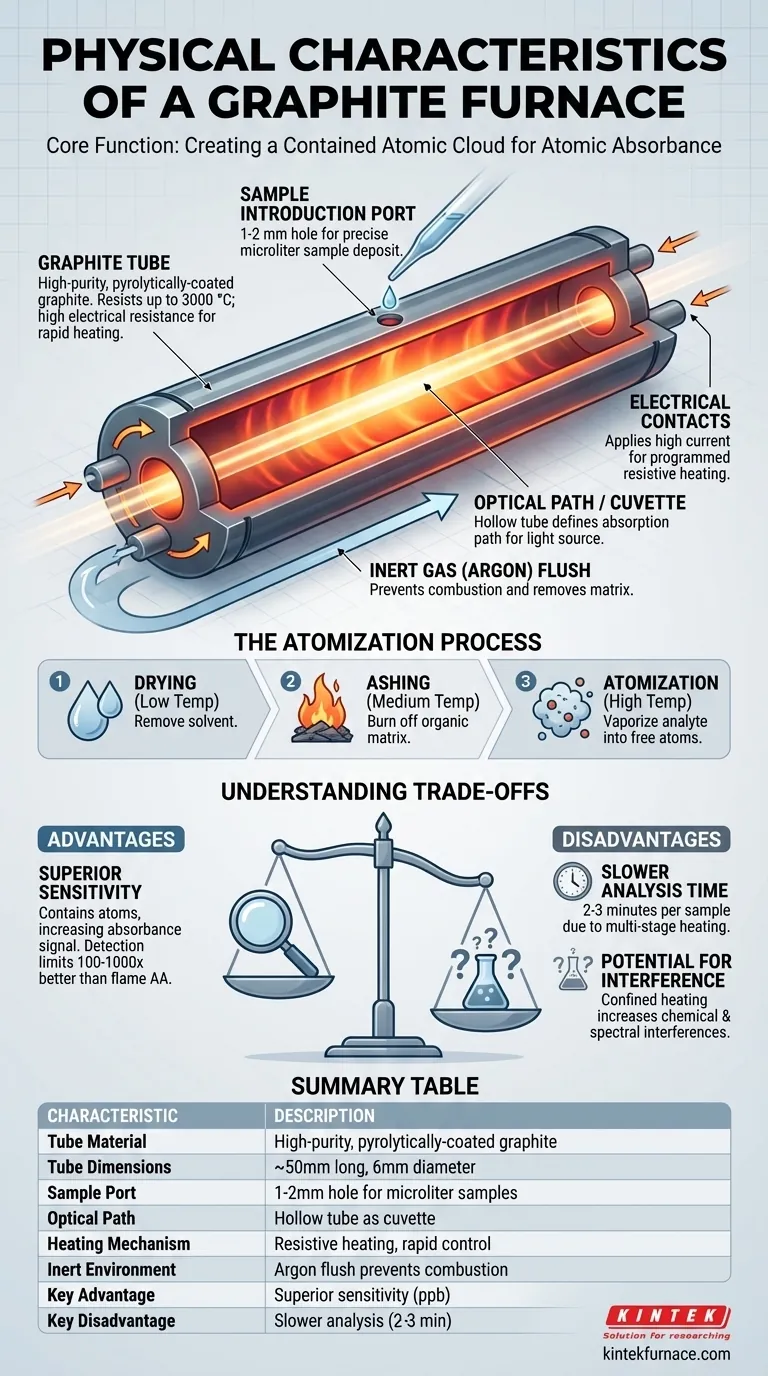
At its core, a graphite furnace is a small, hollow graphite tube. It is typically about 50 mm (2 inches) long and 6 mm (0.25 inches) in diameter, featuring a small hole in the center of the top wall for sample introduction. This furnace is placed in the light path of an atomic absorption (AA) spectrophotometer, allowing radiation to pass directly through its length.
The graphite furnace's simple physical design—a small, resistive-heated tube—is deceptive. It is a highly engineered micro-furnace designed to contain and concentrate a sample, creating a dense atomic vapor for achieving maximum analytical sensitivity.

