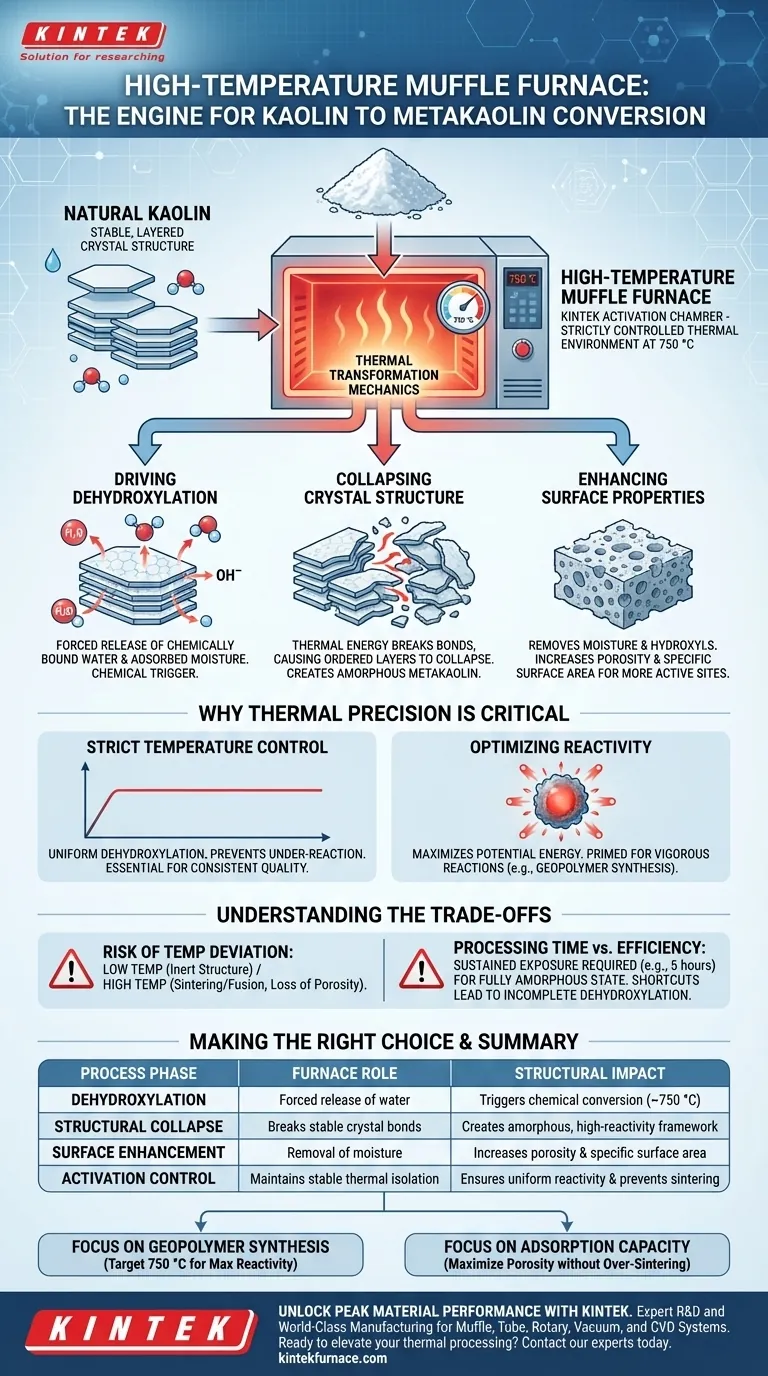
A high-temperature muffle furnace functions as the critical activation chamber in the pretreatment of natural kaolin. By maintaining a strictly controlled thermal environment, typically at 750 °C, it facilitates the dehydroxylation reaction required to strip away the material's crystalline stability and convert it into reactive metakaolin.
The furnace does not simply dry the material; it fundamentally alters its atomic structure. By effectively destroying the layered crystal lattice of natural kaolin, the furnace creates an amorphous, highly unstable framework that serves as the necessary foundation for subsequent chemical synthesis, such as geopolymer production.

The Mechanics of Thermal Transformation
Driving Dehydroxylation
The primary function of the muffle furnace is to force the release of chemically bound water.
Inside the furnace, the intense heat targets hydroxyl groups and adsorbed water within the kaolin structure. This process, known as dehydroxylation, is the chemical trigger that initiates the material's conversion.
