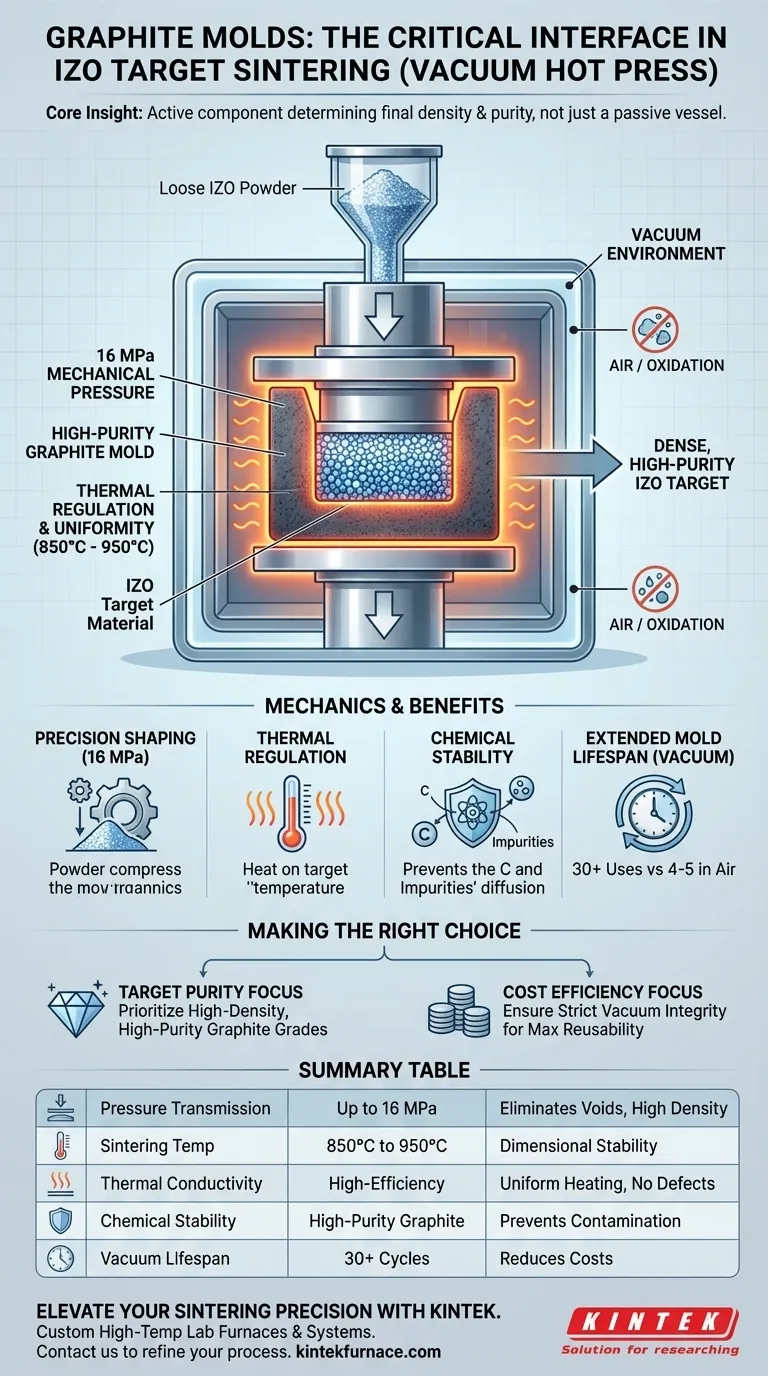
High-purity graphite molds are the critical structural interface in the manufacturing of Indium Zinc Oxide (IZO) targets. They serve as both precise shaping containers and active thermal conductors, transmitting up to 16 MPa of mechanical pressure while ensuring uniform heat distribution at sintering temperatures between 850°C and 950°C.
Core Insight: The graphite mold is not merely a passive vessel; it is an active component in determining the final density and purity of the IZO target. Its ability to withstand extreme pressure while chemically isolating the material is what allows for the creation of contamination-free semiconductor components.

The Mechanics of Densification
The vacuum hot press sintering process relies on the mold to convert loose powder into a solid, high-performance solid.
