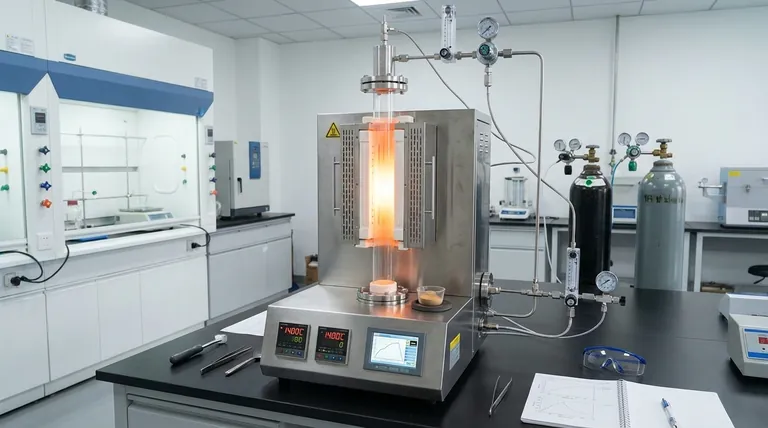
In practice, vertical tube furnaces are used for a vast range of high-temperature processes where precision is paramount. Their applications span from advanced materials research, like creating graphene and testing aerospace components, to foundational industrial processes such as heat-treating metals, synthesizing chemicals, and calibrating high-temperature sensors. They are the tool of choice when a process requires exceptional temperature uniformity and tightly controlled atmospheric conditions.
The core value of a vertical tube furnace isn't just its ability to get hot, but its capacity to create a highly uniform and controlled thermal environment. This precision is what enables its use in sensitive scientific research and high-stakes industrial manufacturing.

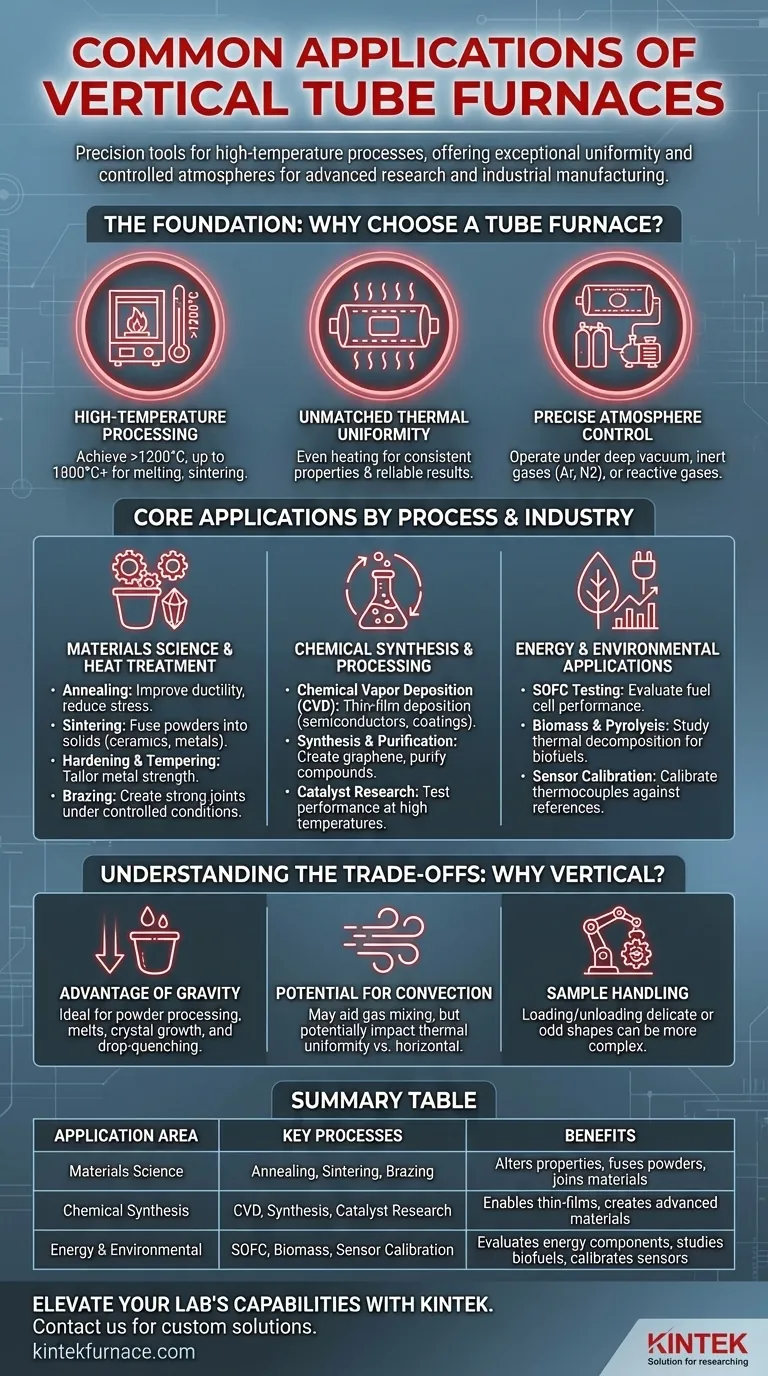
The Foundation: Why Choose a Tube Furnace?
