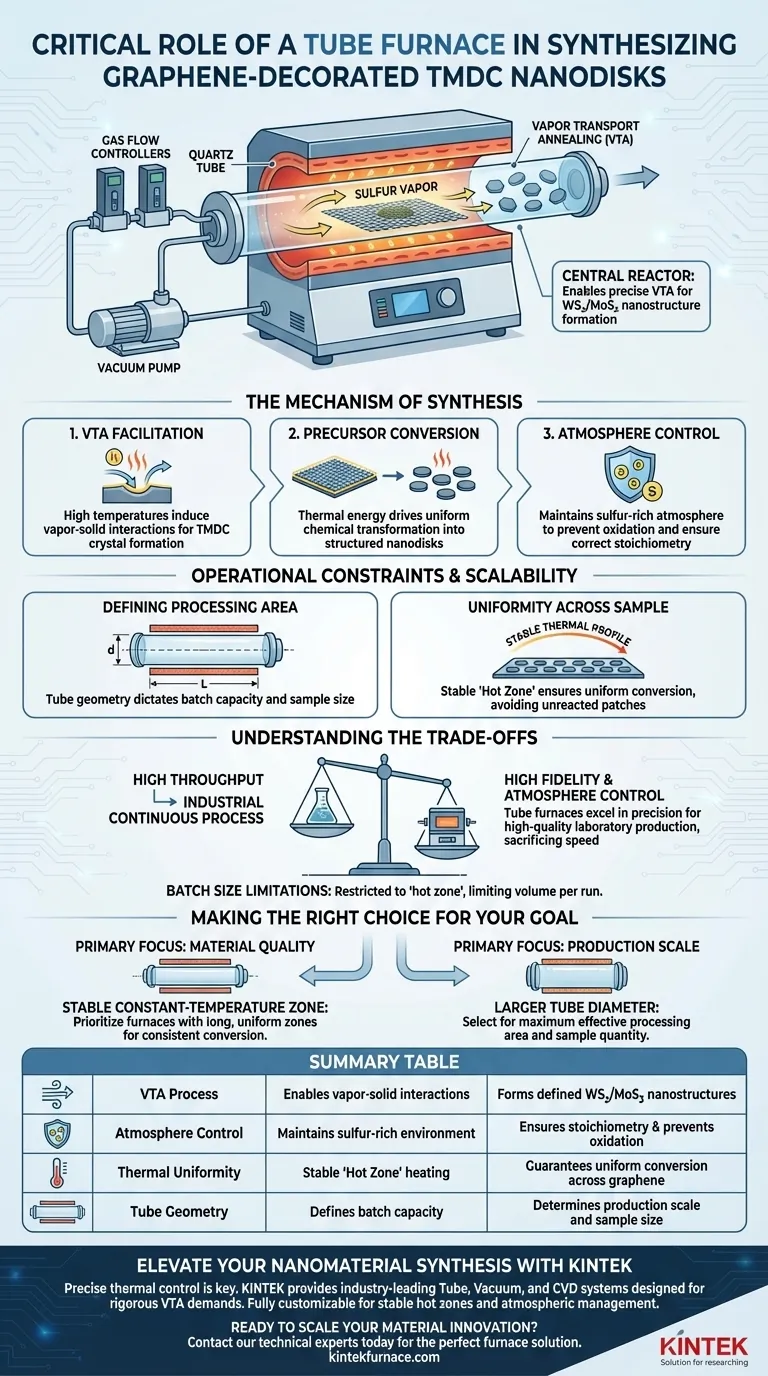
The Tube Furnace functions as the central reactor for the synthesis of graphene-decorated Transition Metal Dichalcogenide nanodisks (TMDC-NDs). Its primary role is to facilitate Vapor Transport Annealing (VTA), providing the precise thermal environment needed to convert precursor materials into specific nanostructures like Tungsten Disulfide (WS2) or Molybdenum Disulfide (MoS2) within a sulfur-rich atmosphere.
The Tube Furnace is not merely a heater; it is the control vessel for Vapor Transport Annealing, ensuring that precursors coated on graphene undergo a uniform chemical transformation into defined nanodisks.

The Mechanism of Synthesis
Facilitating Vapor Transport Annealing (VTA)
The core function of the Tube Furnace in this context is enabling Vapor Transport Annealing.
This process relies on high temperatures to induce chemical reactions between the solid precursors and the surrounding vapor.
