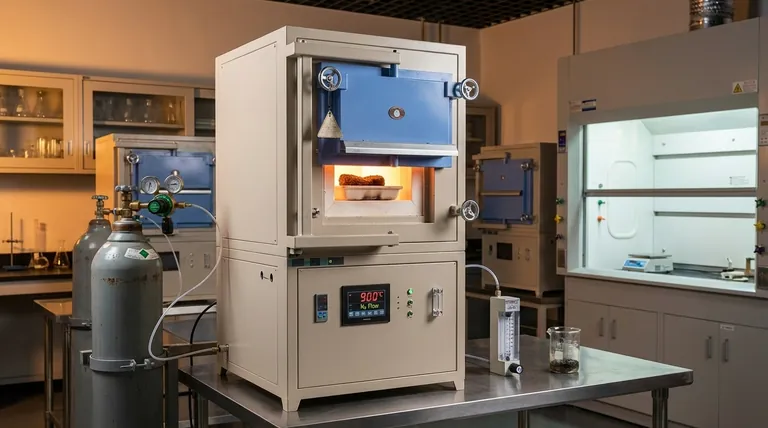
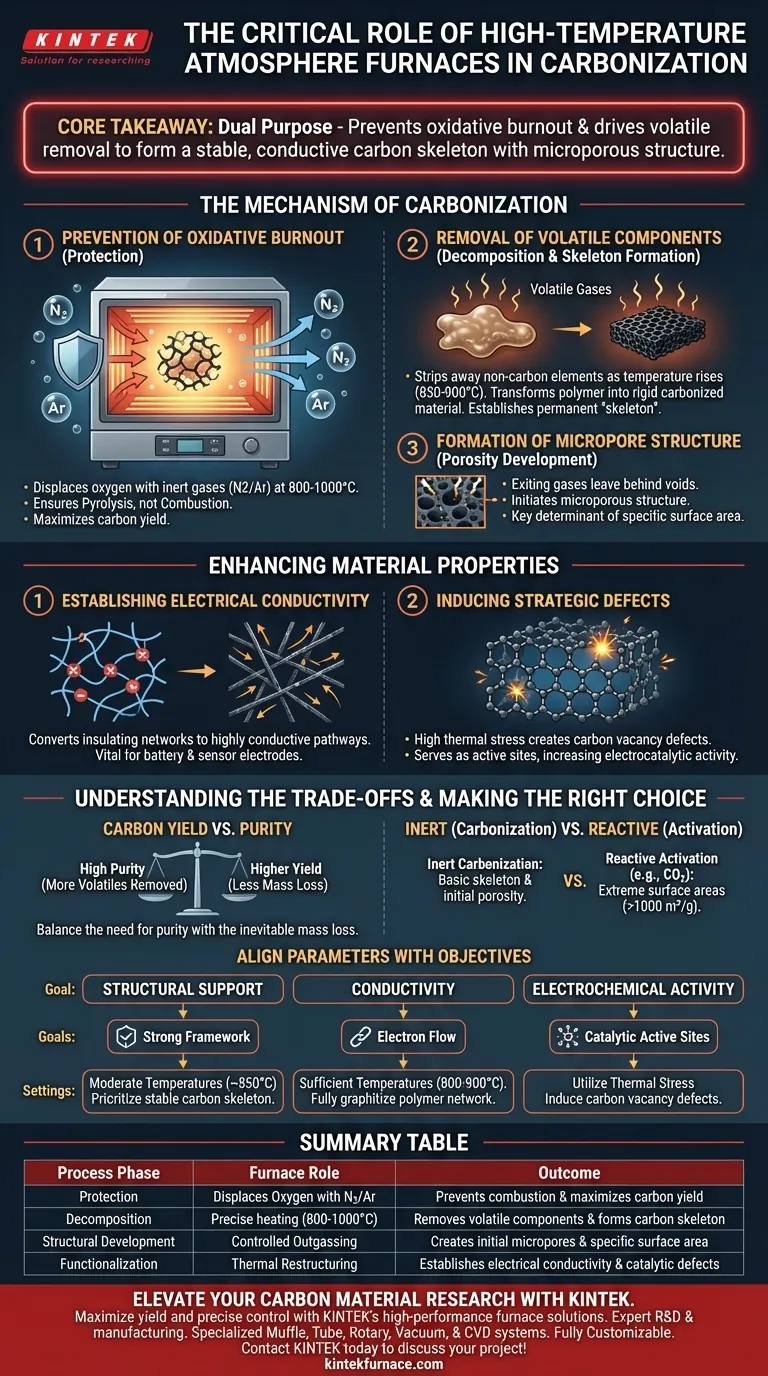
A high-temperature inert atmosphere furnace acts as the critical control vessel for converting organic precursors into functional carbon materials. It creates a strictly oxygen-free environment—typically using nitrogen or argon at temperatures between 800 °C and 1000 °C—to prevent combustion while thermal energy fundamentally restructures the material.