The Core Function: Creating a Contained Atomic Cloud
The entire purpose of the furnace is to take a tiny liquid sample and efficiently convert it into a cloud of free, ground-state atoms that can absorb light. Its physical characteristics are all in service of this goal.
The Graphite Tube
The main body is a tube made of high-purity, pyrolytically-coated graphite. This material is chosen for its ability to withstand extreme temperatures (up to 3000 °C) and its high electrical resistance, which allows it to heat up rapidly when a current is applied.
The Sample Introduction Port
A small hole, typically 1-2 mm in diameter, is drilled into the top of the tube. This allows the tip of an autosampler pipette to enter and deposit a precise, microliter-sized volume of sample onto the tube's internal surface.
The Optical Path
The hollow, cylindrical shape of the tube is critical. It serves as the cuvette or absorption cell. Light from the instrument's source lamp is directed through the tube from end to end, creating a defined path length for the measurement.
How the Design Enables Atomization
The furnace's physical structure enables a precisely controlled, multi-stage heating process that is impossible to achieve with other methods like flame AA.
Electrical Contacts
The furnace is held between two electrical contacts. When the instrument applies a high current, the tube's natural resistance causes it to heat almost instantly. This allows for a programmed sequence of temperature steps.
The Temperature Program
The sample is not atomized instantly. First, it is gently dried to remove the solvent. Then, it is ashed (or pyrolyzed) at a higher temperature to burn off organic matrix components. Finally, the temperature is rapidly increased to the atomization step, where the analyte of interest is vaporized into a dense cloud of free atoms.
An Inert Environment
During operation, the furnace is constantly flushed with an inert gas, typically argon. This serves two key purposes: it prevents the hot graphite tube from combusting in the presence of air, and it helps to sweep away the smoke and vaporized matrix during the ashing step.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The furnace design provides incredible benefits but also introduces specific limitations compared to other atomic absorption techniques.
Advantage: Superior Sensitivity
The key advantage of the furnace is its ability to contain atoms. In flame AA, atoms rush through the flame and disperse quickly. In a graphite furnace, the atomic vapor is confined within the small tube for a second or more, dramatically increasing the absorbance signal and providing detection limits 100 to 1000 times better than flame AA.
Disadvantage: Slower Analysis Time
Each measurement requires a full temperature program—drying, ashing, atomization, and cooling—which can take 2-3 minutes per sample. This is significantly slower than the near-instantaneous readings from flame AA.
Disadvantage: Potential for Interference
Because the entire sample matrix is heated in a confined space, the potential for chemical and spectral interferences is higher than in a flame. Careful method development is required to mitigate these effects.
The Significance of the Design
The physical characteristics of the graphite furnace are directly linked to its analytical purpose and performance.
- If your primary focus is ultra-trace analysis: The furnace's small, enclosed design is its greatest strength, concentrating atoms to achieve parts-per-billion (ppb) or lower detection limits.
- If your primary focus is understanding the measurement: The hollow tube defines the optical path for absorption, while the material properties of graphite enable the rapid, controlled heating central to the entire process.
Ultimately, the graphite furnace is a miniature, high-temperature environment engineered for one purpose: to maximize the interaction between light and the atoms of interest.
Summary Table:
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Tube Material | High-purity, pyrolytically-coated graphite for high temperatures and electrical resistance |
| Tube Dimensions | Approximately 50 mm long, 6 mm diameter |
| Sample Port | 1-2 mm hole for precise microliter sample introduction |
| Optical Path | Hollow tube serving as cuvette for light absorption |
| Heating Mechanism | Resistive heating via electrical contacts for rapid temperature control |
| Inert Environment | Argon gas flush to prevent combustion and remove matrix |
| Key Advantage | Superior sensitivity with detection limits 100-1000x better than flame AA |
| Key Disadvantage | Slower analysis time (2-3 minutes per sample) |
Need a high-temperature furnace tailored to your lab's unique requirements? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise fit for your experimental needs, enhancing sensitivity and efficiency in applications like atomic absorption. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can elevate your analytical processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision



















