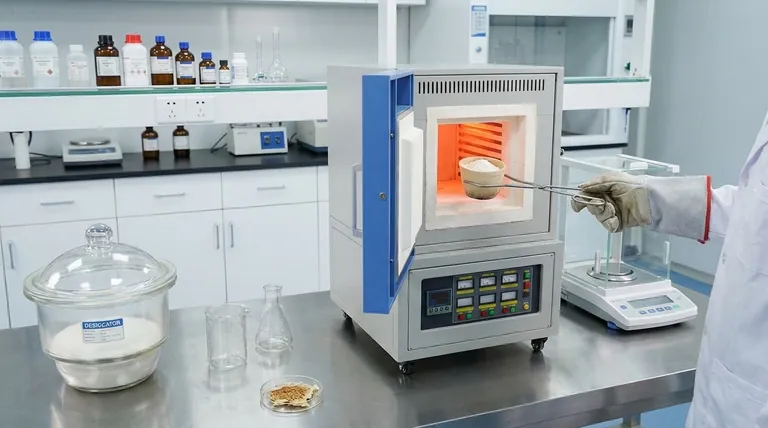
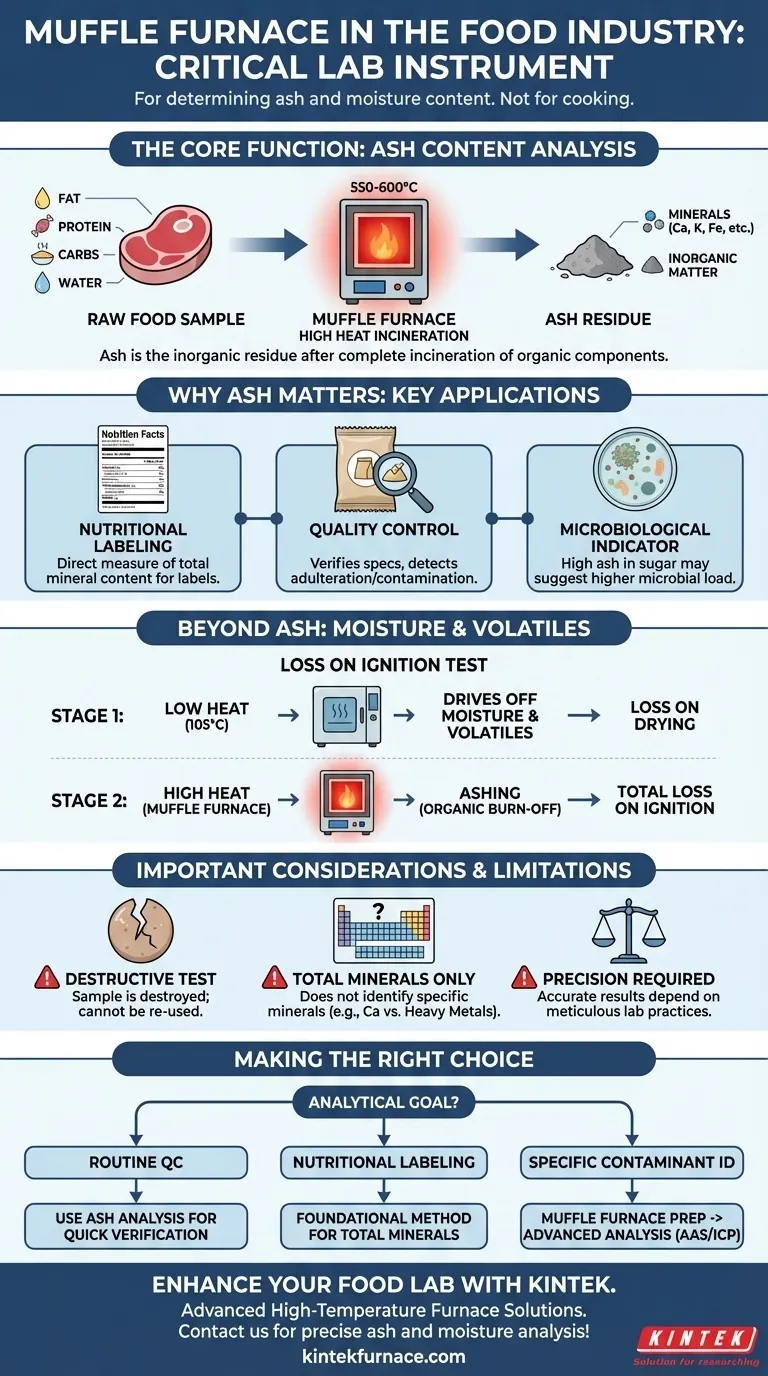
In the food industry, a muffle furnace is a critical laboratory instrument used primarily for determining the ash and moisture content of food products. This process, known as incineration or "ashing," involves heating a sample at extremely high temperatures to burn off all organic matter, leaving behind only the inorganic, non-combustible minerals. This analysis is fundamental for quality control, nutritional labeling, and regulatory compliance.