Core Takeaway The furnace serves a dual purpose: it prevents the material from burning away (oxidative burnout) and drives the removal of volatile components. This process transforms organic polymers into a stable, conductive carbon skeleton with the initial microporous structure necessary for advanced applications.

The Mechanism of Carbonization
Prevention of Oxidative Burnout
The primary role of the inert atmosphere is protection. Without this controlled environment, high temperatures would cause organic precursors to react with oxygen and burn (combust), leaving little to no residue.
By displacing oxygen with inert gases like nitrogen or argon, the furnace ensures the material undergoes pyrolysis rather than combustion. This preservation is critical for maintaining a high carbon yield and ensuring the structural integrity of the final product.
Removal of Volatile Components
As the temperature rises (typically to 850–900 °C), the furnace facilitates the thermal decomposition of the precursor material. This process strips away non-carbon elements in the form of volatile gases.
The controlled removal of these components is what transforms a soft polymer into a rigid, carbonized material. This step is essential for establishing the material's permanent "skeleton" or physical framework.
Formation of Micropore Structure
The exiting volatile gases leave behind voids within the material matrix. This initiates the development of a microporous structure, which is a key determinant of the material's specific surface area.
This porosity provides the physical space required for subsequent applications, such as supporting active component loading or facilitating adsorption.
Enhancing Material Properties
Establishing Electrical Conductivity
Thermal treatment in an inert atmosphere fundamentally alters the electronic properties of the material. It converts insulating polymer networks (such as polypyrrole) into highly conductive carbon nanowire networks.
This transformation is vital for applications requiring electron transport, such as electrode materials for batteries or sensors.
Inducing Strategic Defects
Beyond simple carbonization, the high thermal stress within the furnace can induce the formation of critical carbon vacancy defects.
These structural imperfections are not failures; they often serve as active sites that significantly increase electrocatalytic activity. For example, these defects can enhance the performance of electrodes in processes like chlorine evolution.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Carbon Yield vs. Purity
While the inert atmosphere maximizes yield by preventing combustion, the carbonization process inherently involves mass loss.
Users must balance the need for high purity (achieved by driving off more volatiles at higher temperatures) against the inevitable reduction in total material mass.
Inert vs. Reactive Processing
It is important to distinguish between carbonization (inert) and activation (reactive).
An inert atmosphere creates the basic carbon skeleton and initial porosity. However, achieving extreme surface areas (e.g., >1000 m²/g) often requires a subsequent step with active agents like CO2, rather than a purely inert environment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the utility of a high-temperature inert atmosphere furnace, align your processing parameters with your specific material objectives:
- If your primary focus is Structural Support: Prioritize the removal of volatile components at moderate temperatures (around 850 °C) to build a stable carbon skeleton for loading active components.
- If your primary focus is Conductivity: Ensure the furnace reaches sufficient temperatures (800–900 °C) to fully graphitize the polymer network and establish electron transport pathways.
- If your primary focus is Electrochemical Activity: Utilize the thermal stress of the process to intentionally induce carbon vacancy defects, which act as catalytic active sites.
Ultimately, the inert atmosphere furnace is not just a heater; it is a precision tool for sculpting the atomic architecture of carbon materials.
Summary Table:
| Process Phase | Furnace Role | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Protection | Displaces Oxygen with N2/Ar | Prevents combustion & maximizes carbon yield |
| Decomposition | Precise heating (800-1000°C) | Removes volatile components & forms carbon skeleton |
| Structural Development | Controlled Outgassing | Creates initial micropores & specific surface area |
| Functionalization | Thermal Restructuring | Establishes electrical conductivity & catalytic defects |
Elevate Your Carbon Material Research with KINTEK
Maximize your carbon yield and achieve precise structural control with KINTEK’s high-performance furnace solutions. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer specialized Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to meet your specific inert atmosphere requirements.
Whether you are developing conductive nanowires or high-surface-area adsorbents, our systems provide the temperature uniformity and atmosphere integrity critical for your success.
Ready to optimize your carbonization process? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project!
Visual Guide
References
- M. Antonia López-Antón, Ana Arenillas. Mercury Removal by Carbon Materials with Emphasis on the SO <sub>2</sub> –Porosity Relationship. DOI: 10.1002/open.202500190
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-precision furnace essential for CZTSSe thin films? Prevent Phase Decomposition and Amorphization
- What is an exothermic atmosphere in furnace applications? Protect Metals from Oxidation Efficiently
- What are the design configurations of retort furnaces? Optimize Your Thermal Processing with the Right Setup
- What is the importance of a dedicated nitriding furnace? Achieve Precision Surface Hardening & Wear Resistance
- Why are high-temperature vacuum or atmosphere furnaces used for annealing metal silicide? Unlock Peak Thermal Stability
- Why is a controlled oxygen environment necessary for high-entropy alloy powders? Master HEA Oxidation & Phase Purity
- Why is a preheated annealing furnace necessary in glass production? Ensure Structural Integrity & Optical Clarity
- Why is uniform atmosphere flow important in a controlled atmosphere furnace? Ensure Consistent Results and Avoid Costly Failures



















