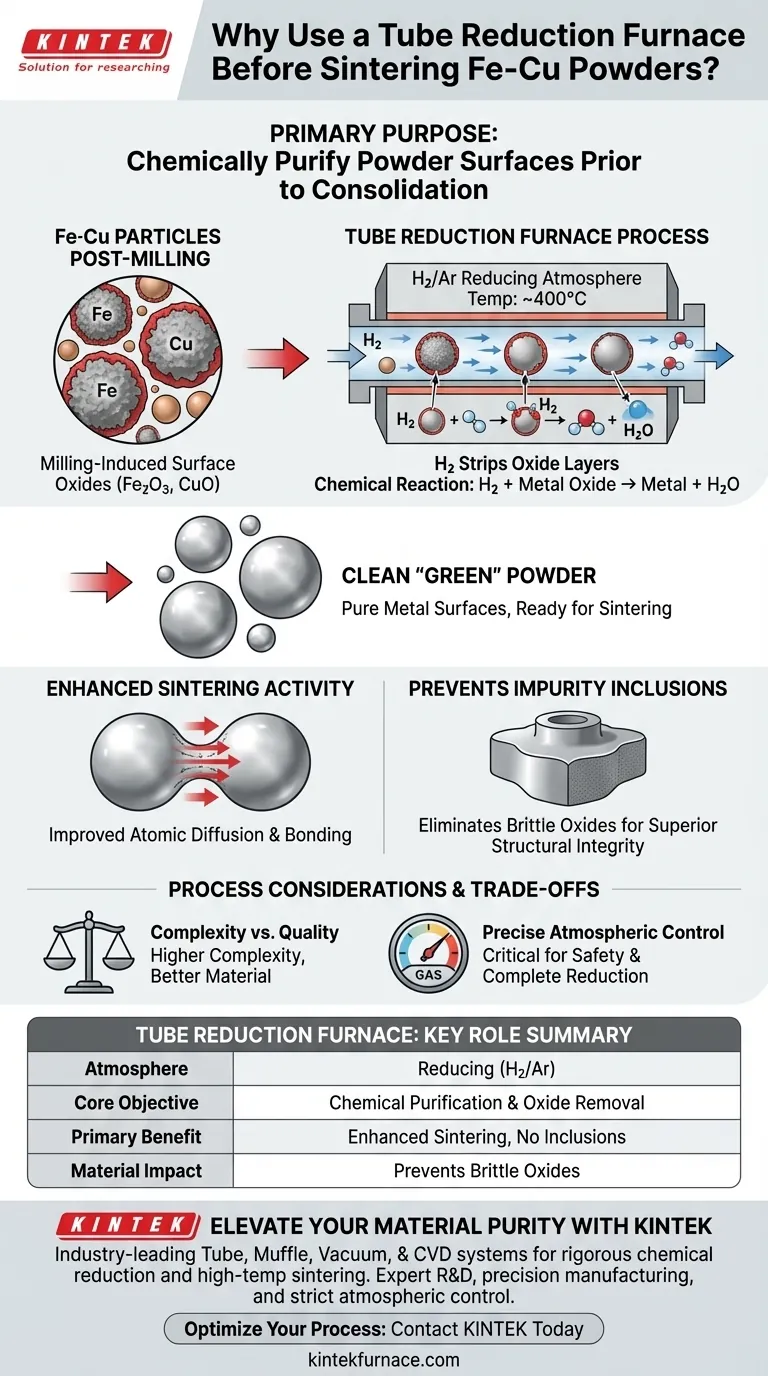
The primary purpose of using a tube reduction furnace is to chemically purify the powder surface prior to consolidation. Specifically, this process utilizes high-temperature hydrogen reduction to strip away the oxide layers that inevitably form during the mechanical ball-milling of Iron (Fe) and Copper (Cu) powders. By removing these oxides, the furnace prepares the "green" powder for effective bonding during the subsequent sintering phase.
By reversing the oxidation caused during milling, this reduction step eliminates barriers to diffusion. This ensures that the final material is formed from high-purity metal surfaces rather than oxide-contaminated particles, leading to superior structural integrity.