A muffle furnace is not used to cook or prepare food. Instead, it acts as an analytical tool that destroys a food sample to reveal its fundamental mineral content, providing essential data for ensuring product quality, safety, and nutritional accuracy.

The Core Function: Ash Content Analysis
The primary application of a muffle furnace in the food industry is for gravimetric ash analysis. This is a quantitative method to measure the total amount of minerals in a food product.
What is "Ash"?
In the context of food analysis, ash is the inorganic residue that remains after all the organic components—such as fats, proteins, carbohydrates, and water—have been completely incinerated by high heat.
This residue consists of the minerals present in the food, including essential nutrients like calcium, potassium, and iron, as well as potential trace contaminants.
The Ashing Process Explained
The procedure is straightforward but requires precision. First, a food sample is carefully weighed. It is then placed in the muffle furnace and heated to a very high temperature, typically between 550°C and 600°C, for several hours.
This extreme heat completely combusts the organic material. After incineration, the remaining ash is cooled in a desiccator (to prevent it from reabsorbing moisture from the air) and weighed again. The weight of the ash is then used to calculate the percentage of total mineral content in the original sample.
Why Mineral Content is Critical
Knowing the ash content is essential for several reasons:
- Nutritional Labeling: It serves as a direct measure of a food's total mineral content, a key component of the nutrition facts panel.
- Quality Control: The ash content of ingredients like flour, spices, or dairy powders is often a specification of quality. An abnormal result can indicate adulteration, contamination, or improper processing.
- Microbiological Indicator: In some products, like sugar, high ash content can suggest a higher microbial load.
Beyond Ash: Determining Moisture and Volatiles
While a drying oven is the standard tool for simple moisture analysis, a muffle furnace is used for a related process called determining volatile matter.
The "Loss on Ignition" Test
This test involves two heating stages. First, the sample is heated at a lower temperature (around 105°C) to drive off all water and other volatile compounds. The sample is weighed to determine this "loss on drying."
Next, the same sample is placed in the muffle furnace at high temperature to perform the ashing. The total weight loss from both steps is called the "loss on ignition," providing a complete profile of the sample's moisture, volatile, organic, and inorganic components.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, the muffle furnace provides specific information and has inherent limitations that are important to understand.
It Is a Destructive Test
The process of incineration completely destroys the sample. The analysis can only be performed on a small, representative portion of the product, and that sample cannot be used for any other tests afterward.
It Measures Total, Not Specific, Minerals
Ash analysis tells you the total quantity of inorganic material, but it does not identify the individual minerals. For example, it cannot distinguish between beneficial calcium and potentially harmful heavy metals.
To identify and quantify specific minerals, the ash residue must be dissolved and analyzed further using more advanced techniques like Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (AAS) or Inductively Coupled Plasma (ICP) analysis.
Precision is Non-Negotiable
The accuracy of the results depends entirely on meticulous lab practices. Errors in initial weighing, incomplete combustion, or allowing the cooled ash to reabsorb moisture from the atmosphere can significantly skew the final data.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The application of a muffle furnace depends directly on your analytical objective.
- If your primary focus is routine quality control: Use ash analysis to quickly verify that ingredients and finished products meet their established mineral content specifications.
- If your primary focus is nutritional labeling: Ash analysis is the foundational, industry-standard method for quantifying the total mineral content required for nutrition facts panels.
- If your primary focus is identifying specific mineral contaminants: Use the muffle furnace as the first step to prepare an ash sample, which you will then analyze with more specialized equipment like an AAS or ICP-MS.
Ultimately, the muffle furnace is an indispensable tool that provides the foundational data needed to guarantee the integrity and quality of food products.
Summary Table:
| Application | Purpose | Key Details |
|---|---|---|
| Ash Content Analysis | Measure total minerals | Heats samples at 550-600°C to incinerate organic matter, leaving inorganic residue |
| Moisture/Volatile Determination | Assess water and volatiles | Uses loss on ignition test for complete sample profile |
| Quality Control | Ensure product standards | Detects adulteration, contamination, and verifies ingredient specs |
| Nutritional Labeling | Provide mineral data | Essential for accurate nutrition facts panels |
Enhance your food lab's analytical capabilities with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all with deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Ensure precise ash and moisture analysis for quality control and compliance—contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can benefit your operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment



















