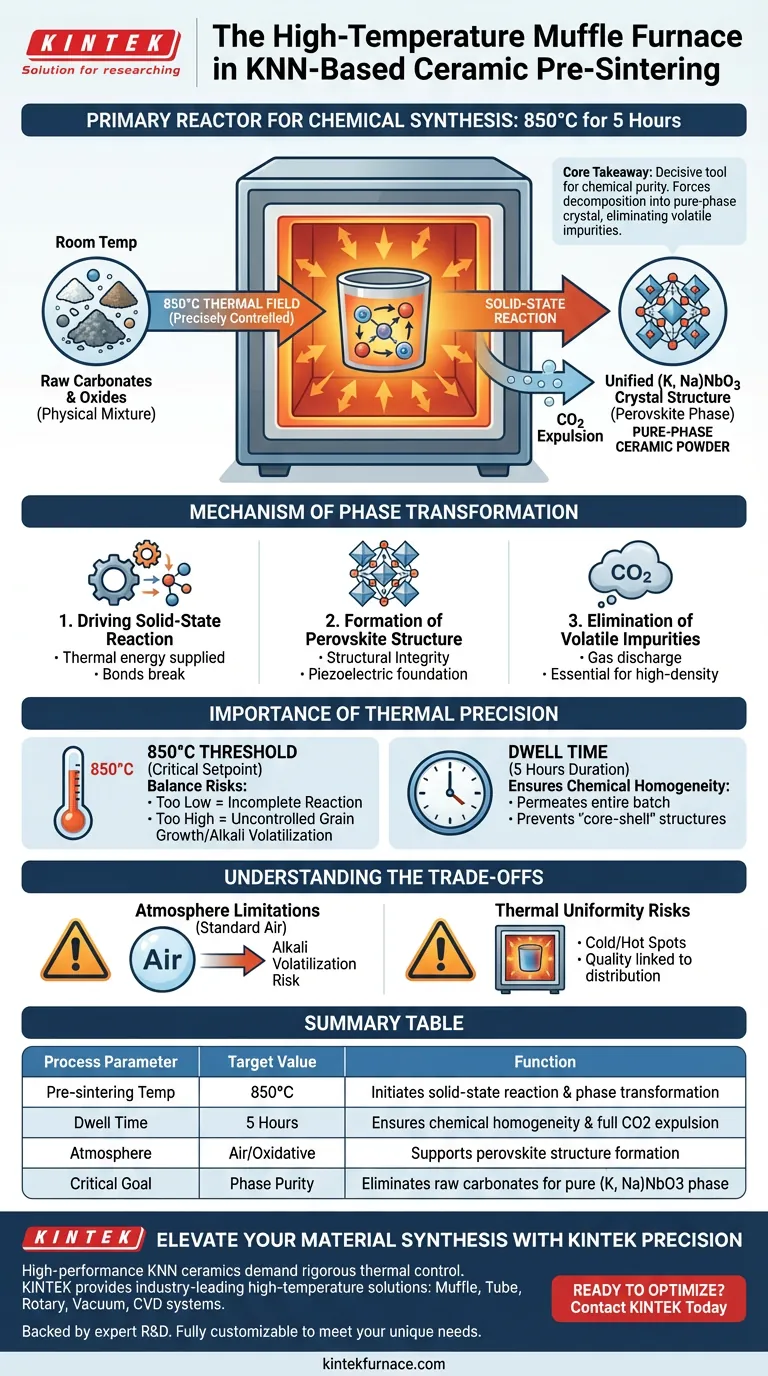
The high-temperature muffle furnace acts as the primary reactor for chemical synthesis during the pre-sintering of KNN-based ceramic powders.
Its function goes beyond simple heating; it provides a precisely controlled thermal field at 850°C, typically maintained for 5 hours. This specific environment drives the critical solid-state reaction between raw carbonates and oxides, ensuring the expulsion of carbon dioxide and the formation of the initial perovskite structure phase.
Core Takeaway The muffle furnace is the decisive tool for ensuring chemical purity before final processing. By maintaining a stable 850°C environment, it forces the complete decomposition of raw ingredients into a pure-phase (K, Na)NbO3 crystal structure, eliminating volatile impurities that would otherwise degrade the final ceramic.
The Mechanism of Phase Transformation
The primary role of the furnace in this stage is to facilitate a chemical change, transforming a mixture of raw ingredients into a unified crystalline compound.
Driving the Solid-State Reaction
The furnace provides the energy required to initiate and sustain a reaction between carbonates and oxides. At room temperature, these materials are merely a physical mixture. The thermal energy supplied by the furnace breaks the chemical bonds of the raw materials, allowing atoms to diffuse and rearrange.
