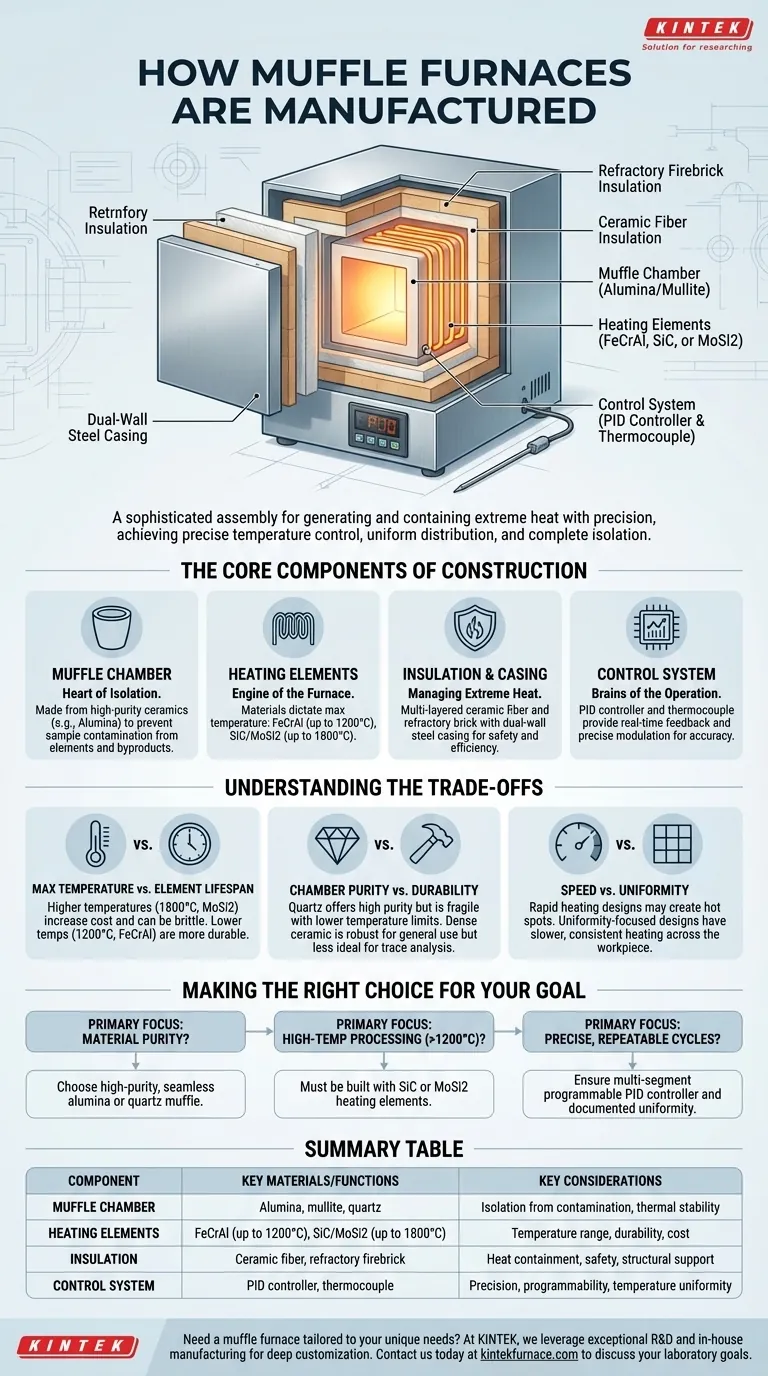
At its core, a muffle furnace is manufactured by constructing a highly insulated box, installing specialized heating elements around a central isolated chamber (the "muffle"), and integrating a sophisticated digital control system. The process is less about mass production and more about the careful assembly and integration of high-performance components designed to generate and contain extreme heat with precision.
The quality of a muffle furnace is not determined by a single manufacturing technique, but by the strategic selection of its core components. The entire process is engineered to achieve three critical goals: precise temperature control, uniform heat distribution, and complete isolation of the sample from contamination.

