In short, the key certifications associated with three-zone split tube furnaces are ISO 9001, CE, and GMP. These marks are not just formalities; they are critical indicators of the furnace's quality, safety, and suitability for specific high-stakes applications, from academic research to industrial manufacturing.
While the certifications provide a baseline of trust, understanding what each one guarantees is essential. The choice of furnace ultimately depends on matching its certified capabilities—from quality management (ISO) and safety compliance (CE) to production standards (GMP)—with the precise demands of your work.

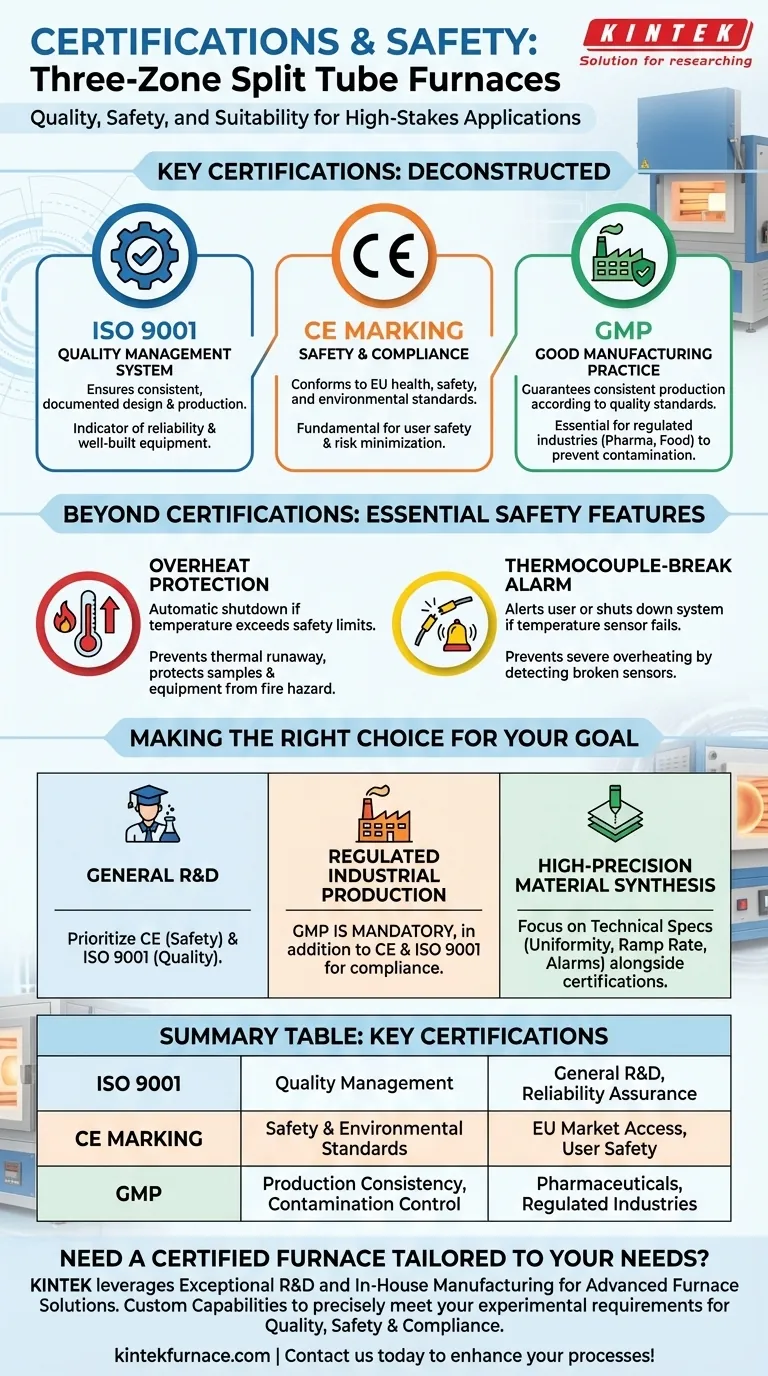
Deconstructing the Key Certifications
Certifications on technical equipment like a three-zone furnace serve as a third-party assurance of quality, safety, and adherence to specific industry standards. They tell you about the manufacturer's processes and the product's compliance with established regulations.
ISO 9001: The Standard for Quality Management
ISO 9001 is an international standard that specifies requirements for a quality management system (QMS).
