At its core, a lab tube furnace is a versatile tool because it provides precise, high-temperature control within a contained and adaptable environment. This combination allows scientists and engineers to systematically manipulate the fundamental structure of materials, making it indispensable for research, development, and specialized processing tasks.
The true versatility of a tube furnace isn't just its ability to get hot; it's the power it gives researchers to control the very essence of a material—its microstructure and crystal composition—to engineer specific, desirable properties.
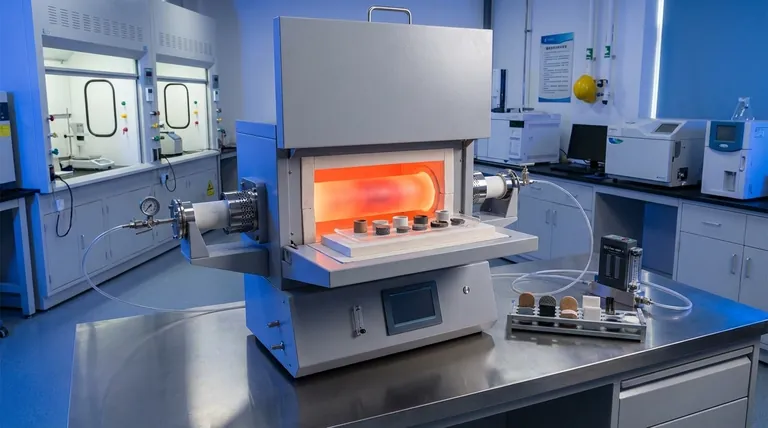

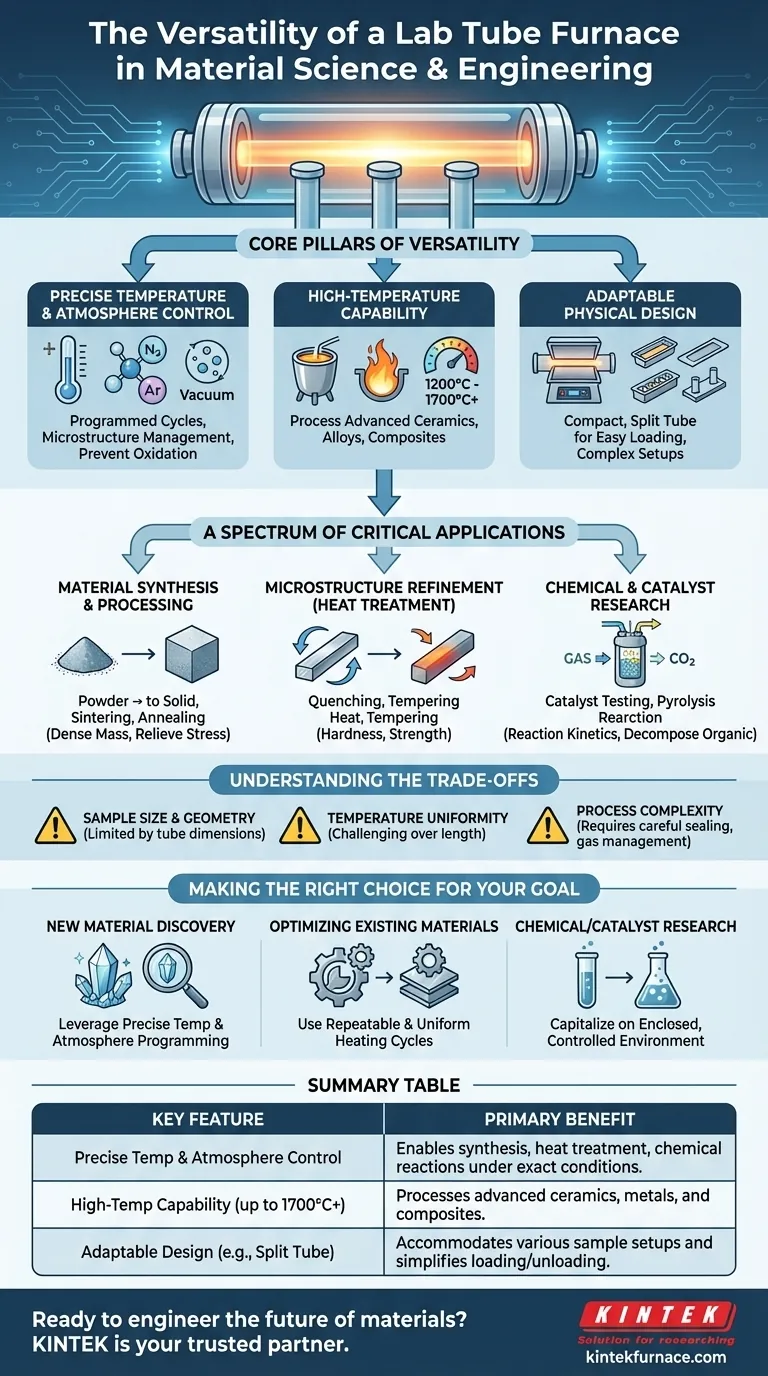
The Core Pillars of Versatility
A tube furnace's flexibility stems from three fundamental characteristics. Each one addresses a critical need in material science and engineering.
