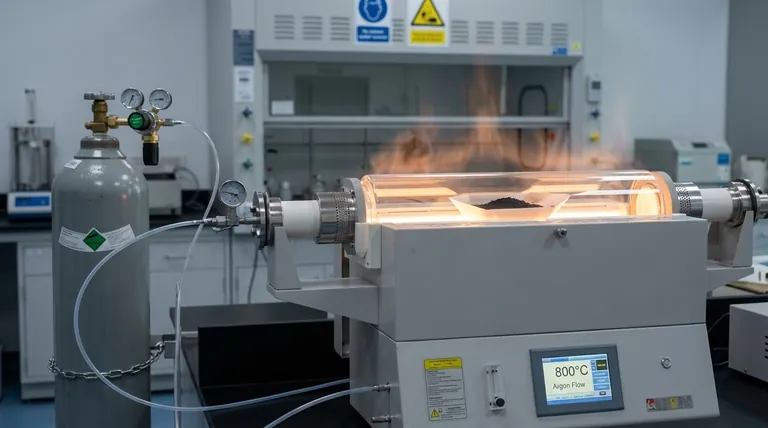
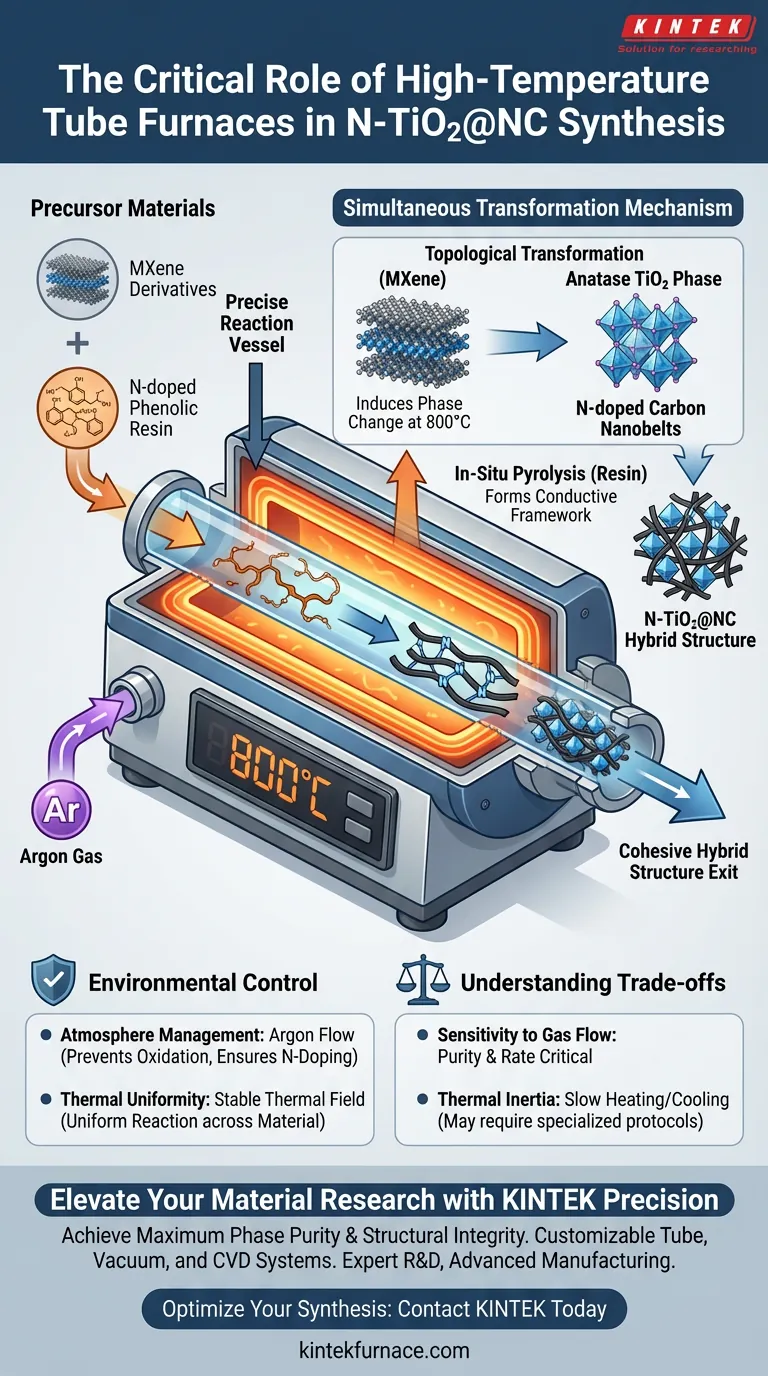
The high-temperature tube furnace serves as the precise reaction vessel required to successfully phase-engineer MXene derivatives into N-TiO2@NC. It functions by maintaining a controlled 800°C environment under a flow of argon gas, which allows for the simultaneous topological transformation of MXene and the in-situ pyrolysis of nitrogen-doped phenolic resin.
Core Takeaway The tube furnace is not merely a heating source; it provides the stable thermal field and atmosphere control necessary to synchronize two distinct chemical processes. This simultaneous reaction is essential for creating a cohesive hybrid structure where active anatase TiO2 coexists with nitrogen-doped carbon nanobelts.

