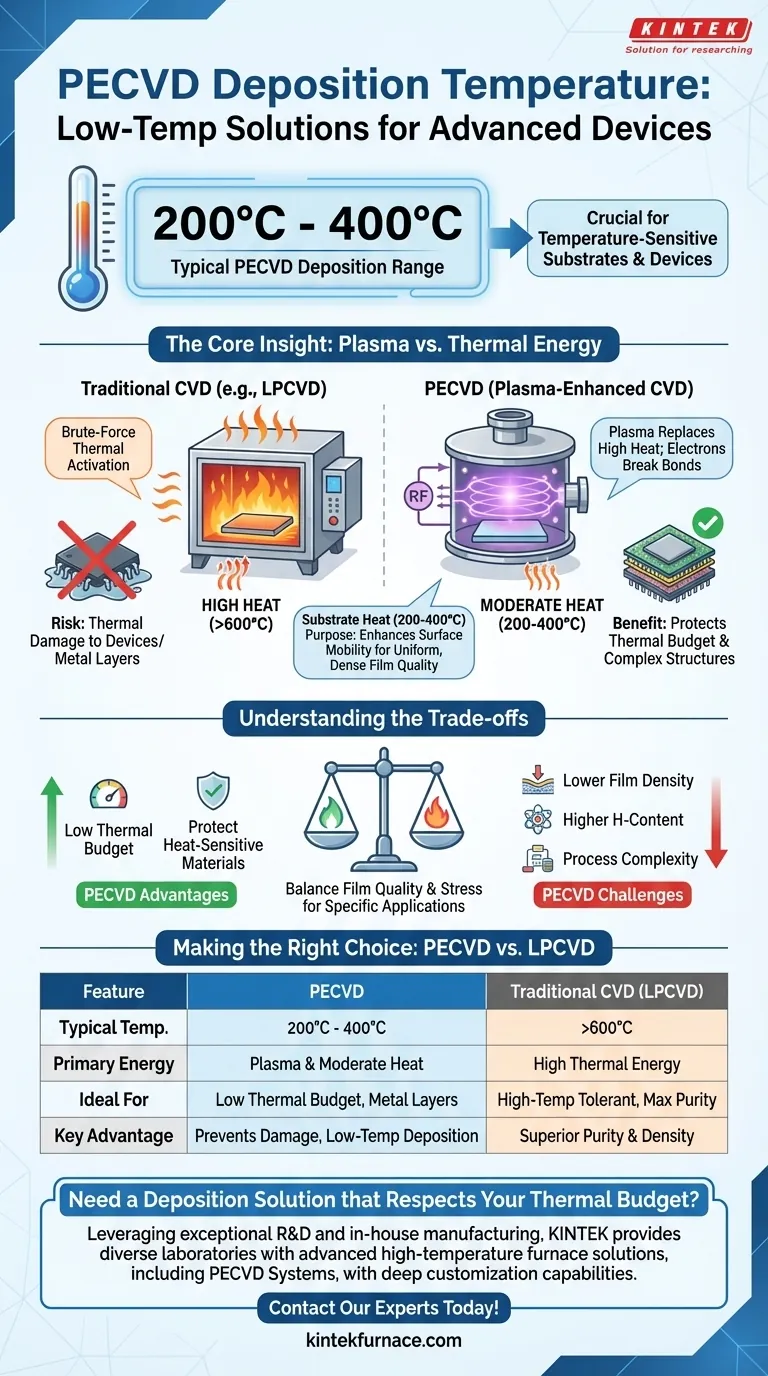
In short, the typical deposition temperature for Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD) is between 200°C and 400°C. This relatively low temperature is the primary reason it is chosen over other methods like Low-Pressure CVD (LPCVD) or thermal oxidation, especially when working with substrates or devices that cannot withstand high heat.
While the number itself is simple, the real insight is understanding why PECVD can operate at low temperatures. It replaces brute-force thermal energy with plasma energy to drive the necessary chemical reactions, opening up possibilities for fabricating complex, multi-layered devices.

Why Temperature is a Critical Constraint in Deposition
In any Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) process, the goal is to break down precursor gases into reactive species that then form a solid thin film on a substrate. The method used to supply this energy is what differentiates the techniques.