Without the enclosed, heated environment of the tube, the necessary vapor-solid interactions required to form the TMDC crystal structure would not occur.
Conversion of Precursors
The synthesis begins with TMDC precursors that are already coated onto a graphene substrate.
The furnace provides the thermal energy required to drive the chemical conversion of these precursors into their final nanodisk forms (WS2 or MoS2).
This ensures the final material is not a random aggregate, but a structured composite where the nanodisks are properly formed on the graphene sheet.
Atmosphere Control
A critical requirement for forming metal dichalcogenides is the presence of sulfur vapor.
The Tube Furnace maintains this specific sulfur atmosphere, preventing oxidation and ensuring the correct stoichiometry of the final nanodisks.
This controlled environment allows for the precise sulfurization of the transition metals, which is essential for the material's electronic properties.
Operational Constraints and Scalability
Defining the Processing Area
The physical geometry of the Tube Furnace directly dictates the production capacity.
The dimensions of the furnace tube (diameter and heated length) determine the maximum size and quantity of samples that can be processed in a single run.
Uniformity Across the Sample
Beyond simple heating, the furnace must maintain a stable thermal profile across the synthesis zone.
This ensures that the conversion of precursors into nanodisks is uniform across the entire graphene surface, avoiding patches of unreacted material.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Batch Size Limitations
While the Tube Furnace offers excellent environmental control, it is inherently limited by its physical volume.
The effective processing area is restricted to the "hot zone" of the tube; placing samples outside this uniform temperature zone can lead to inconsistent nanodisk formation.
Throughput vs. Control
Tube furnaces excel at precision but often sacrifice high-volume throughput compared to continuous industrial processes.
For laboratory or pilot-scale production of high-quality graphene-TMDC heterostructures, the trade-off favors the high fidelity and atmosphere control that the tube furnace provides.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the effectiveness of a Tube Furnace for TMDC-ND synthesis, align your equipment choice with your specific production needs.
- If your primary focus is material quality: Prioritize a furnace with a long, stable constant-temperature zone to ensure the most uniform conversion of precursors into WS2 or MoS2.
- If your primary focus is production scale: Select a furnace with a larger tube diameter to maximize the effective processing area available for your graphene substrates.
The Tube Furnace is the critical bridge that transforms raw precursors into sophisticated, graphene-supported nanostructures through precise environmental control.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role in TMDC-ND Synthesis | Impact on Material |
|---|---|---|
| VTA Process | Enables vapor-solid interactions | Forms defined WS2/MoS2 nanostructures |
| Atmosphere Control | Maintains sulfur-rich environment | Ensures stoichiometry & prevents oxidation |
| Thermal Uniformity | Stable 'Hot Zone' heating | Guarantees uniform conversion across graphene |
| Tube Geometry | Defines batch capacity | Determines production scale and sample size |
Elevate Your Nanomaterial Synthesis with KINTEK
Precise thermal control is the difference between random aggregates and high-fidelity graphene-TMDC heterostructures. KINTEK provides industry-leading Tube, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to meet the rigorous demands of Vapor Transport Annealing (VTA).
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, our systems are fully customizable to your specific research or production requirements, ensuring stable hot zones and precise atmospheric management for consistent nanodisk formation.
Ready to scale your material innovation? Contact our technical experts today to find the perfect furnace solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
References
- Samar Ali Ghopry, Judy Wu. Enhanced Photoresponse in Intermingled WS<sub>2</sub> and MoS<sub>2</sub> Nanodiscs on Graphene Heterostructure Nanohybrids. DOI: 10.1002/admi.202500087
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the main applications of a vertical tube furnace? Leverage Gravity for Superior Thermal Processing
- What components are used in tube furnaces to achieve temperatures above 1200 °C? Key Elements for Extreme Heat
- What is the role of a Tube Furnace or Rotary Furnace in hydrogen reduction roasting? Optimize Lithium Recovery Efficiency.
- What is the purpose of a two-zone tube furnace for nanoparticle selenization? Achieve Precision Vapor Control
- What is the role of high-purity quartz sealed tubes in CVT for BiRe2O6 growth? Achieve Pure Crystal Growth
- What certifications are associated with three-zone split tube furnaces? Key Marks for Quality and Safety
- What core functions does a program-controlled tube furnace perform? Master BN@C Synthesis with Precision
- Why is a continuous flow of high-purity nitrogen necessary during the pyrolysis of carbon materials in a tube furnace?



















