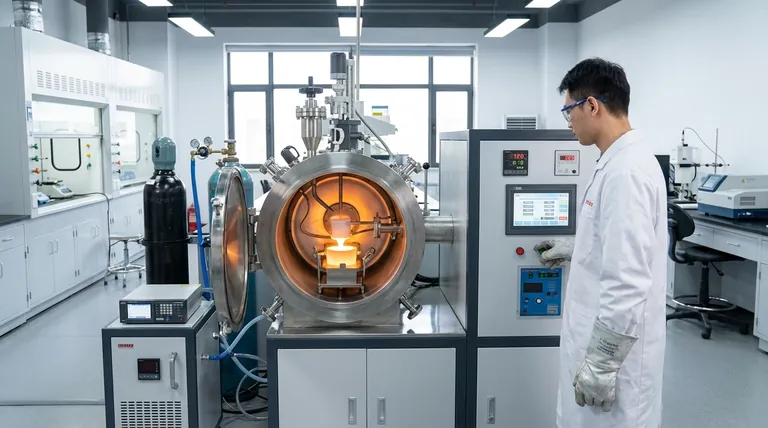
At its core, an induction melting furnace is a specialized tool used to melt electrically conductive metals, ranging from iron and steel to copper, aluminum, and precious metals. Its applications span from large-scale industrial foundries producing hundred-ton melts to small-scale workshops handling less than a kilogram of material for high-value applications.
The true value of an induction furnace is not just its ability to melt metal. Its defining purpose is to use clean, contactless electromagnetic energy to achieve rapid, highly controllable, and pure melts, making it a superior alternative to traditional fuel-fired methods for a wide range of modern industrial processes.

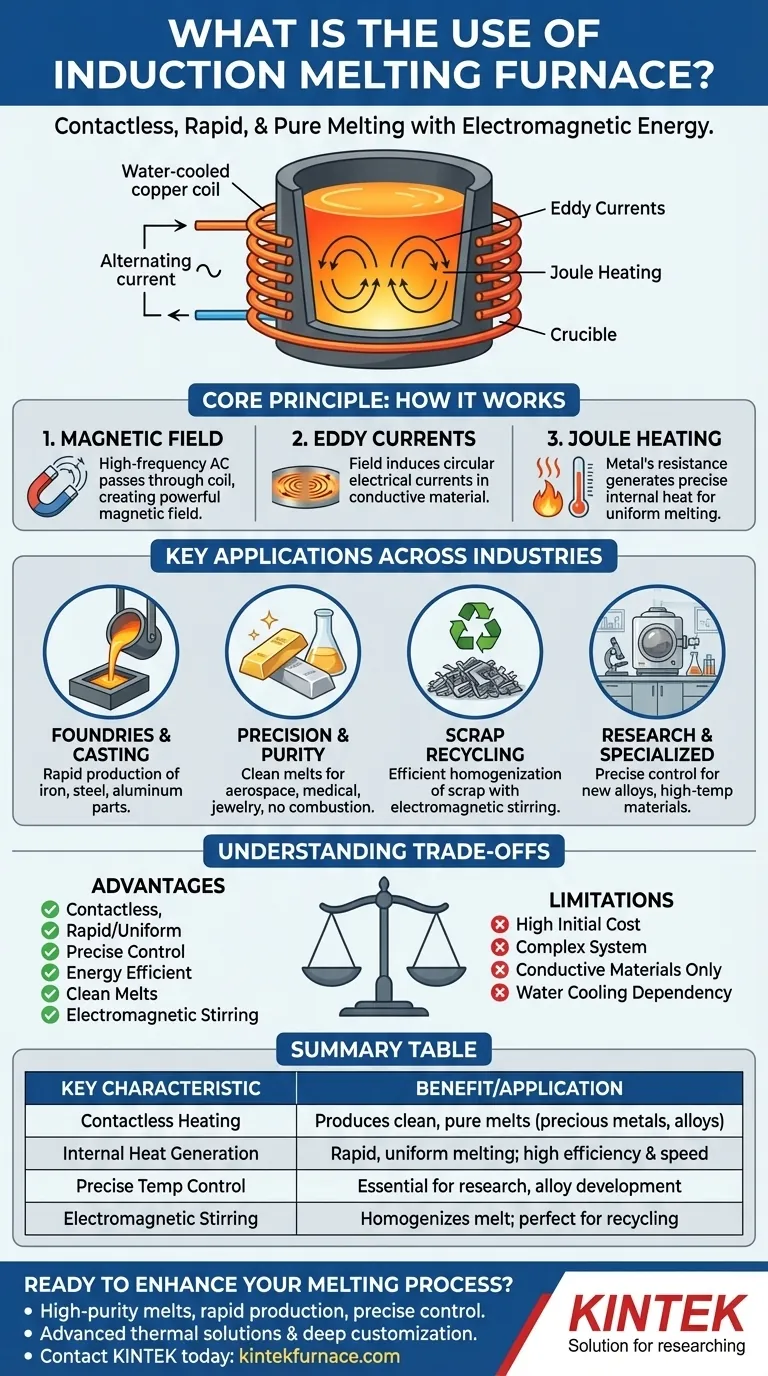
How Induction Melting Works: The Core Principle
To understand the use case for an induction furnace, you must first understand how it fundamentally differs from a traditional furnace that burns fuel. The process is based entirely on the principles of electromagnetism.
