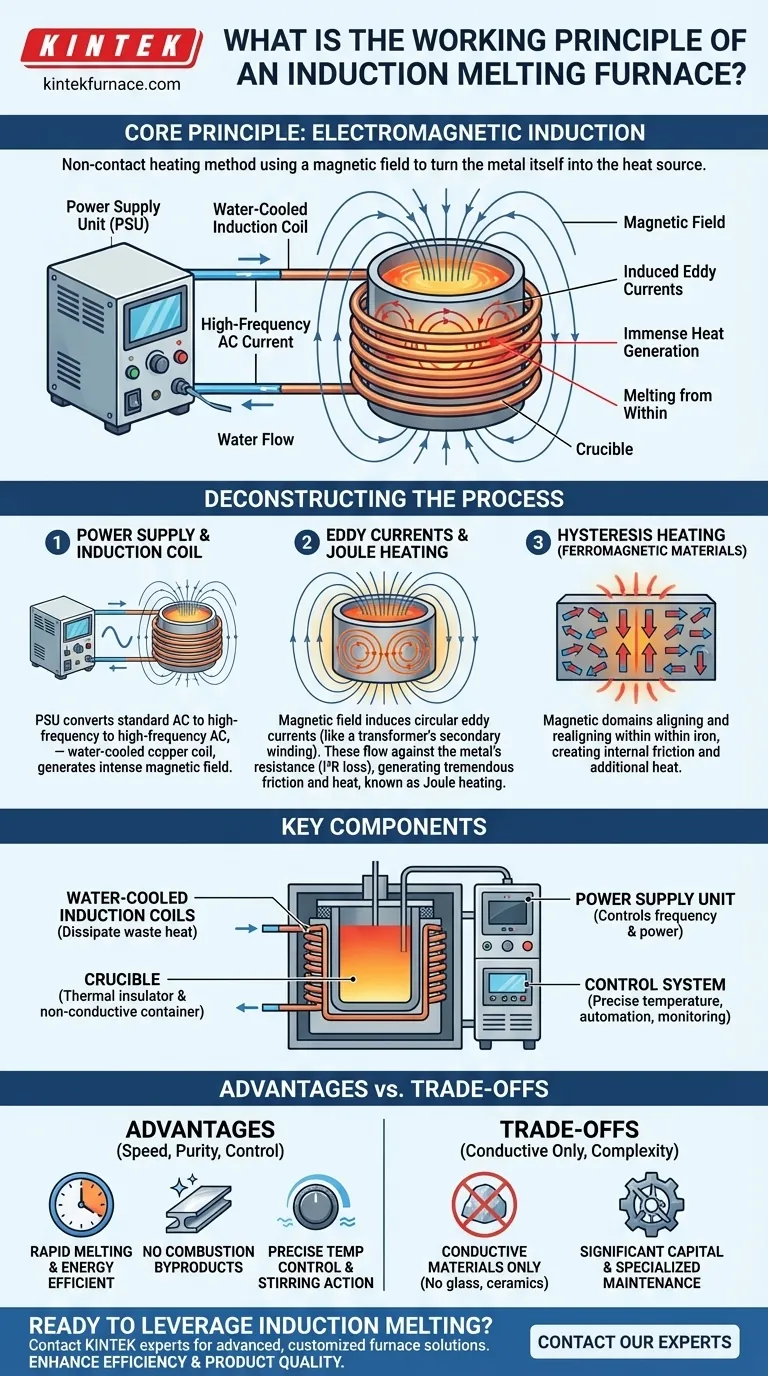
At its core, an induction melting furnace operates on the fundamental principle of electromagnetic induction. When a high-frequency alternating current (AC) is passed through a copper coil, it generates a powerful and rapidly changing magnetic field. This field penetrates any electrically conductive material placed inside the coil, inducing internal electrical currents—known as eddy currents—which generate immense heat and cause the material to melt from within.
The central takeaway is that induction melting is a non-contact heating method. It uses a magnetic field to turn the metal itself into the heat source, resulting in exceptionally fast, clean, and controllable melting compared to traditional fuel-fired furnaces.

Deconstructing the Induction Process
To truly understand its function, we must break down the sequence of events that transforms electrical energy into thermal energy inside the furnace.
The Role of the Induction Coil and Power Supply
The process begins with the power supply. This unit converts standard-frequency utility power (e.g., 50/60 Hz) into a high-frequency alternating current.
This high-frequency AC is then directed into a water-cooled copper coil that wraps around a crucible holding the metal. The flow of current through this coil generates the intense, fluctuating magnetic field that is essential for the entire process.
Generating Heat Through Eddy Currents
When the conductive metal charge is placed within this magnetic field, the field induces circular electrical currents within the metal. These are called eddy currents.
