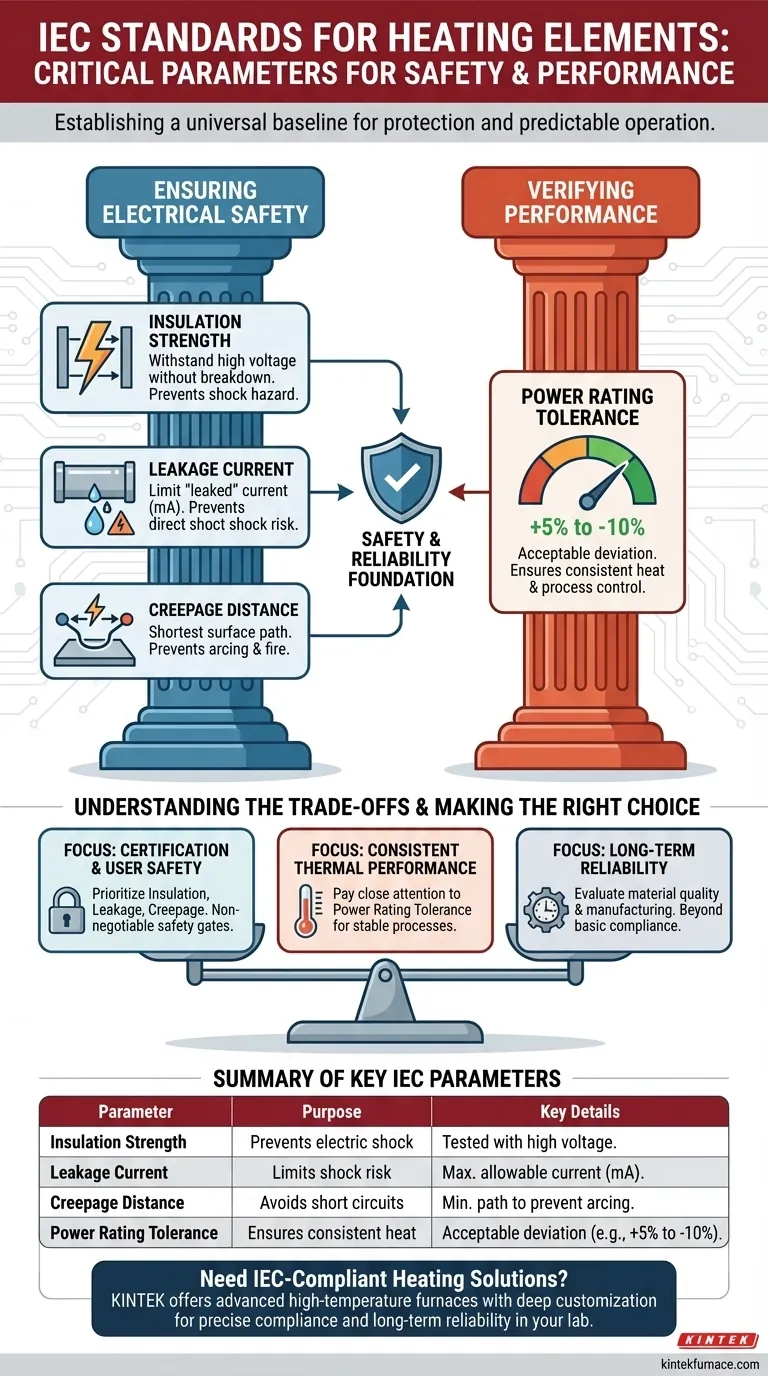
At its core, the IEC standard for heating elements specifies critical parameters designed to ensure electrical safety and predictable performance. It provides specific limits and testing methodologies for insulation strength, leakage current, and creepage distance, while also defining acceptable tolerances for the element's power rating.
The fundamental purpose of these IEC parameters is not merely to define performance, but to establish a universal baseline for safety. They are designed to protect users from electric shock and equipment from fire hazards under both normal and potential fault conditions.