The Role of the Magnetic Field
An induction furnace uses a water-cooled copper coil through which a high-frequency alternating current (AC) is passed. This creates a powerful and rapidly changing magnetic field in the space within the coil.
Generating Heat Through Eddy Currents
When a conductive material, such as a piece of steel or aluminum, is placed inside this magnetic field, the field induces circular electrical currents within the metal itself. These are known as eddy currents.
The metal's natural electrical resistance fights against the flow of these eddy currents, generating immense and precise heat through a phenomenon called Joule heating. This heat is generated inside the material, not applied from the outside, leading to very rapid and uniform melting.
The Added Effect in Ferromagnetic Metals
For magnetic metals like iron, an additional heating effect occurs. The rapidly changing magnetic field causes the metal's magnetic domains to realign constantly, which generates further heat through hysteresis. This makes induction particularly effective for melting iron and steel.
Key Applications Across Industries
The unique characteristics of induction melting make it a critical tool in several distinct sectors, each leveraging a different primary benefit.
Foundries and Metal Casting
This is the most common use. Induction furnaces are used to melt iron, steel, and aluminum to produce molten metal for casting into parts. The speed and energy efficiency are major drivers here, allowing for faster production cycles.
Precious Metals and High-Purity Alloys
In the aerospace, medical, and jewelry industries, metal purity is paramount. Because the induction process does not introduce combustion byproducts (like carbon from a fuel source), it produces exceptionally clean and pure melts. The precise temperature control also prevents the overheating and loss of valuable alloying elements.
Scrap Metal Recycling
Induction furnaces are highly effective at recycling scrap metal. The strong electromagnetic field creates a stirring action in the molten metal bath, which helps homogenize the melt and incorporate new material efficiently.
Research and Specialized Materials
For materials science and high-temperature research, control is everything. An induction furnace allows researchers to precisely control the melting temperature and atmosphere (e.g., melting in a vacuum) to develop new alloys or study material properties. It is also used to process highly durable refractory materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, induction furnaces are not a universal solution. An objective assessment requires understanding their limitations.
Initial Investment and Complexity
Induction systems are technically complex. They consist of a specialized high-frequency power supply, water cooling circuits, and control systems. This results in a higher initial capital cost compared to simpler fuel-fired furnaces.
Material Limitations
The fundamental principle of induction heating relies on the material being electrically conductive. It cannot be used to directly heat non-conductive materials like ceramics or glasses, although a conductive crucible can be used to transfer heat indirectly.
Water Cooling System Dependency
The high-power electrical coils must be continuously water-cooled to prevent them from melting. The entire system is dependent on a reliable, closed-loop cooling system. Any failure in the cooling circuit will immediately shut down the furnace, making it a critical point of maintenance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right melting technology depends entirely on your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is high-purity melts and precise alloy control: The induction furnace is the ideal choice due to its contactless heating and precise temperature regulation.
- If your primary focus is rapid production cycles and energy efficiency: Its fast melting speed and lower energy consumption per ton make it a strong contender against traditional furnaces.
- If your primary focus is operational flexibility: The ability to start and stop the furnace quickly with no lengthy warm-up makes it perfect for workshops that don't operate 24/7.
- If your primary focus is budget and simplicity: The high initial investment and system complexity may make a conventional fuel-fired furnace a more practical starting point for low-volume or less critical applications.
Ultimately, understanding the principles of induction melting empowers you to leverage its unique advantages for cleaner, faster, and more precise metallurgical processes.
Summary Table:
| Key Characteristic | Benefit/Application |
|---|---|
| Contactless Heating | Produces clean, pure melts; ideal for precious metals and high-purity alloys. |
| Internal Heat Generation | Enables rapid, uniform melting; increases energy efficiency and production speed. |
| Precise Temperature Control | Essential for research, alloy development, and preventing loss of valuable elements. |
| Electromagnetic Stirring | Homogenizes the melt; perfect for scrap metal recycling and consistent alloying. |
Ready to Enhance Your Melting Process?
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides advanced thermal solutions for diverse laboratory and industrial needs. Whether your priority is high-purity melts for precious metals, rapid production cycles in a foundry, or precise temperature control for materials research, our expertise can help.
Our product line, including high-temperature Tube Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and custom CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to meet your unique requirements.
Contact us today to discuss how we can provide a melting solution that delivers superior control, efficiency, and purity for your specific application.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of vacuum melting, casting and re-melting equipment? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- How does the Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) process work? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Control
- How does vacuum melting technology contribute to sustainability? Boost Durability and Recycling Efficiency
- What is vacuum induction melting technology and why is it important? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- Why is a Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace essential? Unlock Purity for Aerospace and Semiconductors



