The Core Components of Construction
Manufacturing a muffle furnace is a process of assembling distinct, high-performance systems. Each component is chosen and integrated to solve a specific thermal or atmospheric challenge.
The Muffle Chamber: The Heart of Isolation
The term "muffle" refers to the inner chamber that isolates the material being processed from the heating elements and their byproducts. This is the key to preventing contamination.
This chamber is typically made from high-purity, heat-resistant ceramics like alumina or mullite. These materials are chosen for their excellent thermal stability and chemical inertness, ensuring they do not react with the sample even at high temperatures.
Heating Elements: The Engine of the Furnace
The heat itself is generated by robust electrical heating elements. The choice of element material is a critical manufacturing decision that dictates the furnace's maximum temperature.
For temperatures up to around 1200°C, manufacturers use alloys like iron-chromium-aluminum (FeCrAl). For higher temperatures (up to 1800°C), more advanced materials like silicon carbide (SiC) or molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) are required. These elements are strategically placed around the exterior of the muffle to provide uniform, radiant heat.
Insulation and Casing: Managing Extreme Heat
Containing temperatures that can exceed 1500°C requires a multi-layered insulation strategy. The first layer is typically lightweight ceramic fiber, which provides excellent thermal resistance.
This is often backed by layers of hard refractory firebrick for structural support and additional insulation. The entire assembly is housed within a sturdy, dual-wall steel casing that allows for air circulation to keep the exterior surface safe to the touch.
Control System: The Brains of the Operation
A modern muffle furnace is defined by its precision. This is achieved by integrating a thermocouple with a digital PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) controller.
The thermocouple, a temperature sensor placed inside the chamber, provides real-time feedback. The PID controller then precisely modulates the power sent to the heating elements to follow a pre-programmed heating, soaking, and cooling profile with exceptional accuracy.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The manufacturing choices directly impact furnace performance and cost. Understanding these trade-offs is key to selecting the right instrument.
Maximum Temperature vs. Element Lifespan
Furnaces capable of reaching 1800°C require expensive MoSi2 elements, which can be brittle and may degrade under certain atmospheric conditions. A standard 1200°C furnace uses far more durable and cost-effective FeCrAl elements. The manufacturing cost rises exponentially with the maximum operating temperature.
Chamber Purity vs. Durability
While a quartz muffle offers the highest purity for sensitive analytical work, it is fragile and has a lower temperature limit. A dense, high-alumina ceramic chamber is more robust and suitable for general-purpose applications like ashing or heat-treating metals, but may not be ideal for trace element analysis.
Speed vs. Uniformity
A design that prioritizes rapid heating may have elements placed very close to the chamber, potentially creating hot spots. A manufacturer focused on uniformity will ensure there is adequate space for heat to radiate and distribute evenly, resulting in slower but more consistent heating across the entire workpiece.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The "best" manufactured furnace is the one built for your specific application. When evaluating an instrument, consider the components it was built with.
- If your primary focus is material purity: Choose a furnace manufactured with a high-purity, seamless alumina or quartz muffle to prevent sample contamination from insulation fibers or element byproducts.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature processing (>1200°C): Your furnace must be built with Silicon Carbide (SiC) or Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) heating elements designed for extreme thermal loads.
- If your primary focus is precise, repeatable cycles: Ensure the furnace is manufactured with a multi-segment programmable PID controller and includes documentation of its temperature uniformity testing.
Understanding these manufacturing principles allows you to select a tool that is not just a furnace, but a precise instrument engineered for your specific application.
Summary Table:
| Component | Key Materials/Functions | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Muffle Chamber | Alumina, mullite, quartz | Isolation from contamination, thermal stability |
| Heating Elements | FeCrAl (up to 1200°C), SiC/MoSi2 (up to 1800°C) | Temperature range, durability, cost |
| Insulation | Ceramic fiber, refractory firebrick | Heat containment, safety, structural support |
| Control System | PID controller, thermocouple | Precision, programmability, temperature uniformity |
Need a muffle furnace tailored to your unique needs? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your experimental requirements, enhancing efficiency and results. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment



