At their core, all tube furnaces are designed to solve a fundamental challenge: applying heat evenly and controllably to a sample. The cylindrical design is inherently better at this than a simple box furnace.
High-Temperature Processing
Tube furnaces are engineered to achieve very high temperatures, often exceeding 1200°C and sometimes reaching up to 1800°C or higher with specialized heating elements. This capability is essential for processes like melting metals, sintering ceramics, and certain types of chemical synthesis.
Unmatched Thermal Uniformity
The tubular heating chamber ensures that the sample is heated evenly from all sides. This thermal uniformity is critical for consistent material properties, preventing defects, and achieving reliable results in scientific experiments.
Precise Atmosphere Control
Tube furnaces are easily sealed, allowing for precise atmosphere control. They can operate under a deep vacuum to remove contaminants or be filled with inert gases (like argon or nitrogen) to prevent oxidation. They can also use reactive gases for processes like chemical vapor deposition.
Core Applications by Process and Industry
The combination of heat, uniformity, and atmosphere control makes vertical tube furnaces indispensable across numerous fields. They are typically chosen over horizontal models when gravity can assist the process, such as when dealing with powders, melts, or specific crystal growth methods.
Materials Science & Heat Treatment
This is the most common application area. The goal is to alter the physical or chemical properties of a material using heat.
- Annealing: Softening materials like metals and glass to improve ductility and reduce internal stresses.
- Sintering: Fusing powders together to form a solid mass, used for creating ceramics, metal parts, and composites.
- Hardening & Tempering: Tailoring the strength and toughness of metals for specific applications.
- Brazing: Joining materials, often under vacuum or inert gas to create strong, clean joints for aerospace or medical components.
Chemical Synthesis & Processing
These furnaces act as high-temperature reactors for creating new materials or purifying existing ones.
- Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD): A foundational process in semiconductor and coating industries, where gases react on a heated substrate to form a thin solid film.
- Synthesis & Purification: Creating advanced materials like graphene or polymer composites, and purifying organic or inorganic compounds through processes like sublimation.
- Catalyst Research: Testing the performance and longevity of catalysts at high temperatures in a controlled gas environment.
Energy & Environmental Applications
The precision of tube furnaces is vital for developing and testing next-generation energy and environmental technologies.
- Solid Oxide Fuel Cell (SOFC) Testing: Evaluating the performance and durability of fuel cell components under realistic operating temperatures.
- Biomass & Pyrolysis: Studying the thermal decomposition of organic materials to produce biofuels and other valuable chemicals.
- Sensor Calibration: Calibrating thermocouples and other temperature sensors against a known, stable temperature reference.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly versatile, a vertical tube furnace is not always the default choice. The decision between a vertical and horizontal orientation involves practical trade-offs.
The Advantage of Gravity
The primary reason to choose a vertical furnace is to leverage gravity. This is ideal for processes like crystal growth (e.g., Bridgman method), processing powders that need to remain settled, or melting materials where a crucible is used. Drop-quenching, where a sample is quickly dropped from the hot zone into a liquid, is also only possible with a vertical setup.
Potential for Convection
Natural convection currents can be more pronounced in a vertical tube. This can be beneficial for mixing gases within the chamber but may slightly impact thermal uniformity compared to a horizontal furnace where air is more stratified and stable.
Sample Handling and Observation
Loading and unloading a vertical furnace, especially with delicate or oddly shaped samples, can be more complex than simply sliding a sample boat into a horizontal tube. In-situ observation can also be more challenging.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your specific goal determines whether a vertical tube furnace is the optimal tool.
- If your primary focus is material synthesis from powders or melts: The vertical orientation is superior for ensuring sample integrity and leveraging gravity for crucible-based processes.
- If your primary focus is thin-film deposition via CVD: The vertical orientation can provide excellent gas flow dynamics for uniform coating over a sample.
- If your primary focus is heat treatment of many small, solid parts: A vertical furnace can be ideal for batch processing by loading parts in a basket or crucible.
- If your primary focus is drop-quenching or crystal growth: A vertical furnace is the only practical choice for these gravity-dependent methods.
Ultimately, selecting a vertical tube furnace is a decision to prioritize precise control over your thermal processing environment.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Processes | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Materials Science & Heat Treatment | Annealing, Sintering, Hardening, Brazing | Alters material properties, improves ductility, fuses powders, joins materials under controlled atmospheres |
| Chemical Synthesis & Processing | CVD, Synthesis & Purification, Catalyst Research | Enables thin-film deposition, creates advanced materials like graphene, tests catalyst performance |
| Energy & Environmental Applications | SOFC Testing, Biomass & Pyrolysis, Sensor Calibration | Evaluates fuel cell components, studies biofuel production, calibrates temperature sensors |
Ready to elevate your lab's capabilities with a custom vertical tube furnace? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities. Whether you're in materials science, chemical synthesis, or energy research, we can help you achieve precise temperature control and uniformity. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your high-temperature processes and drive your innovations forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision



