When a furnace manufacturer is ISO 9001 certified, it means their design, production, and service processes are documented, controlled, and consistently reviewed. For you, this translates to a higher likelihood of receiving a reliable and well-built piece of equipment that performs as specified.
CE Marking: A Declaration of Safety and Compliance
The CE mark indicates that the furnace conforms with health, safety, and environmental protection standards for products sold within the European Economic Area (EEA).
This is a fundamental safety certification. It signifies that the equipment has been assessed and meets crucial EU safety directives, covering aspects like electrical safety and electromagnetic compatibility. This is a baseline requirement for ensuring user safety and minimizing operational risk.
GMP: Ensuring Suitability for Sensitive Industries
Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) is a system for ensuring that products are consistently produced and controlled according to quality standards appropriate for their intended use.
This certification is particularly vital for industries like pharmaceuticals, medical devices, and food processing. A GMP-certified furnace is designed and built to prevent contamination and ensure process repeatability, which is non-negotiable in regulated production environments.
Beyond Certifications: Essential Safety Features
While certifications provide a framework, the furnace's built-in safety mechanisms are what protect your samples, your equipment, and your personnel on a daily basis. These features are direct evidence of a manufacturer's commitment to safety.
Overheat Protection
An overheat protection system automatically shuts down the furnace if the temperature exceeds a preset safety limit. This is a critical feature that prevents thermal runaway, which could destroy the sample, damage the heating elements, and create a significant fire hazard.
Thermocouple-Break Alarms
The thermocouple is the sensor that measures temperature. A thermocouple-break alarm alerts the user or shuts down the system if this sensor fails.
Without this feature, a broken thermocouple would report a low temperature, causing the controller to apply maximum power indefinitely. This creates a severe overheating risk, making the alarm an essential failsafe for precise and safe operation.
Understanding the Context and Nuances
Not all certifications are equally important for every application. Understanding this context prevents you from overspending on unnecessary features or, more critically, from acquiring a furnace that fails to meet your compliance needs.
Not All Certifications Are Required for All Users
A university research lab conducting materials science experiments may only require a furnace with a CE mark for safety and ISO 9001 for quality assurance.
However, a pharmaceutical company developing a new drug must use a GMP-certified furnace to comply with regulatory agency requirements (like the FDA). The absence of GMP certification would invalidate their process.
The Importance of Application-Specific Needs
Certifications are a starting point. The primary function of a three-zone furnace is to provide a precise and uniform temperature profile.
Therefore, you must also evaluate its technical specifications, such as temperature uniformity across the zones, maximum operating temperature, and compatibility with the specific process atmospheres (e.g., inert gas, vacuum) your application requires.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Use the certification requirements of your specific field to guide your selection process.
- If your primary focus is general research and development: Prioritize the CE mark for fundamental safety and ISO 9001 as an indicator of manufacturing quality and reliability.
- If your primary focus is industrial production in a regulated field: GMP certification is absolutely mandatory, in addition to CE and ISO 9001, to ensure compliance.
- If your primary focus is high-precision material synthesis: Look beyond certifications to the technical data sheets, focusing on proven temperature uniformity, ramp rate control, and the reliability of the alarm systems.
Ultimately, selecting the right furnace is about aligning the equipment's certified capabilities with the specific technical and regulatory demands of your work.
Summary Table:
| Certification | Key Focus | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| ISO 9001 | Quality management system | General R&D, reliability assurance |
| CE Marking | Safety and environmental standards | EU market access, user safety |
| GMP | Production consistency and contamination control | Pharmaceuticals, medical devices, regulated industries |
Need a certified three-zone split tube furnace tailored to your lab's unique needs? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With strong deep customization capabilities, we precisely meet your experimental requirements for quality, safety, and compliance. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your processes and ensure regulatory adherence!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of integrating multiple heating zones in a tube furnace? Unlock Precise Thermal Control
- What advantages do multi zone tube furnaces offer for chemical reaction studies? Achieve Precise Thermal Control
- How are multi zone tube furnaces used in ceramics, metallurgy and glass research? Unlock Precise Thermal Control for Advanced Materials
- How does a multi-zone tube furnace achieve precise temperature gradient control? Master MoS2 Isotope Monolayer Synthesis
- How are multi zone tube furnaces applied in biomedical research? Unlock Advanced Biomaterial Engineering



