The Mechanics of Oxide Removal
Reversing the Effects of Milling
Mechanical ball-milling is essential for mixing Fe and Cu, but it exposes fresh metal surfaces to oxygen. This creates a surface oxide layer on the particles. The tube reduction furnace is introduced specifically to address and reverse this milling-induced oxidation.
The Role of the Hydrogen Atmosphere
The furnace operates by introducing a reducing atmosphere, typically hydrogen or a hydrogen-argon mix. At high temperatures (e.g., around 400°C), the hydrogen reacts chemically with the oxygen bound to the metal. This reaction strips the oxygen away, effectively "cleaning" the Fe and Cu particles.
Why Pre-Sintering Reduction is Critical
Enhancing Sintering Activity
Sintering relies on atomic diffusion to bond particles together. Surface oxides act as a barrier to this diffusion, inhibiting the bonding process. By removing this layer, the reduction process significantly improves the sintering activity, allowing particles to fuse more readily and completely.
Preventing Impurity Inclusions
If the oxide layer is not removed, those oxides remain trapped within the final material as impurities. These inclusions can weaken the composite and alter its physical properties. The reduction step ensures that metal oxides are not introduced as impurities into the final densified product.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Process Complexity vs. Material Quality
While essential for high-performance composites, adding a reduction step increases process complexity compared to direct sintering. It requires precise control over the atmosphere to prevent safety hazards associated with hydrogen and to ensure complete reduction.
Equipment Distinction
It is important to distinguish this step from the final sintering. While a box furnace is often used for the final sintering to create solid components, the tube furnace is specifically favored for this precursor reduction step due to its ability to maintain the strict atmospheric control required for chemical purification.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine how critical this step is for your specific application, consider the following:
- If your primary focus is Mechanical Strength: You must include the tube reduction step to remove fracture-inducing oxide inclusions and ensure a dense, high-purity final composite.
- If your primary focus is Process Efficiency: You must ensure your reduction parameters (temperature and time) are optimized; insufficient reduction will waste the step, while excessive heat could lead to premature sintering before the final densification stage.
A clean powder surface is the non-negotiable foundation of a high-performance sintered alloy.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Tube Reduction Furnace Role |
|---|---|
| Atmosphere | Reducing (Hydrogen/Argon-Hydrogen) |
| Core Objective | Chemical purification & oxide removal |
| Chemical Reaction | H2 + Metal Oxide → Metal + H2O |
| Primary Benefit | Enhanced atomic diffusion & sintering activity |
| Material Impact | Prevents brittle oxide inclusions in the final product |
Elevate Your Material Purity with KINTEK
Don't let surface oxides compromise the structural integrity of your Fe-Cu composites. KINTEK provides industry-leading Tube, Muffle, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed for the rigorous demands of chemical reduction and high-temperature sintering. Backed by expert R&D and precision manufacturing, our customizable furnaces ensure the strict atmospheric control necessary to eliminate impurities and maximize sintering activity.
Ready to optimize your powder metallurgy process? Contact our experts today to find the perfect high-temp solution tailored to your unique research or production needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What temperature should the furnace be at when loading or unloading samples? Stay Safe and Prevent Damage
- What is the role of a Tube Furnace in TMDC-ND preparation? Master Graphene-Decorated Nanostructure Synthesis
- What are the primary applications of high temperature tube furnaces? Unlock Precise Heat Control for Materials Science
- What metallurgical processes benefit from tube furnaces? Achieve Precise Heat Treatment and Material Control
- How does a tube furnace contribute to the synthesis of electrocatalysts from hydrochar? Precision Thermal Engineering
- Why is a Tube Resistance Furnace with Argon Necessary for TiO2 and Nickel Foam? Protect Substrate and Conductivity
- What critical processing conditions does a horizontal tube furnace provide for 3D porous NiO capacitors?
- What are the industrial design advantages of using a tube furnace for ex-situ reduction of catalysts? Optimize Efficiency



