Think of it like a transformer, where the furnace's coil is the primary winding and the metal to be melted acts as a single-turn secondary winding.
Joule Heating: The Primary Melting Force
The metal has a natural electrical resistance. As the induced eddy currents flow against this resistance, they generate tremendous friction and heat. This effect, known as Joule heating (or I²R loss), is the primary mechanism that raises the metal's temperature to its melting point.
An Added Boost: Hysteresis Heating
For ferromagnetic materials like iron, a secondary heating effect occurs. The rapidly changing magnetic field forces the magnetic domains within the iron to constantly realign, creating internal friction and additional heat. This "hysteresis heating" contributes to the overall efficiency when melting these specific materials.
Key Components of a Modern Furnace
An induction furnace is a system of several critical components working in concert to achieve a controlled melt.
The Crucible
This is the high-temperature-resistant container, typically made of ceramic or graphite, that holds the metal charge. It must be a thermal insulator and electrically non-conductive to avoid being heated by the magnetic field.
Water-Cooled Induction Coils
The copper coils that generate the magnetic field carry immense electrical current and would quickly melt themselves without active cooling. A closed-loop water cooling system constantly circulates water through the coils to dissipate waste heat and maintain structural integrity.
The Power Supply Unit
This is the electronic heart of the furnace. It precisely controls the frequency and power of the AC supplied to the coil, which in turn dictates the rate of heating and the final temperature of the molten metal.
The Control System
Modern furnaces feature advanced control panels and smart controllers. These allow operators to set precise temperature profiles, automate the melting process, and monitor safety systems, ensuring consistent results and reliable operation.
Understanding the Advantages and Trade-offs
No technology is perfect for every situation. Understanding the inherent strengths and weaknesses of induction melting is key to using it effectively.
Key Advantage: Speed and Purity
Because heat is generated directly within the material, melting is extremely rapid and energy-efficient. Furthermore, since there is no combustion, byproducts like gas and soot do not contaminate the metal, resulting in a much cleaner and higher-quality final product.
Key Advantage: Control and Stirring
The power output can be adjusted instantly, offering unparalleled temperature control. The magnetic field also creates a natural stirring action in the molten metal, which promotes a uniform temperature and ensures alloys are mixed homogeneously.
The Primary Limitation: Conductive Materials Only
The foundational principle of induction heating relies on the material being electrically conductive. The process is ineffective for melting non-conductive materials like glass, ceramics, or plastics.
The Hidden Cost: System Complexity
Induction furnaces require a significant capital investment in sophisticated power electronics and a robust water-cooling infrastructure. These systems add complexity and require specialized maintenance compared to simpler fuel-fired furnaces.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your choice of melting technology should be guided by the specific requirements of your final product.
- If your primary focus is rapid production of standard alloys: The high speed, energy efficiency, and consistent output of a standard induction furnace make it the superior choice for high-volume casting.
- If your primary focus is creating high-purity, reactive, or superalloys: A Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace is non-negotiable, as it uses the same principle within a vacuum to prevent any atmospheric contamination.
- If your primary focus is operational flexibility and frequent startups: Look for a modern furnace with zero-voltage sweep technology, which is specifically designed for the demands of frequent on-off cycles in a jobbing foundry.
By understanding that an induction furnace melts metal from the inside out, you can better leverage its unique advantages for speed, purity, and control.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| Core Principle | Non-contact heating via electromagnetic induction, turning the metal itself into the heat source. |
| Primary Heating Mechanism | Joule heating from eddy currents induced within the conductive metal. |
| Key Advantage | Exceptional speed, purity (no combustion byproducts), and precise temperature control. |
| Main Limitation | Only effective for electrically conductive materials (metals). |
| Ideal For | High-volume production, high-purity alloys, and applications requiring homogeneous mixing. |
Ready to leverage the speed and purity of induction melting for your lab or production line?
At KINTEK, we combine exceptional R&D with in-house manufacturing to deliver advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique challenges. Whether you need a standard induction furnace for rapid production or a sophisticated Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) system for superalloys, our deep customization capabilities ensure a perfect fit for your experimental and production requirements.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our induction melting solutions can enhance your efficiency and product quality.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What role does a vacuum induction melting furnace play in Fe-5%Mn-C alloys? Ensure Chemical Integrity and High Purity
- What are the core functions of the High Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace? Optimize DD5 Superalloy Purification
- How has vacuum smelting impacted the development of superalloys? Unlock Higher Strength and Purity
- What is the purpose of vacuum melting, casting and re-melting equipment? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- What are the common applications of Vacuum Induction Melting? Essential for High-Performance Metals and Alloys



