The Role of Thermal Energy in Traditional CVD
Traditional methods like LPCVD are thermally driven. They rely exclusively on high temperatures (often >600°C) to provide the "activation energy" needed to break the chemical bonds in the precursor gases.
This high heat is effective but acts as a major limitation.
The Problem with High-Temperature Processes
Many advanced semiconductor devices have a strict "thermal budget"—the total amount of heat a device can be exposed to before its properties degrade.
High temperatures can melt metal layers (like aluminum, which melts around 660°C), cause unwanted diffusion of dopants between layers, or damage materials with low thermal stability.
How PECVD Achieves Low-Temperature Deposition
PECVD overcomes the high-temperature requirement by introducing another form of energy: plasma. This is the core principle that makes the process so valuable.
The Power of Plasma
A plasma is a state of matter where a gas is energized, typically by a radio frequency (RF) electric field, causing it to become ionized. It's a highly reactive environment filled with ions, radicals, and high-energy electrons.
Bypassing Thermal Activation
In a PECVD reactor, the high-energy electrons in the plasma collide with the precursor gas molecules. These collisions are energetic enough to break the chemical bonds and create the reactive species needed for deposition.
This process effectively replaces the need for high thermal energy to initiate the reaction. The energy comes from the plasma, not from heating the substrate to extreme temperatures.
The Purpose of Substrate Heat (200-400°C)
While the plasma drives the primary reaction, the moderate heat applied to the substrate still serves a crucial purpose. This temperature enhances the surface mobility of the deposited atoms, allowing them to settle into a denser, more uniform, and higher-quality film. It also helps drive off reaction byproducts.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The low-temperature advantage of PECVD is significant, but it comes with trade-offs that must be considered for any specific application.
Film Quality and Composition
Because the deposition occurs at lower temperatures, PECVD films (like silicon nitride or silicon dioxide) often have a higher concentration of incorporated hydrogen compared to their high-temperature LPCVD counterparts. This can impact the film's electrical properties and must be managed.
Film Density and Stress
Films deposited via PECVD may be less dense and have different internal stress levels than those grown at higher temperatures. Managing film stress is critical to prevent cracking or delamination, especially in multi-layer structures.
Process Complexity
A PECVD system is more complex than a simple thermal furnace. It requires an RF power generator, matching networks, and a more sophisticated vacuum system to create and sustain the plasma, adding to the cost and maintenance overhead.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a deposition method is not about which is "best" overall, but which is correct for your specific constraints and desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is depositing films on a finished device with metal layers: PECVD is the default choice to stay below the thermal budget and prevent damage to existing structures.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible film purity and density for a front-end process: A high-temperature method like LPCVD may be superior, assuming your substrate can tolerate the heat.
- If your primary focus is creating conformal coatings over complex topography: LPCVD generally offers better conformality, while PECVD is more directional, though process tuning can improve its performance.
By understanding that PECVD substitutes plasma for heat, you can confidently select the right tool to achieve your specific fabrication goals.
Summary Table:
| Feature | PECVD | Traditional CVD (e.g., LPCVD) |
|---|---|---|
| Typical Temperature Range | 200°C - 400°C | >600°C |
| Primary Energy Source | Plasma | Thermal |
| Ideal For | Substrates with low thermal budgets (e.g., devices with metal layers) | High-temperature tolerant substrates |
| Key Advantage | Prevents damage to heat-sensitive materials | Superior film purity and density |
Need a deposition solution that respects your thermal budget?
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including PECVD Systems, Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, and Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements.
Let us help you select or customize the perfect system for your thin-film fabrication goals.
Contact our experts today to discuss your application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
People Also Ask
- What role does PECVD play in optical coatings? Essential for Low-Temp, High-Precision Film Deposition
- What is PECVD and how does it differ from traditional CVD? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- How is silicon dioxide (SiO2) used in PECVD applications? Key Roles in Microfabrication
- How does plasma vapor deposition work? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- What gases are used in the PECVD system? Optimize Thin Film Deposition with Precise Gas Selection



















