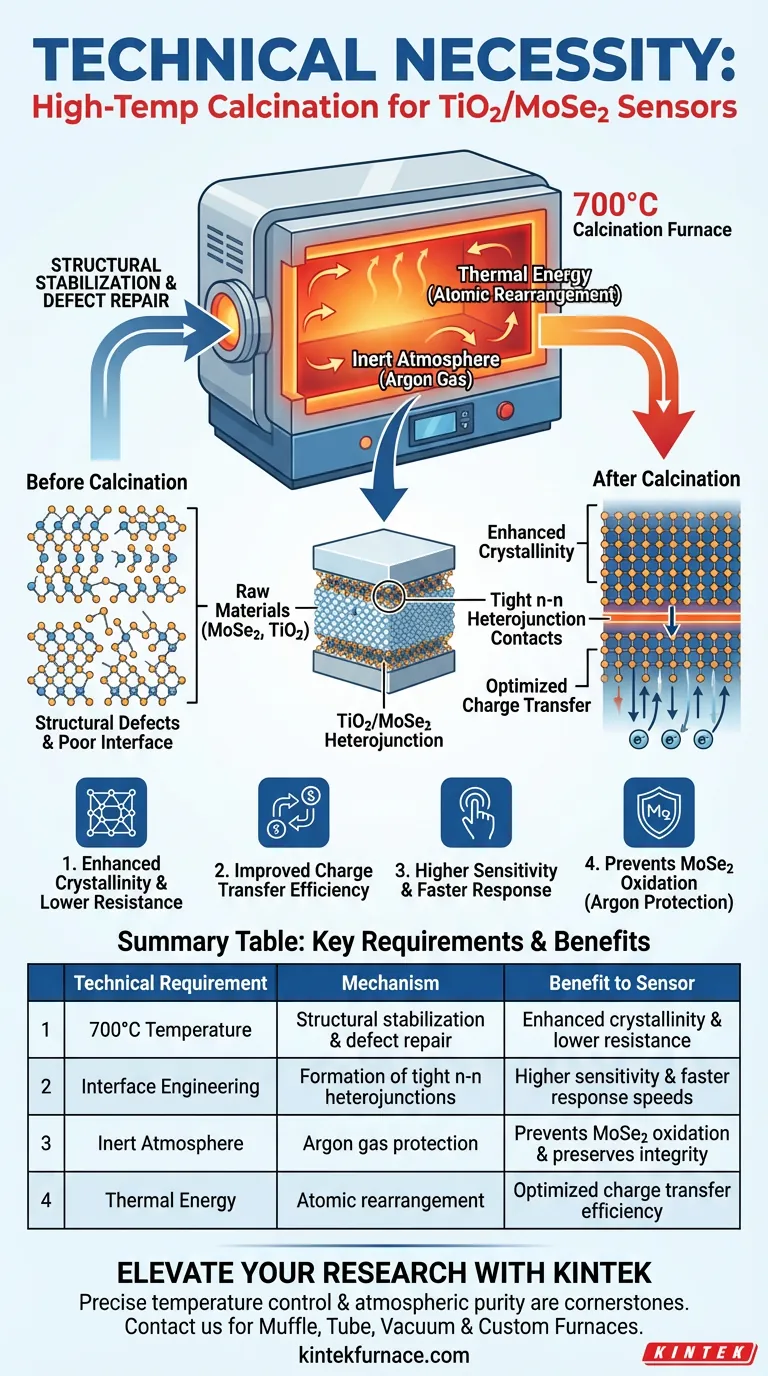
The technical necessity of using a high-temperature calcination furnace lies in its ability to create a precise 700°C environment required for the structural stabilization and defect repair of MoSe2 materials. This thermal treatment is the specific mechanism that enhances material crystallinity, enabling efficient charge transfer and the formation of tight n-n heterojunction contacts between TiO2 and MoSe2.
Core Takeaway The calcination furnace acts as a critical structural engineering tool, using 700°C heat to repair atomic defects and fuse the TiO2 and MoSe2 interface. This process transforms raw materials into a highly sensitive, conductive sensor capable of rapid response times.

The Physics of Structural Transformation
Enhancing Crystallinity and Repairing Defects
The primary function of the furnace is to subject the MoSe2 material to high thermal energy, specifically at 700°C.
At this temperature, the material undergoes a process of structural stabilization. The heat energy allows atoms to rearrange, effectively repairing internal defects and irregularities within the crystal lattice.
This repair process significantly enhances the crystallinity of the material. Higher crystallinity directly correlates to reduced electrical resistance, creating a clearer path for electron flow.