The Mechanism of Transformation
Inducing Topological Changes
The primary role of the furnace is to supply the thermal energy required to alter the physical structure of the starting material. At 800°C, the furnace induces a topological transformation in the MXene derivatives.
This high thermal energy rearranges the atomic structure, converting the precursor material into the desired anatase TiO2 phase. This phase is critical for the material's final electrochemical or catalytic properties.
Facilitating In-Situ Pyrolysis
Simultaneous with the MXene transformation, the furnace drives the pyrolysis of the nitrogen-doped phenolic resin. This process breaks down the organic resin components.
The result is the formation of nitrogen-doped carbon nanobelts. These nanobelts serve as a conductive framework that supports the TiO2, creating the composite "N-TiO2@NC" structure.
The Role of Environmental Control
Atmosphere Management
A critical function of the tube furnace is its ability to maintain a strictly controlled atmosphere. For this synthesis, a continuous flow of argon gas is used.
This inert atmosphere prevents unwanted oxidation or side reactions that would occur in air. It ensures that the nitrogen doping occurs correctly within the carbon structure rather than reacting with environmental oxygen.
Ensuring Thermal Uniformity
Tube furnaces are designed to deliver consistent heat distribution along the length of the tube. This reduces temperature gradients that could lead to uneven reaction rates.
By providing a stable thermal field, the furnace ensures that the conversion of MXene and the carbonization of the resin happen uniformly throughout the sample.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Sensitivity to Gas Flow
While the tube furnace offers excellent atmosphere control, the quality of the final product is highly dependent on the purity and flow rate of the argon. Even minor leaks or fluctuations in gas pressure can introduce oxygen, compromising the nitrogen doping and the purity of the TiO2 phase.
Thermal Inertia
Tube furnaces are excellent for maintaining steady high temperatures, but they can have significant thermal inertia. This means they heat up and cool down relatively slowly compared to other heating methods.
If the reaction requires rapid quenching to freeze a specific crystal structure, a standard tube furnace may require specialized cooling protocols to prevent unwanted phase changes during the cool-down period.
Optimizing the Synthesis Process
To ensure the successful conversion of MXene derivatives into N-TiO2@NC, consider the following based on your specific objectives:
- If your primary focus is Phase Purity: Ensure your tube furnace is calibrated to hold exactly 800°C, as deviations can lead to incomplete topological transformation or the formation of unwanted rutile TiO2.
- If your primary focus is Carbon Structure: Prioritize the stability of the argon flow rate, as the quality of the nitrogen-doped carbon nanobelts relies heavily on an undisturbed inert atmosphere during pyrolysis.
The success of this synthesis relies on treating the tube furnace as a precision instrument for atmosphere and temperature control, rather than a simple heating device.
Summary Table:
| Key Parameter | Role in Synthesis | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature (800°C) | Induces topological transformation | Converts precursors to Anatase TiO2 phase |
| Inert Atmosphere (Argon) | Prevents oxidation and side reactions | Ensures successful nitrogen doping in carbon |
| Thermal Uniformity | Provides stable thermal field | Ensures uniform reaction across the material |
| In-situ Pyrolysis | Breaks down organic resin components | Forms conductive nitrogen-doped carbon nanobelts |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK Precision
Achieving the perfect N-TiO2@NC structure requires more than just heat; it demands the absolute thermal stability and atmospheric purity that only a high-performance system can provide. KINTEK empowers researchers and manufacturers with industry-leading laboratory high-temperature furnaces, including specialized Tube, Vacuum, and CVD systems.
Backed by expert R&D and advanced manufacturing, our furnaces are fully customizable to meet your unique synthesis protocols—ensuring your MXene derivatives transform with maximum phase purity and structural integrity.
Ready to optimize your synthesis? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your custom furnace needs.
Visual Guide
References
- Hui Zhang, ZhengMing Sun. Phase Engineering of <scp>MXene</scp> Derivatives Via Molecular Design for High‐Rate Sodium‐Ion Batteries. DOI: 10.1002/eem2.12692
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
People Also Ask
- What are some common applications of vertical tube furnaces? Unlock Precision in High-Temp Processes
- How do vertical tube furnaces contribute to advancements in material science and industrial production? Unlock Precision in Material Innovation
- What reaction conditions does a vacuum/atmosphere tube furnace provide for Ti2AlN? Achieve Precise Synthesis Control
- Why do vacuum tube furnaces require strict pressure control for Borophene synthesis? Master Single-Phase Integrity
- What is the function of a Tube Furnace in the thermal oxidation of Ti6Al4V alloy? Enhance Hardness & Wear Resistance
- What are the physical characteristics of a graphite furnace used in atomic absorbance measurements? Uncover Its Design for Ultra-Trace Analysis
- What role does a high-temperature quartz tube furnace play in CMSM production? Master Carbonization Precision
- What is the role of a Tube Furnace in TMDC-ND preparation? Master Graphene-Decorated Nanostructure Synthesis



