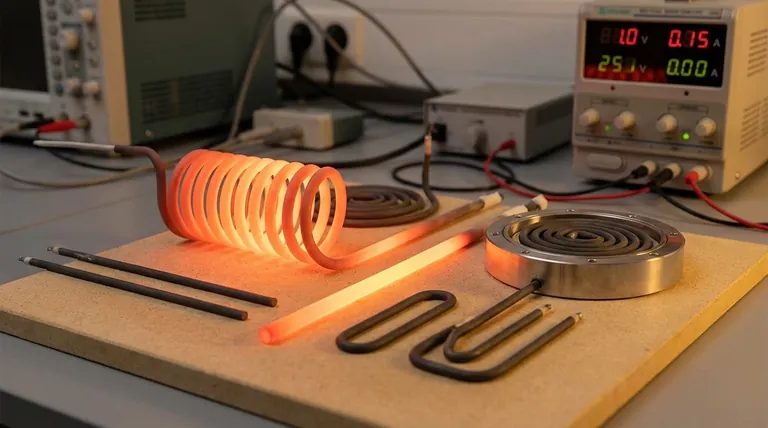

The Core Pillars of IEC Compliance: Safety and Reliability
The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) standards, particularly the IEC 60335 series which covers the safety of household and similar electrical appliances, establish a framework for designing safe heating elements. This framework is built on two primary pillars: preventing electrical hazards and ensuring reliable operation.
Ensuring Electrical Safety
The most critical function of the standards is to prevent electricity from harming the user or damaging the equipment. This is achieved by specifying limits on three key parameters.
Insulation Strength
Insulation strength, often verified through a dielectric strength test, measures the ability of the insulating material within the heater (typically Magnesium Oxide or MgO) to withstand high voltage without breaking down. A failure here could allow live voltage to reach the metal sheath of the heater, creating a severe shock hazard.
The standard defines the specific test voltage and duration to ensure the element's insulation is robust enough for its intended application.
Leakage Current
Leakage current is the small amount of electrical current that inevitably "leaks" from the live conductor through the insulation to the grounded outer sheath. While some leakage is normal, excessive current indicates poor insulation quality or moisture absorption.
IEC standards set a strict maximum allowable leakage current (often measured in milliamps) because it poses a direct risk of electric shock, especially in appliances used in wet or damp environments.
Creepage Distance
Creepage distance is the shortest path along the surface of an insulating material between two conductive parts, such as the heater terminal and its grounded casing. Inadequate distance can allow an electrical arc to form, particularly in the presence of moisture or contamination.
This can lead to a short circuit, creating a significant fire hazard. The standard specifies minimum creepage distances based on the voltage, material properties, and expected level of environmental pollution.
Verifying Performance and Durability
Beyond immediate safety, the IEC standard also ensures the heating element performs as the manufacturer claims.
Power Rating Tolerance
This parameter defines the acceptable deviation between the element's stated power (in Watts) and its actual measured power output. A common tolerance might be +5% to -10%.
This is crucial for process control, ensuring the element delivers consistent heat. An element that is significantly underrated will not perform its function, while an overrated one can cause overheating, damage the target material, and present a fire risk.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Complying with IEC standards is not a simple checklist; it involves understanding the context and potential failure points.
Standard vs. Application-Specific Needs
IEC standards provide a fundamental baseline for safety, particularly for consumer and general industrial products. However, they are not a substitute for application-specific risk assessment.
Mission-critical applications in medical, aerospace, or explosive environments often require adherence to even stricter, more specialized standards that build upon the IEC framework.
Manufacturing Quality vs. Compliance
A heating element can be designed to pass a one-time IEC test but may lack the long-term durability to remain safe. The quality of raw materials—such as the purity of the MgO insulation and the grade of the sheath alloy—plays a massive role in reliability.
A low-quality element may absorb moisture over time, causing its leakage current to increase and eventually fail or become a safety hazard, even though it initially passed inspection. True compliance is about sustained safety, not just initial certification.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When selecting or designing a heating element, use the IEC parameters to guide your engineering decisions based on your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is product certification and user safety: Prioritize insulation strength, leakage current, and creepage distance as non-negotiable gates for preventing shock and fire.
- If your primary focus is consistent thermal performance: Pay close attention to the specified power rating tolerance to ensure your process is stable and repeatable.
- If your primary focus is long-term reliability: Look beyond the basic compliance certificate and evaluate the manufacturer's material sourcing and quality control processes.
Ultimately, viewing these IEC parameters as a framework for robust engineering is the key to developing safe, reliable, and effective heating applications.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Purpose | Key Details |
|---|---|---|
| Insulation Strength | Prevents electric shock | Tested with high voltage for breakdown resistance |
| Leakage Current | Limits shock risk | Maximum allowable current in milliamps |
| Creepage Distance | Avoids short circuits | Minimum path length to prevent arcing |
| Power Rating Tolerance | Ensures consistent heat | Acceptable deviation (e.g., +5% to -10%) |
Need reliable heating elements that meet IEC standards? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise compliance with IEC parameters for safety and performance in your lab. Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and enhance your application's reliability!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions



