Collapsing the Crystal Structure
Natural kaolin possesses a stable, layered crystal structure that makes it chemically inert.
The thermal energy provided by the furnace breaks these bonds, causing the ordered layers to collapse. This results in the formation of amorphous metakaolin, a disordered state that is essential for high chemical reactivity.
Enhancing Surface Properties
Beyond structural collapse, the calcination process significantly alters the physical landscape of the material.
By removing internal moisture and hydroxyls, the furnace increases the mineral's porosity and specific surface area. This creates more active sites, which is vital whether the end goal is chemical synthesis or enhancing adsorption capacity for applications like drug delivery.
Why Thermal Precision is Critical
Strict Temperature Control
The muffle furnace provides a stable isolation chamber, ensuring the material is exposed to a consistent temperature (e.g., 750 °C) without fluctuation.
This consistency is non-negotiable. Without a strictly controlled thermal environment, the dehydroxylation process becomes uneven, leaving parts of the kaolin under-reacted and chemically weak.
Optimizing Reactivity
The ultimate goal of using this specific equipment is to maximize the material's potential energy.
The resulting metakaolin is chemically "hungry." Because the furnace has stripped away its stable structure, the material is primed to react vigorously in subsequent processes, such as serving as the active foundation for geopolymer synthesis.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Risk of Temperature Deviation
While high heat is necessary, precision is more important than raw power.
If the furnace temperature is too low, the layered crystal structure will not fully break down, leaving the material inert. Conversely, if the temperature spikes too high beyond the optimal range, the material may sinter (fuse together), causing a loss of porosity and a drastic drop in reactivity.
Processing Time vs. Efficiency
Achieving a fully amorphous state requires sustained exposure.
As noted in industrial contexts, this process may require continuous heating for several hours (e.g., 5 hours). Cutting this time short to save energy often results in incomplete dehydroxylation, rendering the pretreatment ineffective for advanced applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To utilize a muffle furnace effectively for kaolin conversion, align your process parameters with your specific end-use requirements:
- If your primary focus is Geopolymer Synthesis: Target higher temperatures (around 750 °C) to ensure the complete destruction of the crystal lattice for maximum chemical reactivity.
- If your primary focus is Adsorption Capacity: Ensure the process maximizes porosity and specific surface area by fully removing adsorbed water and hydroxyl groups without over-sintering the material.
Mastering the thermal pretreatment process transforms abundant natural clay into a high-performance industrial feedstock.
Summary Table:
| Process Phase | Furnace Role | Structural Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Dehydroxylation | Forced release of chemically bound water | Triggers chemical conversion at ~750 °C |
| Structural Collapse | Breaks stable crystal bonds | Creates amorphous, high-reactivity framework |
| Surface Enhancement | Removal of moisture and hydroxyls | Increases porosity and specific surface area |
| Activation Control | Maintains stable thermal isolation | Ensures uniform reactivity & prevents sintering |
Unlock Peak Material Performance with KINTEK
Precise thermal control is the difference between inert clay and high-performance metakaolin. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK provides industry-leading Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems tailored to your laboratory's most demanding high-temperature requirements.
Whether you are optimizing geopolymer synthesis or refining material porosity, our customizable furnaces ensure the structural precision your research deserves.
Ready to elevate your thermal processing? Contact our experts today to find the perfect furnace solution for your unique needs.
Visual Guide
References
- Mukesh Kumar, Sudhanshu Sharma. Natural kaolin-derived ruthenium-supported nanoporous geopolymer: a sustainable catalyst for CO <sub>2</sub> methanation. DOI: 10.1039/d5cy00021a
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of bottom load furnaces? Unlock Superior Thermal Uniformity and Control
- What is the primary function of a high-temperature furnace for nanocolloid study? Expert Thermal Performance Insights
- How are muffle furnaces utilized in high-temperature sintering within the pharmaceutical industry? Unlock Precision in Drug Delivery and Implants
- How is the chamber temperature displayed in the muffle furnace? Get Accurate Readings for Your Lab
- Why is a box muffle furnace required for In2O3 nanofibers? Expert Synthesis & Pre-Oxidation Guide
- Why is an industrial muffle furnace required for Zirconia supports? Engineering High-Performance Catalyst Platforms
- How are muffle furnaces manufactured? Discover Precision Engineering for Your Lab
- What are the key operational features of modern muffle furnaces? Enhance Precision and Efficiency in Your Lab



















