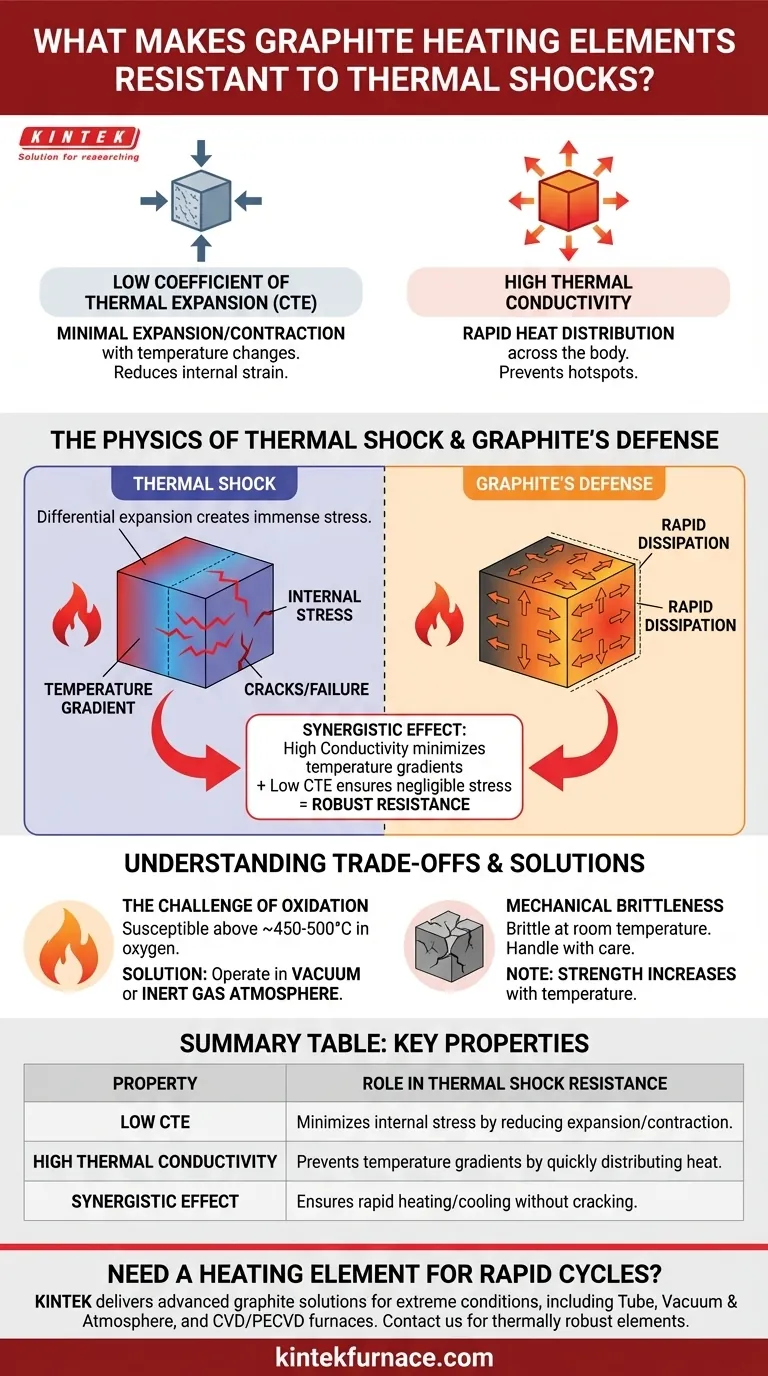
At its core, graphite's remarkable resistance to thermal shock stems from two fundamental physical properties: its extremely low coefficient of thermal expansion and its high thermal conductivity. When a material is heated or cooled rapidly, these two characteristics work in tandem to prevent the buildup of internal stresses that would cause other materials to fracture.
Thermal shock failure occurs when a material expands or contracts at different rates across its structure, creating immense internal stress. Graphite avoids this failure because it expands very little when heated and quickly dissipates temperature differences across its body.

The Physics of Thermal Shock
To understand why graphite is so robust, we must first define the problem it solves. Thermal shock is a rapid, transient mechanical load caused by a sudden change in temperature.
The Role of Temperature Gradients
When you rapidly heat or cool an object, a temperature gradient forms. The surface temperature changes instantly, while the core temperature lags behind.
For example, plunging a hot ceramic dish into cold water causes the outer layer to contract quickly while the inside remains expanded.
Stress and Material Failure
This difference in expansion or contraction between the cool exterior and the hot interior creates immense internal stress. In brittle materials, this stress can easily exceed the material's strength, resulting in cracks and catastrophic failure.
Why Graphite Excels Under Thermal Stress
Graphite's atomic structure and properties make it uniquely suited to withstand these internal stresses. It mitigates both the cause and the effect of thermal gradients.
Property 1: Low Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (CTE)
Graphite has a very low coefficient of thermal expansion. This means that for a given change in temperature, it simply does not expand or contract very much.
Think of it like this: if the material barely changes its size when the temperature changes, there is very little internal strain to begin with. This property directly reduces the "stress" side of the thermal shock equation.
Property 2: High Thermal Conductivity
Graphite is an excellent thermal conductor, meaning it transfers heat very efficiently.
When a graphite heating element is powered on or off, its high conductivity allows heat to spread or dissipate throughout its entire volume almost instantly. This prevents the formation of significant temperature gradients between the surface and the core, minimizing the root cause of thermal stress.
The Synergistic Effect
These two properties create a powerful synergistic effect. The high thermal conductivity minimizes the temperature differences, and the low CTE ensures that any minor temperature differences that do arise create negligible internal stress.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While exceptional in thermal shock resistance, graphite is not without its operational limitations. Understanding these is critical for successful implementation.
The Challenge of Oxidation
Graphite's primary weakness is its susceptibility to oxidation at high temperatures (typically above 450-500°C) in the presence of oxygen.
When used as a heating element, it must be operated in a vacuum or an inert gas atmosphere (like argon or nitrogen) to prevent it from literally burning away. This is the most significant trade-off and a critical design constraint for any furnace or system using graphite heaters.
Mechanical Brittleness
At room temperature, graphite is more brittle than most metals. It requires careful handling during installation to prevent chipping or cracking. However, an interesting property of graphite is that its strength actually increases with temperature, making it very robust during operation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right heating element requires matching the material's properties to your primary operational goal.
- If your primary focus is rapid heating and cooling cycles: Graphite is a superior choice due to its combined low thermal expansion and high thermal conductivity, which are the exact properties needed to resist thermal shock.
- If your primary focus is sustained high-temperature operation: Graphite's high sublimation point makes it excellent for this, but you must operate it in a vacuum or inert atmosphere to prevent oxidation and ensure a long service life.
Ultimately, graphite's inherent physical properties make it an engineered solution for the most demanding high-temperature applications.
Summary Table:
| Property | Role in Thermal Shock Resistance |
|---|---|
| Low Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (CTE) | Minimizes internal stress by reducing expansion/contraction during temperature changes. |
| High Thermal Conductivity | Prevents temperature gradients by quickly distributing heat, eliminating stress-causing hotspots. |
| Synergistic Effect | Combined properties ensure rapid heating/cooling without cracking or failure. |
Need a heating element that thrives under rapid thermal cycles? At KINTEK, we leverage our advanced R&D and in-house manufacturing to deliver graphite heating solutions engineered for extreme conditions. Our high-temperature furnaces—including Tube, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems—are built with deep customization to match your unique experimental needs. Contact us today (#ContactForm) to enhance your lab's performance with reliable, thermally robust heating elements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights


