Precision Shaping Under Pressure
The primary function of the graphite mold is to act as a shaping container for the IZO powder.
It must maintain rigorous dimensional stability while transmitting significant mechanical force—specifically 16 MPa—to the internal powder.
This pressure is essential for eliminating voids between powder particles, ensuring the final target achieves the high density required for effective sputtering.
Thermal Regulation and Uniformity
Graphite is selected for its excellent thermal conductivity.
During the sintering process, the mold acts as a medium to transfer heat evenly to the ceramic powder inside.
This prevents thermal gradients (hot or cold spots), which ensures the material sinters uniformly and prevents structural defects in the final target.
Material Purity and Chemical Stability
For semiconductor applications, the chemical interaction between the mold and the target material is a critical concern.
Preventing Contamination
High-purity graphite molds offer exceptional chemical stability at elevated temperatures.
This stability prevents carbon or other impurity elements from diffusing into the IZO material.
By isolating the powder, the mold ensures the target retains the high purity levels necessary for semiconductor performance.
Operating Temperature Resilience
The mold is designed to operate specifically within the 850°C to 950°C range for IZO targets.
At these temperatures, lesser materials might warp or degrade, but high-quality graphite maintains its regular geometric shape.
The Economic and Operational Impact of Vacuum
Understanding the interaction between the graphite mold and the vacuum environment is essential for operational efficiency.
Combating Oxidation
Graphite is susceptible to oxidation and rapid degradation when heated in air.
The vacuum environment protects the mold from this oxidation loss, preserving its structural integrity.
Maximizing Mold Lifespan
The protective nature of the vacuum drastically extends the service life of the mold.
While a mold might only last 4-5 cycles in air, a vacuum environment can extend this to over 30 uses.
This significantly reduces material costs and ensures consistent product dimensions over larger production runs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the effectiveness of your sintering process, align your operational focus with the capabilities of the mold.
- If your primary focus is Target Purity: Prioritize high-density, high-purity graphite grades to eliminate any risk of particle diffusion or chemical contamination during the 950°C peak.
- If your primary focus is Cost Efficiency: Ensure strict vacuum integrity to prevent oxidation, potentially increasing mold reusability from a few cycles to dozens.
Ultimately, the quality of your IZO target is directly limited by the thermal and mechanical stability of the graphite mold shaping it.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Specification/Role | Impact on IZO Target |
|---|---|---|
| Pressure Transmission | Up to 16 MPa | Eliminates voids; ensures high density |
| Sintering Temperature | 850°C to 950°C | Maintains dimensional stability & shape |
| Thermal Conductivity | High-efficiency transfer | Uniform heating; prevents structural defects |
| Chemical Stability | High-purity graphite | Prevents carbon diffusion and contamination |
| Vacuum Lifespan | 30+ Cycles | Reduces oxidation and lowers production costs |
Elevate Your Sintering Precision with KINTEK
High-performance IZO targets demand the perfect balance of pressure, temperature, and purity. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK provides a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, alongside specialized high-temp lab furnaces tailored for your unique sintering requirements.
Whether you are scaling semiconductor production or optimizing lab-scale research, our customizable solutions ensure maximum mold lifespan and material integrity. Contact KINTEK today to discover how our high-temperature expertise can refine your manufacturing process.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
- 9MPa Air Pressure Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role do hot press furnaces play in powder metallurgy? Achieve High-Density Components Efficiently
- How do hot press furnaces contribute to graphene synthesis? Unlock High-Quality Material Production
- What are the advantages of using a HIP sintering system over conventional sintering for Bismuth Telluride composites?
- How does a graphite mold influence high-entropy alloys in VHPS? Enhance Strength via In-Situ Carbides
- What are the advantages of using a Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) system for UHTCs? Master Rapid Densification
- Why is a Vacuum Hot Press (VHP) furnace more suitable for preparing ODS alloys? Superior Uniformity & Density
- What are the core functions of a vacuum hot pressing furnace in the densification of Cr2AlC ceramics?
- How does the programmable pressure function of a vacuum hot press furnace influence the quality of IZO targets?



