Formation of the Perovskite Structure
The ultimate goal of this thermal treatment is the synthesis of the (K, Na)NbO3 (KNN) crystal phase. The furnace ensures the material achieves a complete perovskite structure. This structural integrity is the foundation for the piezoelectric properties of the final ceramic; without this specific phase formation, subsequent processing steps will fail.
Elimination of Volatile Impurities
During the reaction, the furnace facilitates the discharge of carbon dioxide (CO2). This is a byproduct of decomposing the carbonate raw materials. The muffle furnace ensures this gas is fully expelled, leaving behind a pure-phase ceramic powder free of residual carbon, which is essential for high-density sintering later on.
The Importance of Thermal Precision
Achieving the correct chemical phase requires more than just high heat; it requires stability and duration.
Maintaining the 850°C Threshold
The specific temperature of 850°C is critical for KNN-based powders. If the temperature is too low, the solid-state reaction will remain incomplete, leaving unreacted raw materials. If it is too high, one risks uncontrolled grain growth or volatilization of alkali elements (Potassium and Sodium). The muffle furnace must maintain this exact setpoint to balance these risks.
The Role of Dwell Time
The reference specifies a dwell time of 5 hours. This duration is necessary to ensure the reaction permeates the entire powder batch, not just the surface. The furnace's ability to hold this temperature constantly ensures chemical homogeneity throughout the material, preventing "core-shell" structures where the inside of a particle differs from the outside.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While the high-temperature muffle furnace is essential, it is important to recognize potential pitfalls in the process.
Atmosphere Limitations
Standard muffle furnaces typically operate in an air atmosphere. While this is suitable for the oxidative sintering required for KNN, it lacks the ability to suppress the volatilization of alkali elements (Potassium and Sodium) as effectively as a sealed, atmosphere-controlled environment might.
Thermal Uniformity Risks
The quality of the powder is directly linked to the uniformity of the furnace's "thermal field." If the furnace has cold spots, the powder in those areas may contain unreacted carbonates. Conversely, hot spots can lead to excessive coarsening of the particles. The effectiveness of the process is limited by the furnace's ability to distribute heat evenly.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The way you utilize the muffle furnace determines the quality of your precursor powder.
- If your primary focus is Phase Purity: Ensure your furnace can maintain the 850°C setpoint with less than ±5°C deviation to guarantee the complete elimination of carbonates.
- If your primary focus is Particle Morphology: Strictly control the 5-hour dwell time; exceeding this may cause the initial particles to fuse or grow too large before the final sintering stage.
Success in KNN ceramics begins with the rigorous control of this pre-sintering thermal environment.
Summary Table:
| Process Parameter | Target Value | Function in KNN Synthesis |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-sintering Temp | 850°C | Initiates solid-state reaction & phase transformation |
| Dwell Time | 5 Hours | Ensures chemical homogeneity & full CO2 expulsion |
| Atmosphere | Air/Oxidative | Supports perovskite structure formation |
| Critical Goal | Phase Purity | Eliminates raw carbonates for pure (K, Na)NbO3 phase |
Elevate Your Material Synthesis with KINTEK Precision
High-performance KNN ceramics demand rigorous thermal control. KINTEK provides industry-leading high-temperature solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, specifically engineered to maintain the precise thermal fields required for phase-pure synthesis.
Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, our lab furnaces are fully customizable to meet your unique research or production needs. Ensure chemical purity and structural integrity in every batch.
Ready to optimize your pre-sintering process?
Visual Guide
References
- Michaela Roudnická, Dalibor Vojtěch. Hydrogen Embrittlement of Ti-Al6-V4 Alloy Manufactured by Laser Powder Bed Fusion Induced by Electrochemical Charging. DOI: 10.3390/met14020251
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of a laboratory resistance furnace in Al-Li alloy prep? Achieve Optimal Smelting Quality
- How long does it take for a muffle furnace to reach its maximum temperature? Optimize Your Lab's Heating Process
- How is a muffle furnace applied in the food industry? Essential for Ash and Moisture Analysis
- What maintenance procedures are recommended for muffle furnaces? Ensure Accuracy and Safety in Your Lab
- What electrical precautions should be taken when setting up a muffle furnace? Essential Safety Tips for Your Lab
- What key components are used in vacuum muffle furnaces to ensure precise gas dispersion? Discover the MFC and BPR System
- What are the standard features of box furnaces? Unlock Precision and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- What role does the Muffle Furnace play in the pretreatment of K-Mo catalyst precursors? Key for Thermal Oxidation



