Precise Temperature and Atmosphere Control
The ability to execute a programmed heating and cooling cycle with high precision is paramount. This control allows researchers to dictate a material's final properties by carefully managing its crystal structure and microstructure.
Furthermore, the enclosed tube design enables the introduction of specific gases or the creation of a vacuum. This atmospheric control is essential for preventing oxidation or facilitating specific chemical reactions during processing.
High-Temperature Capability
Tube furnaces are designed to reach very high temperatures, often exceeding 1200°C or even 1700°C.
This capability makes them suitable for processing a vast range of materials, including advanced ceramics, metal alloys, and composites that require significant thermal energy for synthesis or modification.
Adaptable Physical Design
The compact size of a lab tube furnace makes it an efficient fit for research environments.
Designs like the split tube furnace, which opens into two halves, are particularly versatile. This allows for easy placement and removal of samples and complex experimental setups, significantly reducing operational downtime and accommodating a wide variety of sample configurations.
A Spectrum of Critical Applications
The furnace's core features enable a wide array of processes, each targeting a different material outcome.
Material Synthesis and Processing
This includes sintering, where powdered materials like ceramics or metals are heated to form a dense, solid mass. It also covers annealing, a process used to relieve internal stresses and improve a material's ductility and toughness.
Microstructure Refinement (Heat Treatment)
Processes like quenching (rapid cooling) and tempering (reheating to a lower temperature) are classic heat treatments. They are used to achieve specific microstructures that result in desired properties like hardness or strength in metals and alloys.
Chemical and Catalyst Research
In chemical engineering, tube furnaces are used to test the performance of catalysts by heating them with reactant gases. They are also used for processes like pyrolysis, where organic materials are thermally decomposed without oxygen to produce valuable gases and chars.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly versatile, the design of a lab tube furnace comes with inherent limitations that are important to recognize.
Sample Size and Geometry
The tubular chamber, by its nature, limits the size and shape of the sample. This makes the furnace ideal for research, development, and small-batch processing but unsuitable for large-scale industrial production.
Temperature Uniformity
Achieving perfect temperature uniformity along the entire length of the heating zone can be a challenge. Hot zones are typically most uniform in the center, which must be accounted for in sample placement for sensitive experiments.
Process Complexity
While offering great control, maintaining a perfectly pure or inert atmosphere requires careful sealing, gas flow management, and often a vacuum system. Complex setups can introduce potential points of failure if not managed correctly.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The versatility of a tube furnace means it can be applied to different objectives. Your primary goal should dictate how you leverage its capabilities.
- If your primary focus is new material discovery: Leverage the furnace's precise temperature programming and atmosphere control to explore how different processing conditions create novel material structures and properties.
- If your primary focus is optimizing existing materials: Use the furnace's repeatable and uniform heating cycles for heat treatments like annealing and tempering to consistently enhance mechanical properties.
- If your primary focus is chemical or catalyst research: Capitalize on the enclosed, controlled environment to study reaction kinetics and catalyst stability under specific and repeatable thermal conditions.
Ultimately, a lab tube furnace is a foundational tool that transforms theoretical material concepts into tangible, engineered reality.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|
| Precise Temperature & Atmosphere Control | Enables synthesis, heat treatment, and chemical reactions under exact conditions. |
| High-Temperature Capability (up to 1700°C+) | Processes advanced ceramics, metals, and composites. |
| Adaptable Design (e.g., Split Tube) | Accommodates various sample setups and simplifies loading/unloading. |
Ready to engineer the future of materials?
A lab tube furnace is the cornerstone of precise material research and development. Whether your goal is material discovery, process optimization, or catalyst testing, you need a furnace that delivers reliable performance and customization.
KINTEK is your trusted partner. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD furnace systems, all customizable for your unique experimental needs.
Contact our experts today to discuss how a KINTEK furnace can become the versatile core of your lab.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing



