Improving Charge Transfer Efficiency
The ultimate goal of improving crystallinity is to optimize the electrical properties of the sensor.
By repairing defects that would otherwise act as traps for charge carriers, the calcination process improves the charge transfer efficiency. This ensures that the electrical signals generated by gas detection are transmitted effectively through the material.
Optimizing the Heterojunction Interface
Forming Tight n-n Contacts
Beyond the individual materials, the furnace is essential for engineering the interface where TiO2 and MoSe2 meet.
Precise temperature control ensures the formation of tight n-n heterojunction contacts. This physical intimacy between the two semiconductors is what allows the sensor to function as a cohesive unit rather than two separate materials.
Boosting Sensitivity and Response Speed
The quality of the heterojunction contact dictates the performance metrics of the final sensor.
A well-calcined interface results in significantly increased sensitivity to target gases. Furthermore, the efficient charge transfer across this tight junction improves the response speed, allowing the sensor to react rapidly to environmental changes.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
The Critical Role of Atmosphere
While high temperature is necessary for structural repair, it presents a significant chemical risk to MoSe2.
MoSe2 is highly susceptible to oxidation when exposed to oxygen at these high temperatures. If the furnace environment is not strictly controlled, the selenide will degrade, destroying the chemical integrity of the sensor.
Managing Environmental Controls
To mitigate oxidation, the calcination process requires an inert protective atmosphere, typically provided by high-purity argon gas.
The furnace setup must allow for the introduction of argon to create an oxygen-free environment. Without this protective gas flow, the benefits of the 700°C heat are negated by the chemical destruction of the active sensing material.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure you fabricate a functional high-performance sensor, apply the following principles:
- If your primary focus is Sensor Sensitivity: Prioritize reaching the 700°C threshold to maximize crystallinity and ensure the formation of tight n-n heterojunctions.
- If your primary focus is Material Longevity: rigorous control of the Argon atmosphere is required to prevent oxidation and preserve the specific adsorption capacity for gases like SO2.
Mastering the calcination process is the difference between a collection of raw powders and a high-precision sensing device.
Summary Table:
| Technical Requirement | Mechanism | Benefit to Sensor |
|---|---|---|
| 700°C Temperature | Structural stabilization & defect repair | Enhanced crystallinity & lower resistance |
| Interface Engineering | Formation of tight n-n heterojunctions | Higher sensitivity & faster response speeds |
| Inert Atmosphere | Argon gas protection | Prevents MoSe2 oxidation & preserves integrity |
| Thermal Energy | Atomic rearrangement | Optimized charge transfer efficiency |
Elevate Your Semiconductor Research with KINTEK
Precise temperature control and atmospheric purity are the cornerstones of successful TiO2/MoSe2 heterojunction fabrication. At KINTEK, we understand that a difference of a few degrees or a trace of oxygen can determine the success of your sensor research.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of high-performance laboratory solutions, including:
- Muffle & Tube Furnaces: Perfect for 700°C structural stabilization.
- Vacuum & CVD Systems: Ensuring the oxygen-free environments your materials demand.
- Rotary & Custom Furnaces: Tailored specifically for unique material synthesis needs.
Don't compromise on your crystallinity or sensitivity. Contact our technical team today to find the customizable high-temperature system that fits your lab's unique requirements and drive your innovation forward.
Visual Guide
References
- Lanjuan Zhou, Dongzhi Zhang. TiO2 Nanosphere/MoSe2 Nanosheet-Based Heterojunction Gas Sensor for High-Sensitivity Sulfur Dioxide Detection. DOI: 10.3390/nano15010025
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- Why is calcination essential for NaFePO4 phase formation? Engineering High-Performance Sodium Iron Phosphate
- Why is precise superheat temperature control required? Unlock High-Quality Soft Magnetic Nanocrystalline Alloys
- What is the purpose of preheating low carbon steel molds to 300 °C before the casting of Mg-Zn-xSr alloys?
- How do heating devices and alkaline impregnation tanks coordinate in biochar activation for maximum adsorption?
- What key process environments does a Molecular Beam Epitaxy (MBE) system provide? Optimize CaF2 Thin Film Growth
- How do high-temperature annealing furnaces ensure equilibrium in Bi2Se3-Nd2Se3 alloys? Expert Thermal Control Solutions
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum drying oven for magnesium slag? Preserving Sample Integrity
- Why is a constant temperature drying oven used for activated carbon? Ensure Pore Integrity and Adsorption Efficiency



















